In today’s connected world, cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated, with social engineering being one of the most pervasive threats. Protecting yourself from such tactics is crucial to ensuring personal and organizational cybersecurity. This article outlines key strategies, tools, and insights to help you stay cyber aware.
1. Protect Yourself from Social Engineering
What is Social Engineering?
Social engineering is a type of cyberattack that manipulates individuals into giving away personal or confidential information. Unlike conventional hacking techniques that focus on exploiting software flaws, social engineering takes advantage of human behavior and psychology. It can manifest in various ways, including fraudulent emails, deceptive phone calls, or even in-person encounters.
For instance, you might get an email appearing to be from your bank, requesting your login information.While the email may look legitimate, it’s actually a ploy to steal your information. Understanding the nature of these attacks is the first step toward defending yourself.
Why You Need to Stay Cyber Aware
Cyber awareness is crucial because social engineering attacks are becoming more sophisticated.Not being aware of these tactics makes you more vulnerable to exploitation.. Whether you’re an individual protecting your personal data or an organization safeguarding its assets, understanding these risks helps you stay a step ahead of attackers.

2. Social Engineering Tactics and Cyber Awareness
Phishing and How to Avoid It
Phishing is a prevalent type of social engineering where attackers craft deceptive emails or messages that appear to come from legitimate sources. These messages typically include harmful links or attachments designed to compromise your security.
To protect yourself:
- Always verify the sender’s email address.
- Avoid clicking on links in unsolicited messages.
- Use anti-phishing tools and enable email filters.
Pretexting: Recognizing Deceptive Scenarios
Pretexting involves creating a false narrative to trick victims into sharing information. For example, an attacker might pretend to be a coworker asking for access to a shared drive.
The best defense is to question every request, especially if it involves sensitive information. Always confirm the identity of the requester through official channels.
Baiting: Staying Alert to Enticements
Baiting uses enticing offers, like free software or gifts, to lure victims into a trap. Once the victim takes the bait, their system could be infected with malware.
Avoid downloading anything from unverified sources, and always be cautious of “too good to be true” offers.
Tailgating: Protecting Physical Access
Tailgating happens when an unauthorized person gains access to a secure area by following someone else. This often occurs in workplaces where employees hold the door open for others without verifying their identity.
To prevent this, always ensure that only authorized individuals enter secure areas, even if it feels impolite.
3. Cyber Awareness: Recognizing Social Engineering
Signs of Social Engineering Attempts
Recognizing the signs of social engineering attempts is essential to protect yourself and others from falling victim to these attacks. Social engineers exploit human psychology, and understanding their tactics can save you from significant losses.
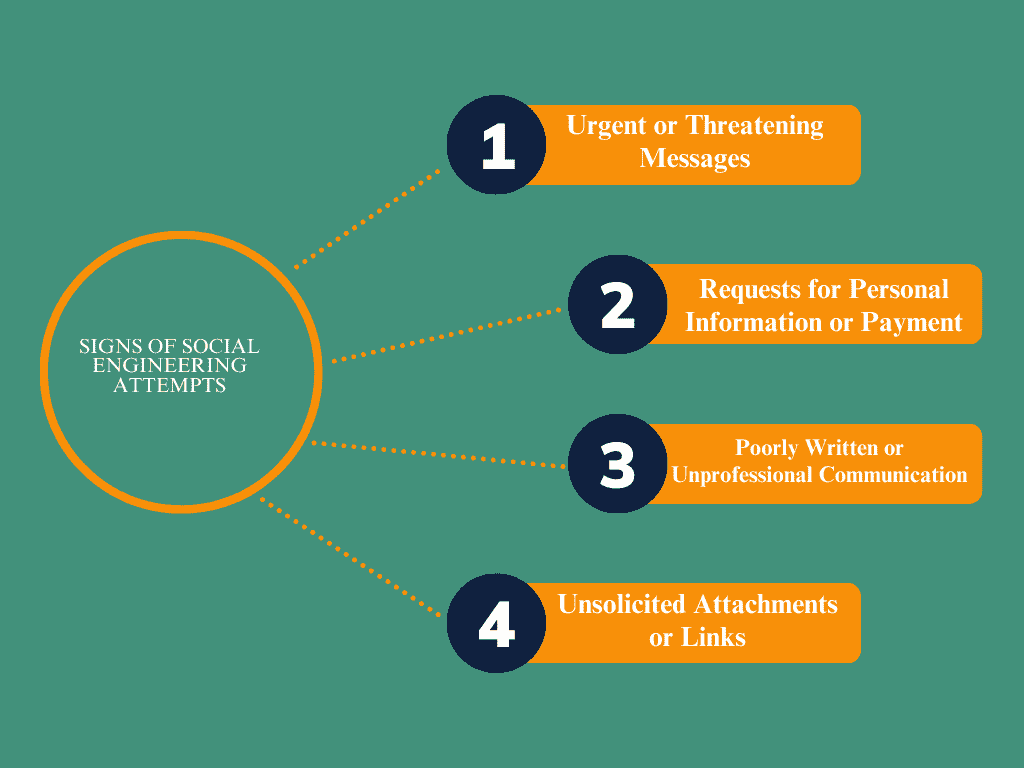
- Urgent or Threatening Messages
A common sign of social engineering is the sense of urgency conveyed in messages. Attackers often create panic by using phrases like “Act now!” or “Your account will be locked!” These messages are crafted to pressure you into acting quickly, often before you have a chance to properly verify the legitimacy of the request.. If you receive a message that demands instant attention, pause and evaluate its legitimacy before taking any action. Cybercriminals may even threaten to delete your account or freeze your assets to push you into acting quickly. - Requests for Personal Information or Payment
