1. Introduction
As the healthcare industry moves deeper into the digital age, the need for secure, accessible, and flexible data storage and processing solutions has become more critical. Cloud computing offers a powerful solution, enabling healthcare providers to store and manage large volumes of data, streamline workflows, and enhance patient care. However, with this convenience and scalability comes the responsibility to secure patient data, which includes highly sensitive personal and medical information. This article will discuss how cloud computing supports the healthcare sector by addressing data security challenges, the benefits it brings, and future trends.
1.1 The Importance of Data Security in Healthcare
Patient data, including personal health records, treatment histories, and insurance information, is among the most sensitive data types. Protecting this data is crucial because breaches can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and compromised patient care. Data security is essential for maintaining patient trust and for healthcare providers to comply with strict regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe. Cloud computing provides various tools and technologies that ensure this data remains protected.
1.2 Cloud Computing as a Solution
Cloud computing not only secures patient data but also allows healthcare providers to focus on delivering better care by offering on-demand access to data from anywhere. By using the cloud, hospitals and clinics can access real-time patient data, helping improve decision-making and emergency responses. Cloud computing solutions also allow for scalable storage, meeting the needs of both large and small healthcare providers.
2. The Role of Cloud in the Healthcare Industry
Cloud computing has transformed healthcare operations by improving data management, enabling remote care, and enhancing communication among providers. These advancements provide better and more accessible patient care across a variety of healthcare settings.
2.1 Cloud Storage and Data Management
Cloud storage provides a streamlined, secure, and easily accessible solution for data storage, enabling users to manage and retrieve data efficiently from virtually anywhere. Hospitals and clinics handle massive amounts of data daily, including patient records, imaging files, and lab results. Cloud storage reduces the need for physical storage, which can be costly and difficult to manage. Additionally, cloud storage solutions offer data redundancy, meaning data is backed up across multiple locations, ensuring that it remains accessible and safe even if one server fails.
2.2 Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring
With the rise of telemedicine, cloud technology has become indispensable. Patients who live in remote or underserved areas can access healthcare services without traveling, and chronic conditions can be monitored remotely. Through cloud platforms, doctors can review patient data, prescribe medication, and provide consultations. Remote patient monitoring devices, like heart rate monitors and glucose sensors, transmit data to the cloud, where it can be analyzed in real time by healthcare providers.
2.3 Collaboration and Communication Among Providers
Cloud computing facilitates better communication and collaboration among healthcare providers. With centralized, cloud-based systems, doctors, nurses, and specialists can access up-to-date patient information, improving care coordination. For instance, in a case where a patient is referred from a primary care provider to a specialist, cloud systems allow for seamless data transfer, so the specialist has the complete patient history.
3. Types of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Healthcare providers use different cloud types based on their specific needs and resources. Each type offers unique advantages and potential challenges.
