Introduction to Cyber Security and Data Protection in Financial Institutions
Financial institutions, such as banks and investment firms, manage vast amounts of sensitive data, including personal information, financial records, and transaction details. Protecting this data from cyber threats is crucial to prevent fraud, theft, and data breaches. Effective cyber security measures help maintain customer trust and ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
Key Cyber Security Challenges Faced by Financial Institutions

Financial institutions face unique challenges in protecting their data due to the evolving nature of cyber threats. Some of the most common threats include:
1Evolving Cyber Threats
Financial institutions are prime targets for cybercriminals using advanced tactics such as phishing, malware, and ransomware. These attacks evolve rapidly, making it challenging to keep up with the latest vulnerabilities and ensuring that systems remain secure.
2 Insider Threats
Internal employees or personnel can pose significant risks to cybersecurity. This threat may arise from malicious actions or accidental mishandling of sensitive data, which can lead to unauthorized access, breaches, or data leaks.
3 Regulatory Compliance
Financial institutions must adhere to strict regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Compliance with these frameworks is complex and requires ongoing updates to meet the ever-evolving legal requirements.
4 Third-Party Risk
Financial institutions often rely on third-party vendors for various services, creating additional points of vulnerability. If vendors don’t follow strong security practices, they can become entry points for cybercriminals, leading to breaches or compromised data.
5 Data Privacy and Protection
Financial institutions handle massive amounts of sensitive customer data, including personally identifiable information (PII) and financial transactions. Protecting this data from breaches, leaks, or unauthorized access is crucial, and any failure in this area can result in severe financial and reputational damage.
6 Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs are prolonged, targeted attacks often aimed at gaining unauthorized access to networks for extended periods. Financial institutions are particularly vulnerable to these sophisticated attacks, which can evade detection for long periods, leading to significant data breaches or financial losses.
These challenges demand proactive strategies and advanced security solutions to protect against both internal and external threats in the financial industry.
Essential Data Protection Practices for Financial Institutions
To ensure the security of sensitive data, financial institutions need to implement key data protection practices, such as:
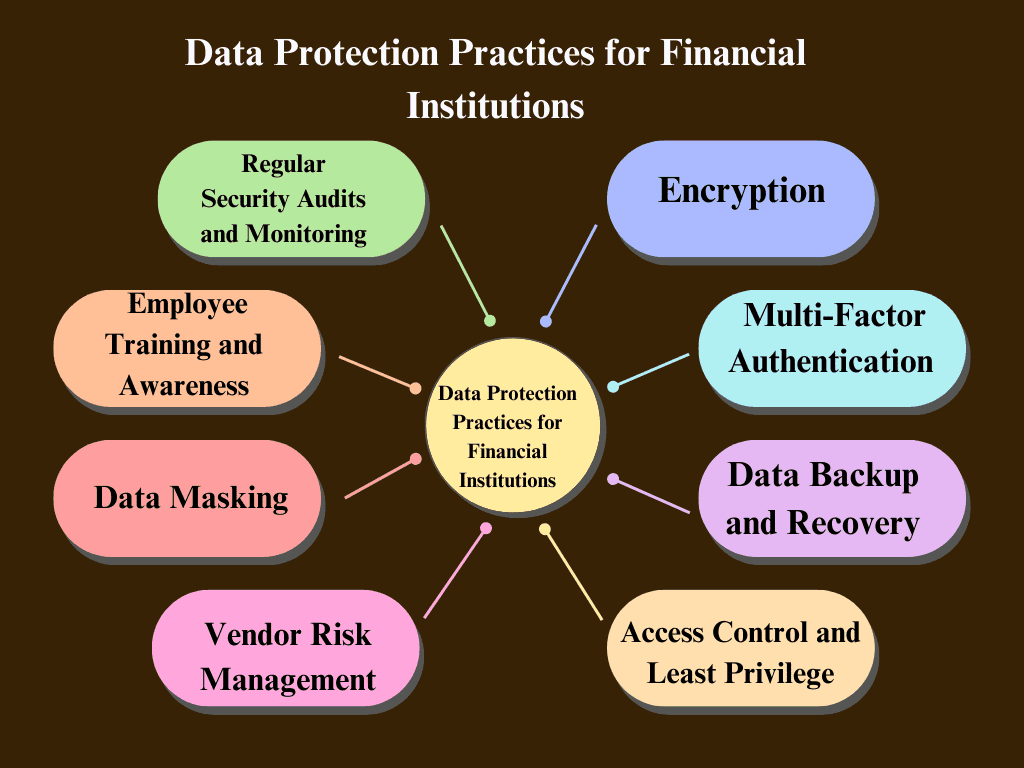
1Encryption
Encrypting both data in transit and at rest ensures that even if sensitive information is intercepted or stolen, it cannot be accessed without the correct decryption key, keeping it secure from unauthorized users.