Any unsolicited request for personal details, financial information, or payment should raise a red flag. Cybercriminals often pose as bank officials, government employees, or even tech support representatives, asking for sensitive data like social security numbers or bank account credentials. Legitimate organizations will never ask for such information via email or text messages. Always verify such requests through official channels, such as calling the organization’s known phone number, not using the contact details provided in the email or message. - Poorly Written or Unprofessional Communication
Poor grammar, spelling mistakes, or unprofessional tone are other telltale signs of a phishing attempt. While legitimate companies take care to maintain professional standards in their communication, social engineers often don’t, leading to sloppy or awkwardly worded messages. If you notice these signs, treat the message with suspicion. This is especially important when the sender is claiming to be a well-known institution like your bank, an e-commerce website, or a service provider. - Unsolicited Attachments or Links
Be wary of unsolicited emails that contain attachments or links, especially if the sender is unknown. Cybercriminals often embed malware in attachments or use links to redirect you to fake websites that capture your login credentials. Always hover over links to check their actual destination before clicking on them. And never download attachments from unknown or suspicious sources.
Real-Life Examples and Lessons
One of the most notorious examples of social engineering occurred in 2020, during the Twitter hack, where attackers used social engineering techniques to infiltrate the company’s internal systems. The attackers were able to gain access to employee credentials through targeted phishing attacks, leading to the compromise of high-profile accounts, including those of celebrities, politicians, and tech leaders. They used the hijacked accounts to post fraudulent messages, causing confusion and financial losses.
This incident highlighted several lessons for individuals and organizations:
- Even Highly Secure Organizations Are Vulnerable: Twitter, a tech giant with significant cybersecurity resources, fell victim to social engineering. This demonstrates that no system is entirely safe from human error, underscoring the importance of user vigilance and continuous training.
- Multi-layered Defense is Key: Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA) are essential, but employees must also be trained to recognize and report phishing attempts.
- Accountability and Transparency: Prompt and transparent communication during an attack can limit its damage and help restore trust.
The Twitter hack serves as a reminder that social engineering is not just about technology; it’s about people. Continuous awareness and vigilance are critical in preventing such attacks.
4. Stay Cyber Aware: Preventing Social Engineering Attacks
Strong Password Strategies
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to defend yourself against social engineering attacks is through strong, unique passwords. Cybercriminals often rely on the fact that people use simple or reused passwords across multiple accounts. If they gain access to one account, they can easily compromise others. Here’s how you can ensure your passwords are secure:
- Create Strong Passwords
Your passwords should contain a combination of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Steer clear of using easily guessable details, like your name, birthdate, or common words, when creating passwords or security questions.. The longer the password, the harder it is for cybercriminals to crack, so aim for at least 12 characters. - Use Unique Passwords for Each Account
Never reuse passwords across multiple sites. A breach at one service can lead to the compromise of other accounts if the same password is used. Use different passwords for your email, bank accounts, and social media platforms. - Password Manager Tools
To manage multiple strong passwords, consider using a password manager. These tools store all your login credentials securely and can generate complex, random passwords for you. This way, you only need to remember one master password.

