Cloud computing has revolutionized the way organizations operate, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. However, as businesses increasingly migrate to the cloud, they face a spectrum of vulnerabilities that can compromise data integrity, security, and compliance. This article delves into the common vulnerabilities associated with cloud computing, the risks they pose, and strategies to mitigate them.
1. Introduction to Cloud Computing Vulnerabilities
1.1 Definition and Significance
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet, allowing organizations to access servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics on demand. Instead of relying on local servers or personal devices, businesses can utilize these resources remotely, making operations more flexible and scalable. The significance of cloud computing lies in its ability to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enable businesses to innovate rapidly. However, this convenience comes with a downside: vulnerabilities that can expose sensitive data and systems to various threats.
1.2 Evolution of Cloud Computing and Emerging Risks
Cloud computing has evolved significantly since its inception. Initially focused on basic storage solutions, it has transformed into complex systems that integrate various services like Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS). With this evolution, new risks have emerged, including advanced cyber threats, compliance issues, and the challenges of managing multi-cloud environments. Organizations must recognize these evolving risks and implement strategies to mitigate them effectively.
1.3 Impact of Vulnerabilities on Organizations
The impact of cloud vulnerabilities can be profound. Data breaches can lead to severe financial losses, sometimes amounting to millions of dollars in recovery costs, legal fees, and fines. Additionally, organizations may suffer reputational damage, losing the trust of customers and partners. Legal and compliance consequences can arise from failing to protect sensitive information, resulting in lawsuits and regulatory penalties. Furthermore, operational disruptions caused by breaches can hinder productivity and affect service delivery, leading to further losses.
2. Common Types of Cloud Computing Vulnerabilities
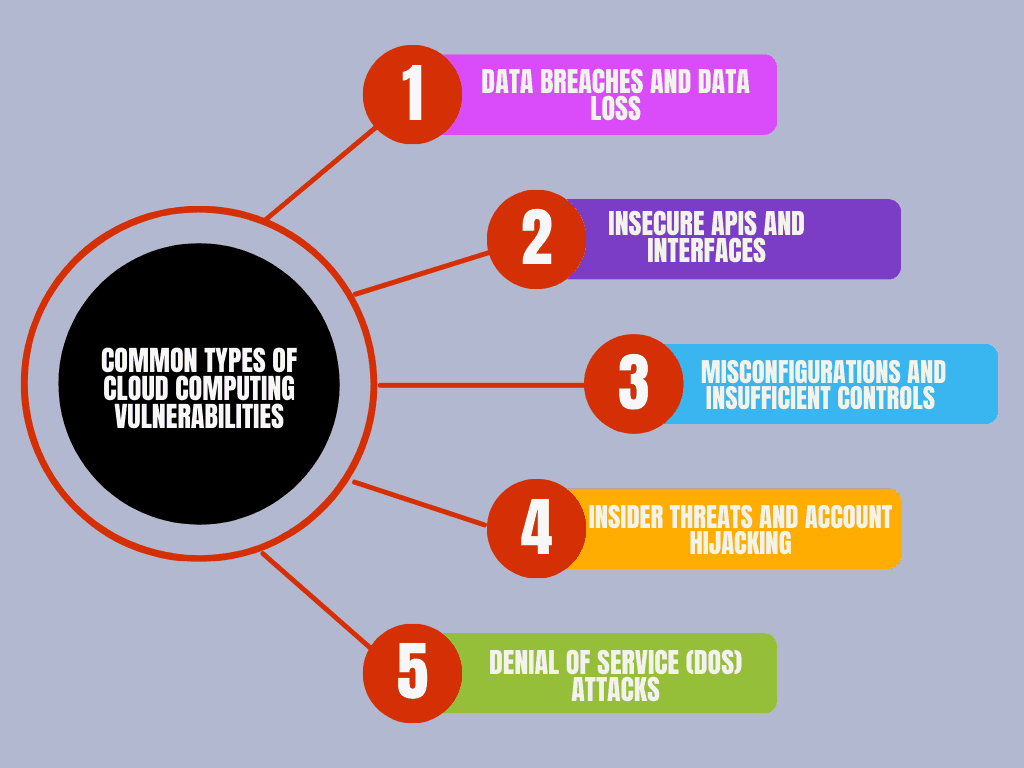
2.1 Data Breaches and Data Loss
Data breaches happen when unauthorized parties infiltrate cloud storage to access confidential information. This can result from various factors, such as weak passwords, phishing attacks, or software vulnerabilities. Data loss can occur due to accidental deletions, hardware failures, or malicious actions. Organizations must implement robust data protection measures, such as regular backups and recovery solutions, to mitigate these risks and ensure that data remains accessible and secure.