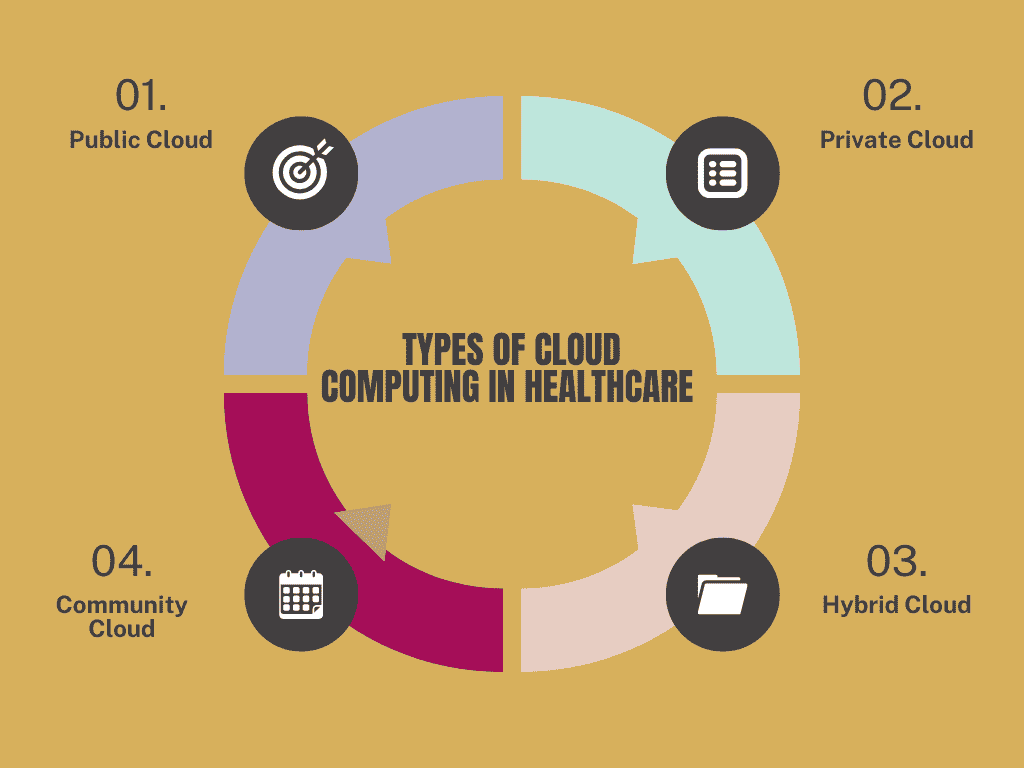
3.1 Public Cloud
Public clouds are shared infrastructures managed by third-party providers, making them cost-effective and ideal for non-sensitive data. They are highly scalable, allowing healthcare organizations to expand resources as needed. However, because public clouds are shared, they have more limited control over data security, which can be a disadvantage for healthcare providers handling sensitive patient information.
3.2 Private Cloud
Private clouds offer dedicated resources and are hosted on a private network. These clouds are highly secure and allow healthcare providers more control over their data. Private clouds are ideal for handling sensitive patient information because they offer enhanced security and compliance capabilities, including encryption and access control. Private clouds, while offering enhanced control and security, tend to be costlier and may present greater challenges in scaling compared to public cloud solutions.
3.3 Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud integrates features of both public and private cloud environments, creating a flexible, blended solution. Healthcare providers can store sensitive data in the private cloud while utilizing the public cloud for less sensitive operations. This approach provides flexibility and allows for both secure data handling and scalable resources.
3.4 Community Cloud
Community clouds are designed for specific industries or groups with similar needs. In healthcare, a community cloud may serve hospitals, research institutions, and public health organizations. This setup allows these entities to share resources while ensuring data privacy and security.
4. Data Security Challenges in Healthcare
The healthcare industry encounters distinct challenges in safeguarding data, given its sensitive nature and strict privacy requirements. These challenges arise from both external threats and the internal complexities of handling sensitive data.
4.1 Common Security Threats
Healthcare data is a lucrative target for cybercriminals because of the personal information it contains. The healthcare industry encounters distinct challenges in safeguarding data, given its sensitive nature and strict privacy requirements. These attacks can lead to data breaches, compromising patient information and damaging a healthcare provider’s reputation. Cloud providers offer solutions like multi-factor authentication, encryption, and firewalls to mitigate these risks.
4.2 Risks Associated with Cloud Computing
While the cloud offers many advantages, it also presents certain risks, such as potential data leaks and compliance issues. Data is stored off-site and managed by a third party, which can raise concerns about unauthorized access or accidental exposure. Healthcare providers must carefully select cloud providers that comply with healthcare regulations and implement strict security measures to safeguard patient information.
5. How Cloud Enhances Data Security in Healthcare
Cloud providers employ a range of technologies to protect healthcare data, helping healthcare organizations meet strict security standards.
5.1 Encryption and Data Privacy Measures
Encryption is essential for protecting healthcare data. Cloud providers use advanced encryption algorithms to ensure that data is unreadable to unauthorized users. Encryption applies to both stored data (data at rest) and data being transferred between locations (data in transit).
5.2 Compliance with Regulations
Cloud providers prioritize compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR. These regulations mandate that healthcare organizations establish targeted security protocols to safeguard patient information. Leading cloud providers ensure that their services meet these regulatory standards, helping healthcare organizations avoid penalties and legal issues.