2 Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing MFA adds a crucial layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods, such as passwords, biometrics, or one-time codes, making It becomes considerably more difficult for attackers to obtain unauthorized access.
3 Data Backup and Recovery
Regular data backups are critical for ensuring data integrity and availability. A robust disaster recovery plan helps financial institutions quickly restore operations in the event of a cyberattack, system failure, or data corruption.
4 Access Control and Least Privilege
Limiting access to sensitive data based on roles and the principle of least privilege ensures that employees and third parties can only access the data necessary for their tasks, reducing the risk of insider threats and data breaches.
5 Regular Security Audits and Monitoring
Conducting regular security audits and continuously monitoring systems for unusual or suspicious activity helps financial institutions identify vulnerabilities and potential threats early, allowing them to take immediate corrective action.
6 Employee Training and Awareness
Ensuring that all employees are aware of cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts and understanding the importance of strong passwords, is key to reducing human error, which is a common cause of data breaches.
7 Data Masking
Masking sensitive information in non-production environments ensures that data used in testing or development cannot be exploited. This practice reduces the risk of exposure during processes that don’t require access to actual data.
8Vendor Risk Management
Financial institutions must assess the cybersecurity practices of third-party vendors to ensure they meet data protection standards. Conducting regular assessments and requiring compliance with cybersecurity frameworks minimizes the risk of a breach through a third-party service provider.
By implementing these essential practices, financial institutions can greatly enhance the security of their sensitive data and protect against both internal and external cyber threats.
Cyber Security Strategies for Financial Institutions
A comprehensive cyber security strategy is essential for protecting financial institutions from cyber threats. Key strategies include:

- Risk Assessment: Conducting regular risk assessments helps identify potential vulnerabilities in a financial institution’s systems and networks.
- Cyber Security Frameworks: Adopting established cyber security frameworks, such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, provides a structured approach to managing cyber risks.
- Employee Training: Training employees on best practices for cyber security helps prevent insider threats and reduces the likelihood of accidental data breaches.
Data Protection Regulations in Financial Institutions
Compliance with data protection regulations is a crucial aspect of cyber security in financial institutions. Important regulations include
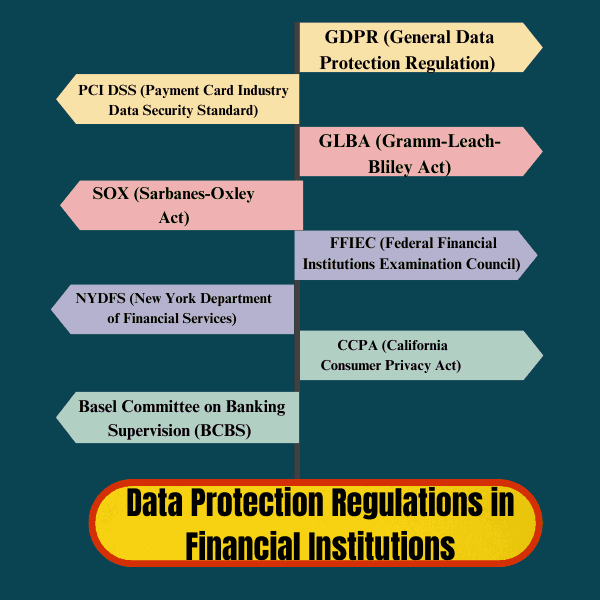
1 GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
Financial institutions operating within the European Union (EU) must comply with GDPR. This regulation focuses on the protection of personal data, requiring organizations to ensure data privacy, obtain explicit consent from individuals for data processing, and implement strong data security measures. Non-compliance can lead to heavy fines.
2 PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
PCI DSS applies to any financial institution or organization handling credit card transactions. It sets stringent requirements for securely processing, transmitting, and storing payment card data to prevent fraud and breaches. Compliance is crucial to maintaining customer trust and avoiding penalties.
3 GLBA (Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act)
This U.S. law requires financial institutions to explain their information-sharing practices and protect sensitive data. Under GLBA, institutions must implement administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to ensure the security and confidentiality of customer information.