2.2 Insecure APIs and Interfaces
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) play a vital role in facilitating interaction and data exchange among various software applications.. However, insecure APIs can become easy targets for attackers. If APIs lack proper authentication, encryption, or input validation, they can be exploited to access sensitive data or perform unauthorized actions. Organizations must conduct thorough security assessments of their APIs and implement best practices to secure them, such as using secure coding practices and conducting regular vulnerability assessments.
2.3 Misconfigurations and Insufficient Controls
Misconfigurations are one of the most common causes of cloud vulnerabilities. Organizations may unintentionally expose their data by failing to configure security settings correctly. For example, leaving storage buckets publicly accessible can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive files. Insufficient controls, such as inadequate access management, can further exacerbate these risks. Regularly reviewing and auditing configurations and controls is essential for ensuring that cloud environments are secure and compliant.
2.4 Insider Threats and Account Hijacking
Insider threats can come from employees, contractors, or partners who have legitimate access to the cloud environment. These individuals may intentionally or unintentionally compromise security, leading to data breaches or other incidents. Account hijacking occurs when attackers gain access to user accounts through methods such as phishing or credential stuffing. Organizations must implement strict access controls, monitor user activity, and conduct employee training to reduce the risk of insider threats and account hijacking.
2.5 Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks aim to overwhelm a service, making it unavailable to legitimate users. Attackers may flood a cloud service with excessive traffic, causing disruptions and downtime. These attacks can be particularly damaging for organizations that rely on cloud services for critical operations. Implementing traffic management solutions, such as rate limiting and load balancing, can help mitigate the impact of DoS attacks and ensure service availability.
3. Understanding the Risks Associated with Cloud Vulnerabilities
3.1 Financial Implications
The financial implications of cloud vulnerabilities can be staggering. A report from IBM indicates that the estimated average expense for a data breach in 2023 reached $4.45 million.This includes costs related to detection, response, and legal fees. Additionally, organizations may face lost revenue due to operational disruptions, reputational damage, and potential fines from regulatory bodies. Businesses must be proactive in assessing their risk exposure and implementing cost-effective security measures to minimize financial losses.
3.2 Reputational Damage
Reputational damage is one of the most challenging consequences of a data breach. When customers discover that their personal information has been breached, they often experience a loss of trust in the organization. Studies have shown that 70% of consumers would stop doing business with a company that has experienced a data breach. Rebuilding trust can take years, and organizations may face long-term effects on their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
3.3 Legal and Compliance Consequences
Organizations must comply with various data protection regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. Failing to protect customer data can result in legal actions, fines, and other penalties. For instance, GDPR violations can lead to fines of up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue, whichever is higher. Organizations must prioritize compliance and ensure they are aware of the legal implications of their cloud security practices.

3.4 Operational Disruptions
Cloud vulnerabilities can lead to significant operational disruptions, affecting an organization’s ability to deliver services. A data breach may result in system outages, impacting productivity and customer service. According to a study by Ponemon Institute, the average time to identify and contain a data breach is 287 days, leading to prolonged disruptions. Organizations must have incident response plans in place to quickly address vulnerabilities and minimize operational impact.