5.3 Role of AI and Machine Learning in Threat Detection
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) help cloud providers detect and respond to potential security threats. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data to identify unusual patterns or behaviors, allowing cloud providers to take proactive measures to prevent breaches.
6. Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
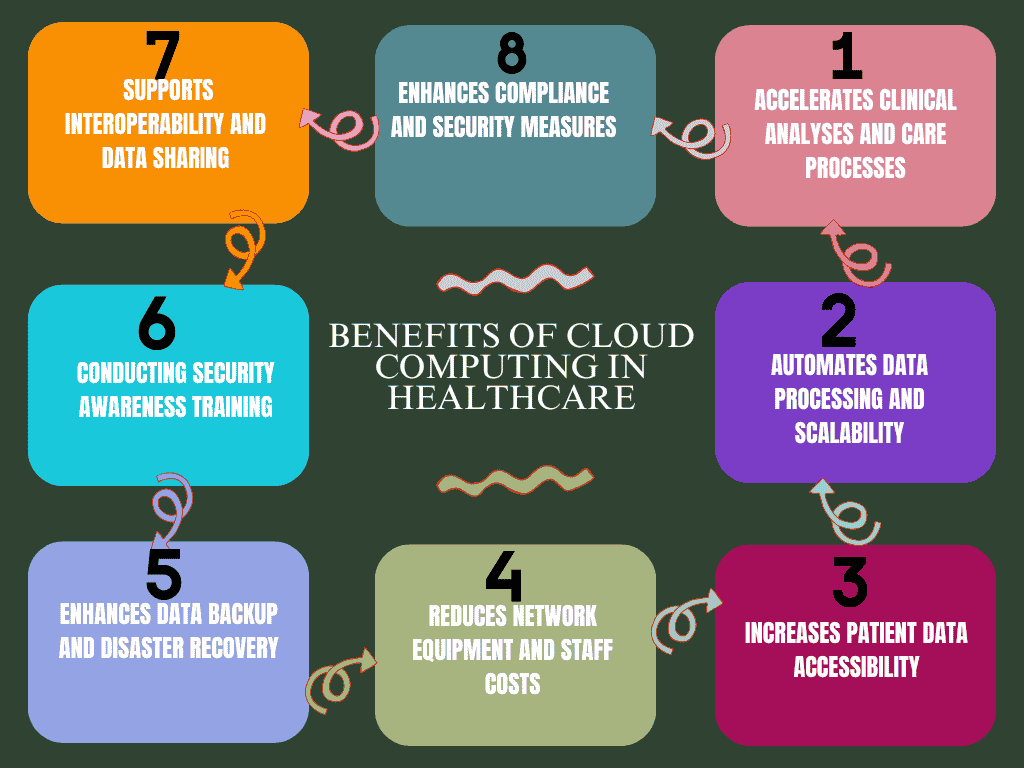
Cloud computing brings numerous benefits to the healthcare industry, from improving patient care and enhancing data accessibility to reducing costs and increasing operational efficiency. With the ability to store, process, and manage vast amounts of data securely, cloud solutions are reshaping how healthcare providers operate and deliver services. Below, we’ll explore the core advantages of cloud computing in healthcare.
6.1 Accelerates Clinical Analyses and Care Processes
Cloud computing enables healthcare providers to access advanced data analytics and computational resources, accelerating clinical research and patient diagnosis. Cloud platforms can process vast datasets quickly, which is essential in areas like genomics, medical imaging, and personalized medicine. With cloud-based solutions, healthcare professionals can analyze patient data rapidly, leading to faster, more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
For instance, a hospital can use cloud-powered AI to process medical imaging data to detect anomalies or diseases in real-time. This acceleration in processing not only helps doctors make better decisions but also reduces the waiting time for patients, thereby improving the overall quality of care.
6.2 Automates Data Processing and Scalability
Cloud solutions provide healthcare organizations with automated data processing capabilities, which allow them to manage large volumes of patient records, billing information, and other critical data seamlessly. Through automation, tasks like data entry, reporting, and even some administrative tasks are simplified, allowing staff to focus on patient care rather than paperwork.