Identifying Suspicious Links and Attachments
Another crucial aspect of staying cyber aware is being cautious about links and attachments.Phishing emails frequently include links to fraudulent websites or attachments that carry malware, aiming to compromise your device or steal personal information.. Here are tips to stay safe:
- Hover Over Links
Before clicking on a link, hover your mouse over it to see the destination URL. If the link doesn’t match the supposed sender or looks suspicious, don’t click it. For example, a link in an email from “your bank” should lead to the bank’s official website. - Check the URL for HTTPS
Legitimate websites use HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), which is indicated by a padlock symbol in the browser’s address bar. Always ensure the website you’re visiting uses HTTPS before entering any sensitive information. - Be Cautious with Attachments
Never open attachments from unfamiliar sources. Malicious files can be disguised as legitimate documents like invoices or job applications. Ensure the file format matches the expected type (e.g., a PDF, not an executable .exe file) and scan it with antivirus software before opening.
Verifying Requests Before Acting
Always double-check any request involving sensitive actions. Whether it’s a financial transaction, a password reset, or sharing confidential information, it’s essential to confirm the legitimacy of the request.
- Contact the Source Directly
If you receive an unexpected request, verify it by contacting the person or organization directly using known contact information, such as phone numbers or email addresses listed on their official website. - Look for Inconsistencies
If a request seems suspicious or doesn’t feel right, trust your gut instinct and proceed with caution.Check for inconsistencies like unexpected deadlines or requests that don’t match the sender’s usual behavior.
Promoting Cybersecurity Education
Promoting cybersecurity awareness across your organization or within your personal network is vital to preventing social engineering attacks. Training employees or family members on identifying phishing emails, malicious links, and suspicious requests can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim.
- Regular Training and Awareness Programs
Organizations should conduct regular cybersecurity training for employees. These programs should cover the latest threats, including phishing, pretexting, baiting, and other social engineering tactics. - Test and Update Training Materials
As threats continue to evolve, it’s crucial to regularly update training materials to stay ahead of potential risks. Simulated phishing campaigns can also be used to test employees’ responses to real-life scenarios, helping reinforce their learning.
5. Building a Culture of Cyber Awareness
Training Employees Against Social Engineering
For organizations, building a culture of cybersecurity awareness is essential. Employees, as the first line of defense, must be equipped with the knowledge to identify and prevent social engineering attacks. Regular training sessions should address the following:
- Recognizing Social Engineering Tactics
Teach employees to identify common social engineering tactics, such as phishing, pretexting, and baiting. Use real-life examples to help them understand the techniques used by attackers. - Creating a Reporting System
Encourage employees to report any suspicious activity or attempts immediately. Reporting allows IT teams to take swift action and protect the organization from potential threats. - Simulated Attacks and Drills
Conduct simulated attacks, such as phishing drills, to test employees’ readiness. This helps them learn how to handle these situations effectively and reinforces their training.
Encouraging Reporting Without Fear
One of the biggest barriers to combating social engineering in organizations is the fear of repercussions. Employees may hesitate to report incidents due to concerns about blame or embarrassment. It’s vital to foster a culture where reporting suspicious activities is encouraged and welcomed.
- Non-punitive Reporting Environment
Ensure that there is no punishment for reporting potential breaches or suspicious activities. When employees feel supported, they are more likely to report incidents in a timely manner. - Clear Reporting Channels
Provide clear instructions on how to report suspicious activities, whether it’s via a dedicated email address, a hotline, or an internal ticketing system. Make sure that the process is straightforward and accessible. - Post-Incident Analysis and Feedback
After an incident, take the time to discuss what went wrong, how the threat was handled, and what can be improved. This helps to refine the company’s response to future threats and reinforces the importance of vigilance.
6. The Role of Technology in Social Engineering Defense
Anti-Phishing Tools and Email Filters
Modern cybersecurity technology plays a crucial role in defending against social engineering attacks. Anti-phishing tools and email filters are essential components of any cybersecurity strategy.