4. Strategies for Mitigating Cloud Computing Vulnerabilities
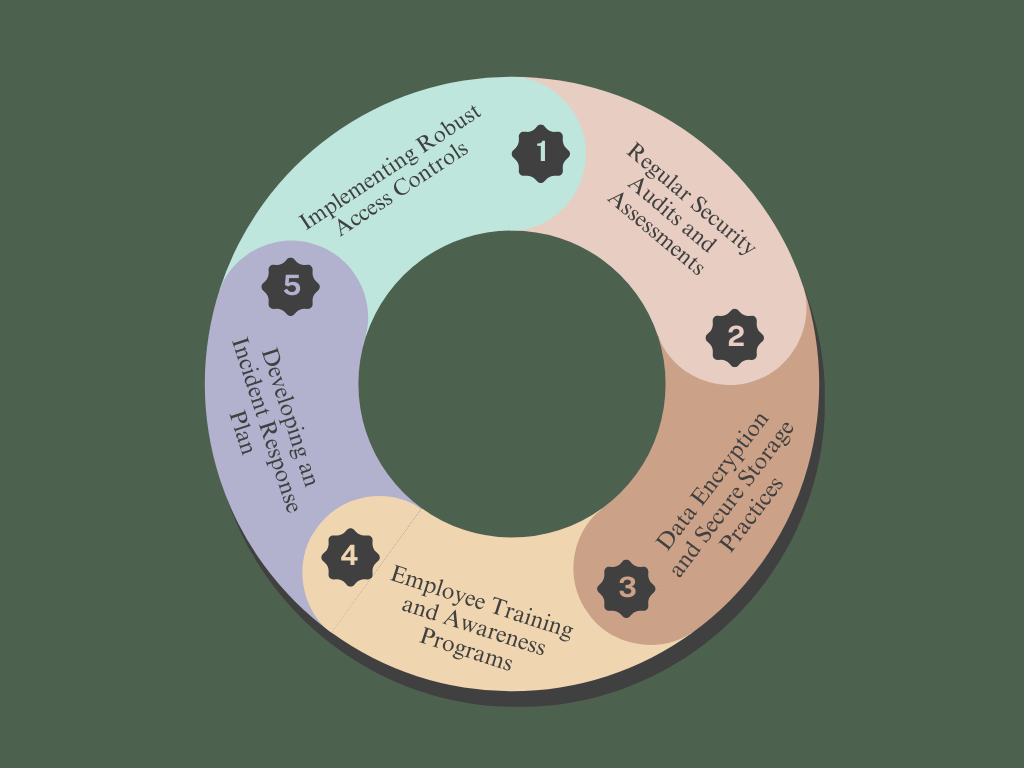
4.1 Implementing Robust Access Controls
Establishing strong access controls is critical for protecting sensitive data in the cloud. Organizations should enforce the principle of least privilege, granting users only the access necessary for their roles. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access. Regularly reviewing and updating access controls is essential for maintaining a secure environment.
4.2 Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Conducting regular security audits and assessments helps organizations identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in their cloud environments. These assessments should include a thorough review of security policies, configurations, and compliance with industry standards. By regularly evaluating their security posture, organizations can proactively address potential risks and enhance their overall cloud security.
4.3 Data Encryption and Secure Storage Practices
Data encryption is a vital component of cloud security. By encrypting sensitive data, organizations can ensure that, even in the event of unauthorized access, the information remains inaccessible and unreadable. Organizations should implement encryption protocols both at rest and in transit. Additionally, following best practices for data storage, such as using secure cloud storage solutions and regularly backing up data, can help protect against data loss.
4.4 Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Employees play a crucial role in cloud security. Conducting regular training sessions on security best practices and raising awareness about potential threats, such as phishing attacks, can empower employees to recognize and report suspicious activities. Organizations should create a culture of security where employees understand their responsibilities in protecting sensitive data.
4.5 Developing an Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan details the actions an organization must follow when faced with a security breach. This plan should include clear roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and procedures for containing and mitigating incidents. Regularly testing and updating the incident response plan is essential to ensure that organizations can respond effectively to emerging threats.