Additionally, cloud infrastructure is inherently scalable, allowing healthcare providers to adjust their resources according to demand. During times of increased patient intake—such as flu seasons or pandemics—cloud providers can instantly scale up storage and processing power, ensuring that healthcare services continue without interruption. This flexibility is invaluable for healthcare organizations, especially those with varying patient loads.
6.3 Increases Patient Data Accessibility
Cloud computing allows authorized healthcare professionals to access patient data securely from anywhere, enabling better coordination and more timely decision-making. This accessibility is especially valuable in emergency situations or when specialists are needed across different locations. For example, a specialist can access a patient’s imaging records remotely to provide a consultation or second opinion without having to be physically present, which can save time and potentially lives.
In a telemedicine setting, cloud technology enables healthcare providers to conduct remote consultations and follow-up appointments, making healthcare accessible to patients in remote or underserved areas. By improving data accessibility, cloud computing enhances the quality of patient care and ensures that healthcare is available when and where it’s needed most.
6.4 Reduces Network Equipment and Staff Costs
Traditionally, healthcare organizations needed to invest heavily in physical servers, networking equipment, and IT infrastructure to manage their data on-site. Cloud computing reduces this need by providing virtual resources that can be accessed and managed over the internet. With cloud-based solutions, healthcare organizations no longer need to maintain and upgrade their hardware frequently, which lowers operational and maintenance costs.
Moreover, the cloud reduces the need for a large in-house IT staff dedicated to server management, as cloud providers handle maintenance, security updates, and technical support. This shift allows healthcare providers to allocate resources more effectively, focusing more on patient care and less on infrastructure management.
6.5 Enhances Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Data loss due to technical failures, natural disasters, or security breaches can have serious consequences for healthcare providers and patients alike. Cloud providers typically offer robust backup and disaster recovery solutions, ensuring that data is always available, even in the event of an unexpected incident. Cloud-based backups are stored across multiple secure locations, providing redundancy that minimizes the risk of data loss.
In the case of a natural disaster, such as a flood or fire at a healthcare facility, the cloud can offer continuous data access from remote locations, ensuring that patient care is not disrupted. By ensuring reliable data backups and disaster recovery options, cloud computing offers healthcare providers peace of mind and helps maintain continuity of care.
6.6 Supports Interoperability and Data Sharing
Interoperability—the ability of different healthcare systems to work together—is essential for effective patient care, especially in complex cases involving multiple specialists or healthcare facilities. Cloud solutions enable interoperability by allowing healthcare systems to connect and share data seamlessly. This connectivity allows healthcare providers to access complete patient records, regardless of where the data is stored.
For instance, if a patient is referred to a specialist in another city, their medical records can be accessed instantly via the cloud, ensuring that the specialist has all necessary information. This seamless data-sharing capability reduces redundancies, minimizes the risk of errors, and ensures that each provider has a comprehensive view of the patient’s health history, contributing to more personalized and effective care.
6.7 Enhances Compliance and Security Measures
Cloud providers are subject to rigorous security standards and are often compliant with healthcare regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. These regulations require specific security measures to protect sensitive healthcare data. By using cloud services, healthcare providers can more easily ensure that they are meeting these compliance standards.
Cloud providers implement advanced security measures, including encryption, access control, and regular audits, to protect data against unauthorized access. These measures enhance data security, reducing the likelihood of breaches and helping healthcare providers maintain patient trust.
7. Key Benefits of Cloud Security in Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, data security is critical due to the sensitivity of patient information, which includes personal identifiers, medical histories, treatment records, and billing information. Cloud security solutions offer robust protection for healthcare data, ensuring that it remains private, accessible, and resilient against cyber threats. This section explores the core benefits of cloud security for healthcare organizations, including enhanced patient data protection, operational efficiency, and scalability.
7.1 Improved Patient Data Protection
One of the primary benefits of cloud security in healthcare is the enhanced protection it provides for patient data. Cloud providers employ advanced security measures, including data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls, which are essential for safeguarding sensitive information against unauthorized access. These security layers help ensure that patient data remains confidential and is only accessible to authorized personnel.