4 SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act)
While primarily focused on corporate governance and financial reporting, SOX requires financial institutions to maintain stringent internal controls and ensure the accuracy and integrity of financial data. Data security practices are integral to complying with SOX standards, particularly in safeguarding financial records.
5 FFIEC (Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council)
These guidelines help U.S. financial institutions manage cybersecurity risks by establishing a framework for risk assessments, threat monitoring, and data protection strategies. Compliance with FFIEC guidelines ensures the resilience of financial systems against cyberattacks.
6 NYDFS (New York Department of Financial Services)
This regulation mandates financial institutions operating in New York to establish comprehensive cybersecurity programs. It requires institutions to perform regular risk assessments, implement access controls, encrypt sensitive data, and report cyber incidents.
7 CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)
Financial institutions serving customers in California must comply with CCPA, which grants individuals greater control over their personal data. The regulation mandates transparency in data collection and processing, along with the right for individuals to request the deletion or access of their data.
8 Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS)
The BCBS provides a global framework for banking institutions to manage cyber risks and enhance data protection. The principles stress the importance of governance, risk management, security monitoring, and incident response for cybersecurity in financial systems.
Compliance with these regulations ensures that financial institutions implement robust security measures, protect sensitive customer data, and avoid costly penalties for non-compliance.
Emerging Cyber Security Technologies for Financial Institutions
Financial institutions are increasingly adopting advanced technologies to enhance cyber security and data protection, including

1 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being used to detect and prevent cyber attacks by analyzing large amounts of data and identifying suspicious patterns in real-time.
2 Blockchain Technology
Blockchain provides a secure and transparent way to record financial transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and data tampering.
3 Advanced Threat Detection Systems
These systems use machine learning and other technologies to monitor networks and detect cyber threats early, allowing institutions to respond before damage is done.
Cyber Security and Data Protection in Digital Banking
As digital banking becomes more popular, financial institutions must take extra precautions to secure their online platforms. Key areas of focus include
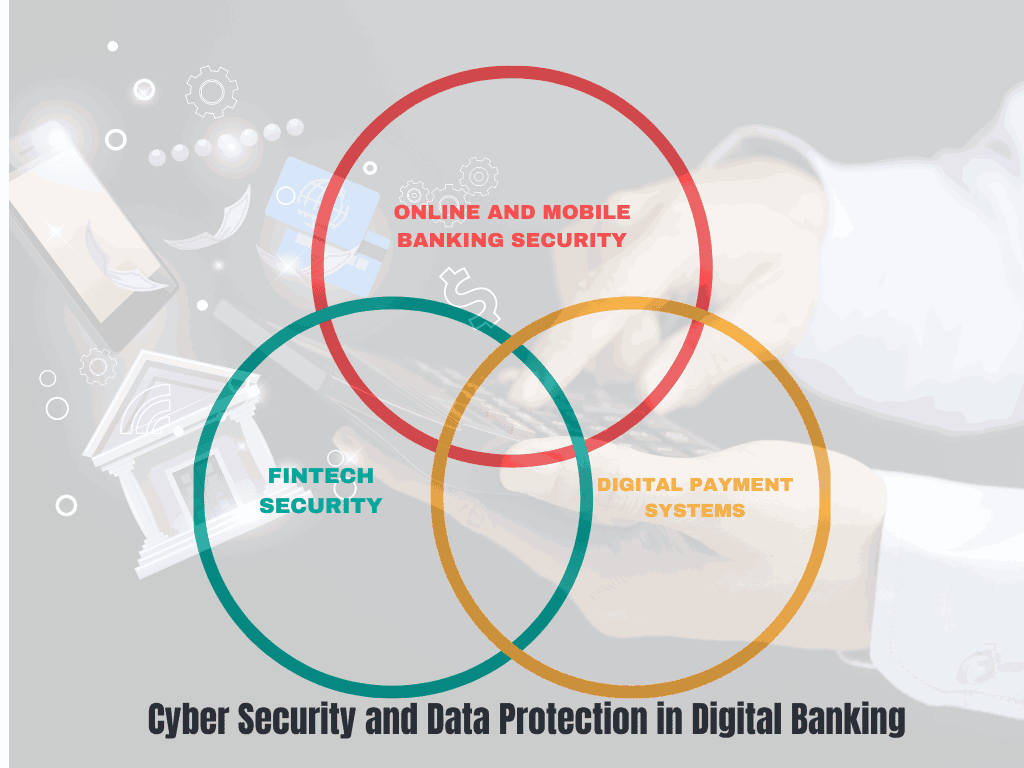
1 Online and Mobile Banking Security
Ensuring that online and mobile banking platforms are secure from cyber attacks by using encryption, MFA, and secure coding practices.