5. Best Practices for Securing Cloud Environments
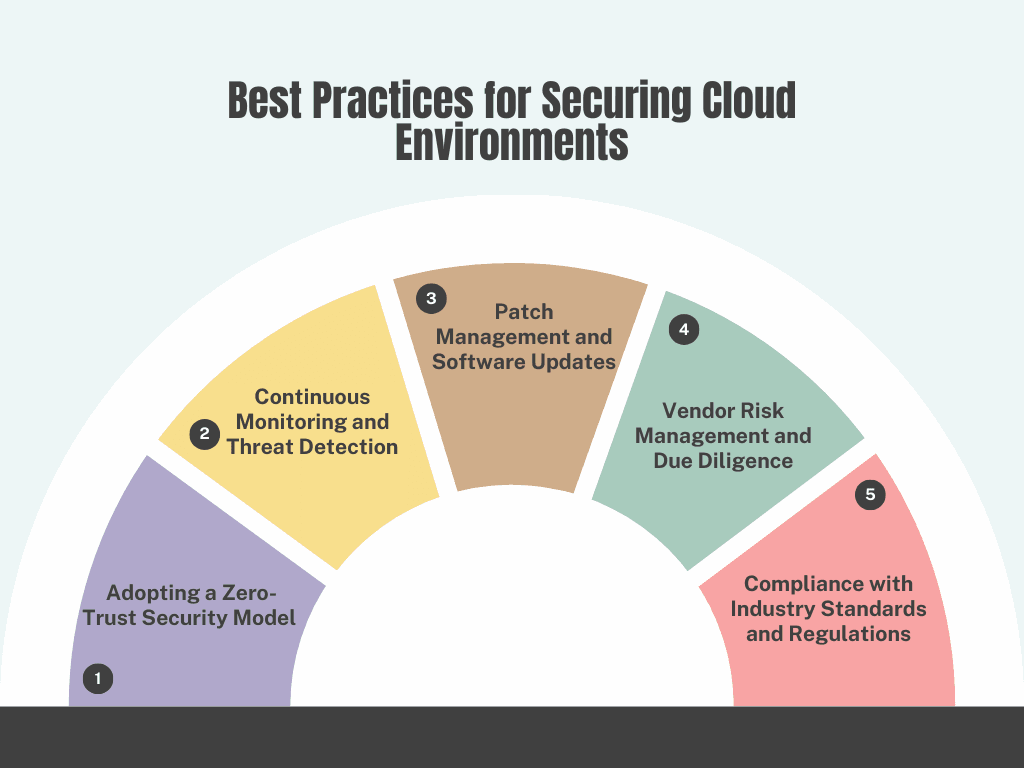
5.1 Adopting a Zero-Trust Security Model
The zero-trust security model operates on the principle that threats can exist both outside and inside the network. This approach requires organizations to verify every user and device attempting to access their systems, regardless of location. By adopting a zero-trust model, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and enhance their overall security posture.
5.2 Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
By adopting continuous monitoring solutions, organizations can identify suspicious activities as they occur in real-time. These solutions can analyze network traffic, user behavior, and system logs to identify anomalies that may indicate a potential breach. By leveraging advanced threat detection technologies, organizations can respond swiftly to emerging threats and minimize potential damage.
5.3 Patch Management and Software Updates
Regularly updating software and applying security patches is crucial for preventing vulnerabilities from being exploited. Cybercriminals frequently exploit outdated software that contains known vulnerabilities.. Organizations should establish a patch management policy to ensure that all systems and applications are regularly updated, reducing the risk of security breaches.
5.4 Vendor Risk Management and Due Diligence
When working with third-party vendors, organizations must conduct thorough due diligence to assess their security practices. This includes reviewing the vendor’s security policies, incident response capabilities, and compliance with industry standards. By ensuring that vendors adhere to strong security measures, organizations can reduce their overall risk exposure.
5.5 Compliance with Industry Standards and Regulations
Staying informed about industry standards and regulations is essential for maintaining compliance and enhancing security. Organizations should regularly review their policies and practices to ensure they align with relevant regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Compliance not only helps organizations avoid legal issues but also strengthens their overall security posture.