In addition, cloud providers regularly perform vulnerability assessments and security audits to identify potential weaknesses and address them proactively. By continuously improving security protocols, cloud providers help healthcare organizations maintain a high level of data protection, which is essential for building patient trust and adhering to regulatory standards.
7.2 Compliance with Healthcare Regulations
Healthcare organizations must comply with strict regulations to protect patient data, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. Failing to adhere to these regulations may lead to substantial fines and harm an organization’s reputation. Cloud providers often have compliance certifications, demonstrating that they meet the necessary regulatory standards.
Many cloud providers are specifically tailored for healthcare, offering HIPAA-compliant solutions that ensure data security and privacy. These solutions include robust access restrictions, detailed audit logs, and encryption of data. By partnering with compliant cloud providers, healthcare organizations can more easily meet regulatory requirements and avoid potential legal and financial repercussions.
7.3 Cost Savings and Operational Efficiency
Implementing robust data security measures can be expensive and resource-intensive for healthcare organizations, especially if managed on-site. Cloud security solutions offer a cost-effective alternative by handling security infrastructure, updates, and monitoring on behalf of healthcare providers. This reduces the need for large in-house IT teams and on-site security equipment, resulting in significant cost savings.
Additionally, cloud providers take on the responsibility of managing security protocols and updating systems to address emerging threats, which minimizes operational downtime. This operational efficiency allows healthcare organizations to focus more resources on core activities, such as patient care and medical research, rather than on maintaining and upgrading security systems.
7.4 Scalability and Flexibility for Healthcare Providers
The cloud provides scalable solutions that can grow with the needs of healthcare providers, offering both flexibility and security. As patient data volumes increase, especially with the adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) and digital imaging, healthcare providers require solutions that can scale quickly without compromising security. Cloud security solutions provide scalability, enabling organizations to grow their storage and processing capacity as required.
With cloud-based security, healthcare providers can also adopt new technologies and tools without undergoing extensive security overhauls. For example, when integrating new telemedicine platforms or remote monitoring systems, cloud security solutions ensure that these additions are protected under the same security protocols. This flexibility allows healthcare providers to innovate and adapt to changing demands without sacrificing data protection.
7.5 Enhanced Threat Detection and Proactive Defense
Cloud security providers use advanced threat detection tools, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), to identify and respond to potential security threats in real time. These tools analyze patterns and behaviors within the network, quickly flagging unusual activity that could indicate a security threat, such as an unauthorized login attempt or suspicious data access. This proactive defense mechanism enables healthcare organizations to respond swiftly to potential breaches, minimizing damage and preventing data loss.
In addition to real-time monitoring, cloud security providers offer automated responses to common threats. For instance, if a phishing attempt is detected, the system can automatically block the email or restrict access to protect the network. This proactive approach strengthens the overall security posture of healthcare organizations, ensuring patient data remains secure.
7.6 Reliable Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Cloud providers offer robust data backup and disaster recovery solutions that ensure patient data remains safe and accessible, even during unexpected incidents such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or equipment failure. Cloud backups are typically stored across multiple data centers in different geographic locations, providing redundancy and ensuring that data can be restored quickly in the event of a loss.
In the healthcare industry, where data continuity is critical for patient care, reliable data backup and disaster recovery solutions are essential. By using cloud-based backup services, healthcare providers can avoid significant disruptions to operations, ensuring that patient records and medical histories are always accessible. This resiliency helps maintain uninterrupted patient care and contributes to greater overall trust in the healthcare system.
8. Applications and Companies Using Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Several applications and companies use cloud technology to improve patient care and data security.
8.1 Overview of Popular Applications
Popular cloud-based applications in healthcare include EHR (Electronic Health Record) systems, telemedicine platforms, and patient management tools. These applications help streamline healthcare delivery and improve patient outcomes.
8.2 Case Studies of Leading Companies
Leading companies like Google Health, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure are making significant strides in healthcare. Google Health, for example, uses cloud solutions to support AI-driven diagnostics, while AWS provides secure data storage for healthcare providers.