2 Fintech Security
Fintech companies often handle sensitive financial data, making it essential for them to implement strong cyber security measures to protect their customers.
3 Digital Payment Systems
With the rise of digital payments, financial institutions need to secure payment processing systems to prevent fraud and data breaches.
The Role of Cyber Security Audits in Financial Institutions
Regular cyber security audits are essential for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance with regulations. Key steps in the audit process include:
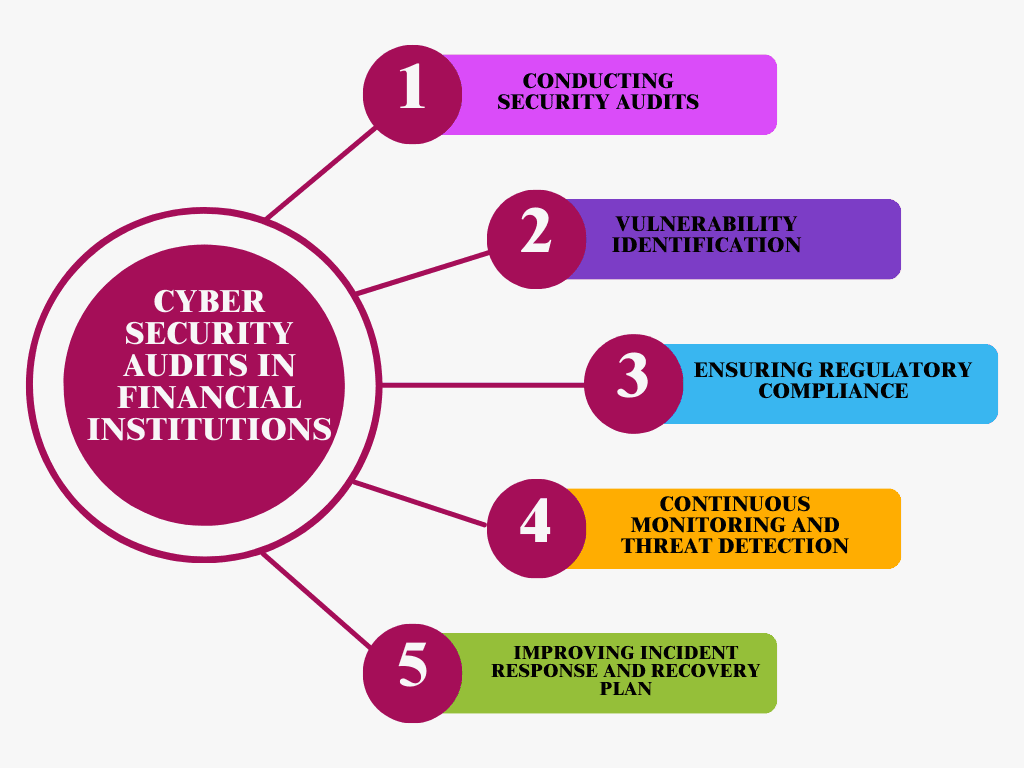
1 Conducting Security Audits
Regular cybersecurity audits are critical for evaluating the security posture of financial institutions. These audits systematically assess systems, networks, and processes to uncover potential weaknesses, vulnerabilities, and areas of non-compliance. By conducting these audits, institutions can ensure they are prepared to defend against cyber threats.
2 Vulnerability Identification
One of the primary purposes of a cybersecurity audit is to identify vulnerabilities within the institution’s infrastructure. These may include outdated software, weak access controls, or misconfigurations that could be exploited by attackers. By identifying and addressing these weaknesses early, institutions can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks.
3 Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Financial institutions must adhere to various regulatory requirements like GDPR, PCI DSS, and others. Cybersecurity audits help institutions ensure they remain compliant with these laws by reviewing data protection measures, encryption practices, and other safeguards. Non-compliance can lead to costly fines and reputational damage, making regular audits essential for maintaining legal and regulatory standards.
4 Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Audits not only identify existing vulnerabilities but also establish systems for continuous monitoring. Real-time monitoring solutions can be assessed during an audit to ensure they are effectively identifying and responding to suspicious activity or potential breaches. This proactive approach helps mitigate threats before they lead to significant damage.