- Phishing Detection Software
Anti-phishing software leverages machine learning and behavioral analysis to identify phishing attempts. These tools examine incoming emails for common phishing signs, like deceptive URLs or suspicious attachments, and automatically block them to protect users. - Spam Filters
Advanced spam filters are essential for blocking unwanted emails before they reach your inbox. These filters analyze the content of messages and classify them based on known spam patterns.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) provides an added layer of security, making it significantly harder for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access. By requiring two or more forms of verification (such as a password and a one-time code sent to your phone), MFA reduces the risk of compromised accounts.
- Types of MFA
MFA can include something you know (password), something you have (smartphone or hardware token), and something you are (biometric data like fingerprints or facial recognition). Combining these factors makes it much harder for attackers to access sensitive information. - Encouraging MFA Adoption
Encourage the use of MFA across all accounts that support it, especially for sensitive platforms like email, banking, and social media.
Cybersecurity Software Solutions
Investing in comprehensive cybersecurity software solutions can provide real-time threat detection and response. These tools offer a multi-layered defense against various types of attacks, including social engineering.
- Real-Time Monitoring
Comprehensive security software offers real-time monitoring of networks and systems. It can quickly detect suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access attempts or unusual login patterns, allowing organizations to act quickly. - Incident Response and Forensics
In the event of a breach, cybersecurity software can assist in incident response and forensics. It helps trace the origins of the attack and understand how the breach occurred, which is crucial for improving defenses in the future.

7. What to Do If Social Engineering Happens
Immediate Actions to Protect Yourself
If you suspect that you’ve been targeted by social engineering, it’s crucial to act swiftly:
- Change Your Passwords
Immediately change passwords for affected accounts. Make sure your new passwords are both strong and unique for each account to enhance security and reduce the risk of breaches. - Notify Relevant Parties
Inform your bank, employer, or any relevant institutions about the potential breach. They can monitor your accounts for suspicious activity and help secure your assets. - Monitor Your Accounts
Monitor your financial and social media accounts regularly for any signs of unusual activity. If you notice anything suspicious, report it right away to prevent potential damage.
Limiting the Impact of a Breach
If you believe a breach has occurred, it’s essential to take quick actions to limit the damage:
- Isolate Affected Systems
If you’re part of an organization, work with your IT team to isolate any compromised systems from the rest of the network. This prevents the attacker from spreading malware or stealing more information. - Document the Incident
Record the details of the breach, including how it happened, what was affected, and what steps you’ve taken. This documentation is essential for learning from the incident and improving future defenses.
8. Stay Safe with Continuous Cyber Awareness
Keeping Up with Emerging Threats
Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics, so staying informed is crucial:
- Follow Cybersecurity Blogs
Subscribe to trusted cybersecurity blogs and websites to stay updated on the latest threats and trends. - Attend Webinars and Conferences
Participate in cybersecurity webinars and conferences to learn from experts and hear about emerging threats and countermeasures.
Reporting Social Engineering Attempts
Reporting any suspicious activities not only protects you but also helps the wider community. Here’s how you can contribute:
- Inform Authorities
If you encounter a scam or a suspicious attempt, report it to relevant authorities such as consumer protection agencies or the platform hosting the scam. - Share Knowledge with Others
Share your experiences with peers and family to raise awareness about common social engineering tactics. The more people who are informed, the harder it will be for cybercriminals to succeed.
By fostering a culture of continuous cybersecurity awareness, you contribute to a safer digital environment for everyone. Stay vigilant, and don’t hesitate to report any suspicious activities you come across.