8.3 Impact on Patient Care and Healthcare Delivery
Cloud-enabled applications improve healthcare delivery by providing more efficient workflows, better data access, and real-time monitoring capabilities.
9. Challenges and Considerations for Implementing Cloud Security
Certainly! Here’s a concise, five-line summary for each heading under Challenges and Considerations for Implementing Cloud Security in healthcare.
9. Challenges and Considerations for Implementing Cloud Security
Implementing cloud security in healthcare is essential for protecting sensitive patient data, but it also brings unique challenges. Healthcare organizations must address these challenges thoughtfully to ensure effective data protection while maintaining accessibility and compliance. Here’s a breakdown of the key considerations when adopting cloud security solutions in healthcare.
9.1 Balancing Accessibility and Security
Healthcare providers need immediate access to patient information for effective care, but this accessibility can increase security risks. Balancing the need for quick access with stringent security measures is challenging. Using tools like role-based access control (RBAC) can help, allowing only authorized personnel to access sensitive data. Multi-factor authentication and encryption further protect patient information. This balance ensures data remains secure yet available when needed.
9.2 Choosing Reliable Cloud Providers
Selecting a trusted cloud provider is critical, as not all providers offer the same security standards. Healthcare organizations should assess a provider’s experience, compliance certifications, and security protocols. Reputable providers will also be transparent about data handling practices and support regulatory compliance. Understanding each provider’s data centers, response times, and terms is essential for a secure choice. Clear responsibilities in case of breaches help mitigate risks.

9.3 Staff Training and Awareness
Even with advanced security measures, human error can still cause data breaches. Proper staff training on data security practices is essential to reduce accidental risks. Regular training on topics like phishing prevention and secure data handling fosters a culture of security awareness. Understanding cloud system usage and best practices further strengthens data protection. By training staff, healthcare providers create a mindful, security-focused workplace.
9.4 Ensuring Compliance with Healthcare Regulations
Healthcare regulations like HIPAA and GDPR set strict standards for data security, which cloud solutions must support. Compliance requires healthcare organizations to use both secure cloud providers and internal policies. Regular audits, encryption, and security assessments ensure ongoing adherence to regulatory standards. Collaboration with cloud providers is essential to uphold these standards. Ensuring compliance helps avoid penalties and maintain patient trust.
9.5 Addressing Data Sovereignty Issues
Data sovereignty laws require healthcare data to be stored within specific geographic regions. For healthcare providers working internationally, navigating these regulations can be complex. Compliance with regional laws ensures data is protected and legally managed. Working with cloud providers that offer regional data centers can help meet sovereignty requirements. Adhering to these laws is crucial for maintaining legal and regulatory standards.
10. Future Trends in Cloud Security for Healthcare
As healthcare continues to embrace digital transformation, cloud security remains a vital focus. Emerging technologies and evolving security practices are shaping the future of secure cloud usage in healthcare. The following trends highlight how advancements in cloud security will better protect patient data and support the needs of healthcare organizations.
10.1 Emerging Technologies in Cloud Security
New technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are enhancing threat detection and response. These tools help identify unusual patterns or suspicious activity in real-time, allowing for proactive defense. Advanced encryption techniques are also becoming standard, improving data confidentiality. Quantum computing is anticipated to play a role in developing even stronger encryption. These technologies provide enhanced data protection for healthcare organizations.
10.2 The Role of Blockchain in Healthcare Data Protection
Blockchain technology is emerging as a powerful tool for securing healthcare data. Its decentralized structure ensures data transparency and immutability, making it difficult for unauthorized users to alter records. Blockchain can securely store patient records, verify data authenticity, and streamline access permissions. In the future, blockchain may become a standard for medical record storage and data sharing. This added security layer strengthens data integrity and patient trust.

10.3 Predictive Security with Artificial Intelligence
AI-driven predictive security is expected to play a significant role in preventing cyber threats before they occur. By analyzing data trends, AI can forecast potential vulnerabilities and implement preventive measures. This approach minimizes the risk of breaches by addressing weaknesses early. Predictive security enables healthcare providers to be proactive rather than reactive. This shift towards preemptive security enhances overall protection.