5 Improving Incident Response and Recovery Plan
Cybersecurity audits help institutions review and refine their incident response and disaster recovery plans. By testing these plans during an audit, institutions can identify gaps in their response procedures, improve communication protocols, and ensure that they can quickly recover from a cyberattack or data breach. This preparedness is crucial for minimizing downtime and mitigating financial and reputational losses.
9. Incident Management and Response in Financial Institutions
Even with the best security measures, cyber attacks can still happen. Having a strong incident management plan in place is crucial. This includes:
Legal and Financial Implications: Cyber attacks can lead to significant legal and financial consequences, including fines, lawsuits, and loss of customer trust.
Incident Response Plans: A well-prepared response plan helps financial institutions react quickly to cyber attacks and minimize damage.
Data Breach Notifications: In the event of a data breach, financial institutions must notify affected individuals and authorities promptly to comply with regulations and maintain customer trust.
Future Trends in Cyber Security and Data Protection in Financial Institutions
The cyber security landscape is constantly evolving. Some future trends to watch for include:
1 AI and Automation in Cybersecurity
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is set to increase, allowing financial institutions to detect and respond to cyber threats more efficiently. AI can help identify patterns and anomalies in real-time, automate threat detection, and reduce the response time to potential attacks, making it a critical tool in future cybersecurity strategies.
2 Cloud-Based Security Solutions
With the growing adoption of cloud computing in financial services, cloud-based security solutions will become integral to safeguarding sensitive data. Financial institutions will need to implement robust cloud security measures such as encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring to protect against data breaches in the cloud environment.
3 Preparing for New Cyber Threats
As cybercriminals develop more sophisticated attack methods, financial institutions must remain vigilant and adaptable. Emerging threats such as quantum computing-powered cyberattacks, deep fakes, and more advanced ransomware will require proactive defenses and continuous updates to security
4 Zero Trust Security Models
The “zero trust” approach, which assumes no one—whether inside or outside the organization—can be trusted by default, is expected to become more prevalent. Financial institutions will implement this model to verify every access request, continuously authenticate users, and enforce strict access controls to minimize insider threats and external breaches.
5 Biometric Authentication
Biometric security methods, such as facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and voice authentication, will continue to gain prominence in financial institutions as a way to enhance security for customers. Biometric data will complement or replace traditional passwords, providing stronger authentication methods that are harder to replicate or steal.
Differences between Cyber Security and Data Protection
| Aspect | Cyber Security | Data Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Protecting systems, networks, and infrastructure from cyber threats. | Ensuring the privacy and proper handling of sensitive data. |
| Primary Objective | Prevent unauthorized access, attacks, or system disruptions. | Safeguard personal and financial data from breaches or misuse. |
| Threat Examples | Hacking, phishing, malware, ransomware attacks. | Unauthorized access, data breaches, improper data sharing. |
| Compliance | Involves cyber security standards like ISO 27001, NIST. | Involves data protection laws such as GDPR, CCPA, PCI DSS. |
| Tools and Techniques | Firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and MFA. | Data encryption, secure data storage, anonymization, and access control. |
FAQs
What is the difference between cyber security and data protection?
Cyber security focuses on protecting a financial institution’s systems, networks, and infrastructure from cyber threats such as hacking, malware, and phishing. Data protection, on the other hand, ensures the privacy and proper handling of sensitive personal and financial data, preventing unauthorized access and misuse.
Why is cyber security important for financial institutions?
Financial institutions handle large volumes of sensitive information and financial transactions, making them prime targets for cybercriminals. Robust cyber security measures help prevent fraud, data breaches, and financial loss, ensuring trust and compliance with industry regulations.
What are common cyber threats facing financial institutions?
Financial institutions commonly face threats such as phishing attacks, ransomware, malware, insider threats, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. These threats can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data, financial loss, and reputational damage.
How can financial institutions ensure compliance with data protection regulations?
Financial institutions must comply with regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and PCI DSS by implementing data encryption, secure data storage, access control mechanisms, and regular audits. Ensuring that employees are trained in proper data handling and cyber security practices is also crucial.
What technologies are emerging in cyber security for financial institutions?
Emerging technologies include artificial intelligence (AI) for detecting cyber threats, blockchain for secure financial transactions, and advanced threat detection systems that use machine learning to monitor and respond to potential cyber attacks in real-time.
Conclusion
Cyber security and data protection are crucial components of any financial institution’s operations. By implementing robust security measures, staying compliant with regulations, and embracing new technologies, financial institutions can protect their assets, maintain customer trust, and minimize the risks associated with cyber attacks.