9 Differences between Recognizing Social Engineering and Preventing Social Engineering Attacks.
| Focus | Identifying the signs of social engineering attempts. | Practical steps to prevent social engineering from affecting you or your organization. |
| Signs of Social Engineering | Describes common tactics, such as urgency, requests for personal info, poor grammar in communication. | Focuses on defending against those signs, such as recognizing phishing attempts and avoiding suspicious links. |
| Real-Life Examples | Uses the Twitter hack of 2020 to highlight how social engineering works in real-world scenarios. | Suggests using multi-factor authentication and secure passwords to mitigate risks. |
| Main Goal | Help readers recognize when they’re being targeted by cybercriminals. | Equip readers with strategies to avoid falling victim to social engineering attacks. |
| Key Strategies | Focuses on how to spot social engineering tactics, such as urgent requests or poorly written communication. | Emphasizes strong passwords, verifying requests, and using cybersecurity tools to prevent attacks. |
| Actionable Advice | Provides practical advice on identifying phishing attempts or scams early. | Suggests actionable steps like using MFA, password managers, and anti-phishing tools to prevent attacks. |
| Examples & Case Studies | Cites high-profile social engineering incidents (like the 2020 Twitter hack) to emphasize lessons learned. | Focuses more on how to protect your digital life proactively by securing your passwords and accounts. |
| Educational Focus | Teaches readers to be aware and recognize social engineering attempts. | Educates readers on defensive techniques and creating awareness within teams or organizations. |
10 FAQs
1. What is social engineering in cybersecurity?
Social engineering in cybersecurity refers to the tactics used by cybercriminals to manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information, typically for fraudulent purposes. These attacks exploit human psychology and emotions, rather than relying solely on technical vulnerabilities. Often, attackers use methods like phishing emails, fake websites, or impersonation over phone calls or social media to trick victims into providing things like passwords, financial details, or personal data. Because these attacks rely on deception and psychological manipulation, they can be particularly dangerous, as they target the human element of security rather than technological defenses.
2. How can I recognize a social engineering attack?
Recognizing a social engineering attack can sometimes be difficult, but there are common signs that can help you identify when you are being targeted. One of the most frequent tactics is creating a sense of urgency, where the attacker might say something like “Your account will be locked unless you act immediately” or “You must respond now to avoid a penalty.” These messages are designed to prompt hasty decisions without allowing you to think through the situation. Another red flag is unsolicited requests for personal information, such as asking for your bank account details or login credentials. Social engineers may also disguise themselves as trusted entities, like a customer service representative, to appear legitimate.
3. How can I protect myself from social engineering attacks?
Protecting yourself from social engineering attacks requires a proactive approach, focusing on both technological tools and common-sense practices. One of the most important steps is to use strong, unique passwords for every account. Weak or repeated passwords make it easier for attackers to gain access to multiple systems once they have cracked one password. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is another effective defense, as it requires an extra layer of verification, such as a one-time code sent to your phone, alongside your password. This makes it much harder for attackers to compromise your accounts, even if they manage to get hold of your password.
4. What should I do if I fall victim to a social engineering attack?
If you realize that you have fallen victim to a social engineering attack, it is important to act quickly to minimize potential damage. First, change your passwords immediately for any accounts that may have been compromised. Make sure the new passwords are strong and unique, ideally using a password manager to keep track of them securely. After updating your passwords, you should notify any relevant parties, such as your bank, employer, or any online service providers, to inform them about the possible breach. They may be able to secure your accounts and prevent further unauthorized activity. It’s also crucial to monitor your financial and online accounts for any unusual activity, such as unauthorized transactions or new login attempts. If you notice anything suspicious, report it immediately to the appropriate authorities. Lastly, consider reporting the incident to local law enforcement or consumer protection agencies, as this can help prevent the attacker from targeting others and could assist in their investigation.
5. How can organizations protect employees from social engineering attacks?
Organizations play a critical role in safeguarding their employees from social engineering attacks by fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness. Regular training programs are essential to help employees recognize the signs of social engineering, such as phishing emails or phone calls from fake customer service representatives. Employees should be taught how to handle suspicious requests and what to do if they encounter them, including reporting them to IT security teams. Encouraging employees to report any security concerns without fear of reprimand is also vital, as it helps catch potential threats early.
Conclusion
Social engineering is a major cybersecurity risk that manipulates human behavior to gain unauthorized access to confidential information. By understanding the tactics used by attackers, such as creating urgency, impersonating trusted entities, and manipulating emotions, individuals and organizations can better prepare to recognize and prevent these attacks. The key to protection lies in a combination of awareness, proactive security measures, and continuous education.
For individuals, adopting strong password practices, enabling multi-factor authentication, and verifying unsolicited requests are crucial steps in securing personal data. Organizations, on the other hand, should prioritize employee training, establish a culture of vigilance, and implement technical defenses like anti-phishing tools to safeguard against such attacks.