10.4 The Rise of Zero-Trust Security Models
The zero-trust security model operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” requiring continuous authentication. This model reduces the risk of unauthorized access by constantly validating users and devices. In healthcare, zero-trust can protect sensitive data across devices and locations. The model also aligns with remote healthcare trends, ensuring data security beyond traditional networks. Zero-trust is likely to become a standard for cloud security in healthcare.
10.5 Increased Focus on Privacy Regulations and Compliance
As data privacy regulations evolve, healthcare providers must adapt to stricter compliance standards. Future regulations are expected to be more comprehensive, covering new data types and emerging technologies. Cloud providers will offer enhanced compliance tools to help healthcare organizations meet these standards. Compliance will be critical in maintaining patient trust and avoiding legal issues. Increased regulatory focus will drive better data protection practices in healthcare.
11 Difference between Public Cloud and Private Cloud
| Aspect | Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | More affordable due to shared resources; cost-effective for non-sensitive data. | Higher cost due to dedicated infrastructure, suited for handling sensitive data. |
| Data Security | Limited control over security; suitable for less sensitive data. | High security with dedicated resources; ideal for protecting sensitive patient data. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; resources can be adjusted easily to meet demand. | Limited scalability due to fixed resources; scaling can require significant investment. |
| Compliance | May lack full healthcare compliance, making it challenging to meet standards like HIPAA. | Designed to meet healthcare compliance standards, including HIPAA and GDPR. |
| Performance | Can vary depending on shared resources and network congestion. | Generally offers more stable performance due to dedicated resources and infrastructure. |
| Customization | Limited customization options, as the infrastructure is shared with other users. | High degree of customization, allowing for tailored configurations to meet specific needs. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for non-sensitive applications, development environments, and temporary projects. | Best for sensitive data storage, mission-critical healthcare applications, and long-term projects. |
12 FAQs
1. What are the main benefits of using cloud computing in healthcare?
Cloud computing in healthcare offers numerous benefits, including improved data accessibility, reduced operational costs, enhanced data security, and streamlined collaboration among healthcare providers. It enables healthcare organizations to store, access, and analyze patient data efficiently, supporting faster diagnoses, better patient care, and flexible scalability to meet fluctuating demands.
2. How does cloud security protect sensitive healthcare data?
Cloud security uses advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access controls to protect sensitive healthcare data from unauthorized access. Cloud providers also implement regular security audits, real-time threat monitoring, and AI-driven detection to identify potential security threats, ensuring that patient data remains safe and compliant with healthcare regulations.
3. What should healthcare organizations consider when choosing a cloud provider?
When choosing a cloud provider, healthcare organizations should assess factors such as compliance certifications (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR), data security measures, scalability, and reliability. Additionally, understanding the provider’s approach to data sovereignty, backup and recovery options, and support services is crucial for ensuring data protection and operational continuity.
4. What are the compliance considerations when using cloud computing in healthcare?
Healthcare organizations using cloud computing must comply with strict data privacy and security regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe. Compliance requires using cloud providers who adhere to these standards and implementing robust internal policies, such as data encryption, access control, and regular security assessments, to ensure patient data is protected.
5. What challenges do healthcare providers face when implementing cloud security?
Implementing cloud security in healthcare involves challenges like balancing data accessibility and security, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, training staff on data protection protocols, and selecting reliable cloud providers. Additionally, healthcare providers must address issues such as data sovereignty and scalability while maintaining a strong focus on protecting sensitive patient information.
13 Conclusion
Cloud computing has become an essential tool in the healthcare industry, offering unparalleled benefits in terms of data accessibility, scalability, and security. By enabling healthcare providers to store, process, and analyze data efficiently, the cloud supports faster diagnoses, enhances patient care, and reduces operational costs. Despite challenges such as ensuring compliance, balancing security with accessibility, and training staff, cloud solutions continue to evolve with advanced security measures, regulatory support, and innovative technologies like AI and blockchain. As the healthcare sector continues to embrace digital transformation, cloud computing stands poised to drive secure, efficient, and patient-centered care, paving the way for a future where healthcare is both accessible and resilient.