6. Tools and Technologies for Cloud Security
6.1 Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Tools
CSPM tools provide organizations with visibility into their cloud environments, helping them manage their security posture. These tools can identify misconfigurations, compliance violations, and potential security risks. By leveraging CSPM solutions, organizations can proactively address vulnerabilities and ensure that their cloud resources are secure.
6.2 Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs)
CASBs act as intermediaries between cloud service users and cloud applications, providing visibility and security policies for data access. These solutions can enforce security policies, monitor user activity, and provide data loss prevention capabilities. Organizations can leverage CASBs to enhance their cloud security and ensure that sensitive data remains protected.
6.3 Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
IDPS tools monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, helping to detect and prevent potential attacks in real time. These systems can analyze traffic patterns, identify anomalies, and respond to threats automatically. By implementing IDPS solutions, organizations can enhance their threat detection capabilities and improve their overall security posture.
6.4 Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Solutions
SIEM solutions aggregate and analyze security data from across the organization, providing insights for threat detection and response. These tools can collect data from various sources, including servers, network devices, and applications, allowing organizations to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security incident. By leveraging SIEM solutions, organizations can enhance their incident response capabilities and improve their overall security posture.
6.5 Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Solutions
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access to sensitive data. This may involve using a mix of passwords, biometric data, or security tokens. Organizations can greatly lower the chances of unauthorized access and strengthen their overall security measures by adopting multi-factor authentication (MFA).
7. Future Trends in Cloud Computing Security
7.1 Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are transforming cloud security by enabling organizations to analyze vast amounts of data and detect anomalies more effectively. These technologies can identify patterns of behavior that may indicate a security threat, allowing for proactive measures to be taken. As AI continues to evolve, organizations will need to integrate these technologies into their security strategies to stay ahead of emerging threats.

7.2 The Role of Blockchain in Enhancing Security
Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent data transactions, making it a valuable tool for enhancing cloud security. Its decentralized nature can help protect data from unauthorized access and tampering. By leveraging blockchain for identity management, access control, and data integrity, organizations can strengthen their cloud security and ensure that sensitive information remains protected.
7.3 Emerging Threats and Evolving Attack Vectors
As technology advances, new threats will emerge, requiring organizations to stay informed and adaptable. Cybercriminals continuously develop new attack vectors, including ransomware, phishing, and advanced persistent threats (APTs). Organizations must regularly assess their security posture and adapt their strategies to counteract these evolving threats effectively.
7.4 Preparing for Quantum Computing Challenges
Quantum computing presents potential security challenges due to its ability to break traditional encryption methods. Organizations must begin preparing for this shift in technology by exploring quantum-resistant algorithms and assessing the impact of quantum computing on their security strategies. By proactively addressing these challenges, organizations can ensure their data remains secure in the future.
8 Differences between general cloud computing vulnerabilities and the specific topic of Data Breaches and Data Loss
| Aspect | Cloud Computing Vulnerabilities | Data Breaches and Data Loss |
|---|
| 1. Definition | General risks associated with using cloud services, including security flaws, misconfigurations, and unauthorized access. | Specific incidents where unauthorized access to sensitive data occurs or when data is lost due to various reasons. |
| 2. Causes | Weak passwords, insecure APIs, insider threats, and misconfigurations. | Accidental deletions, software vulnerabilities, phishing attacks, and hardware failures. |
| 3. Impact on Organizations | Financial losses, reputational damage, legal consequences, operational disruptions. | Direct financial costs due to recovery efforts, potential legal fees, and loss of customer trust. |
| 4. Preventive Measures | Implementing access controls, regular audits, employee training, encryption, and incident response plans. | Regular backups, secure data storage, strong authentication practices, and continuous monitoring. |
| 5. Examples | High-profile data breaches affecting cloud providers, resulting in widespread data exposure. | Instances of companies losing customer data due to misconfigured cloud storage or accidental deletion. |
| 6. Duration of Impact | Vulnerabilities may exist for an extended period until identified and mitigated. | Data breaches and losses can have immediate and long-lasting effects on operations and customer relations. |
| 7. Detection Difficulty | Vulnerabilities can be challenging to detect without regular security assessments. | Data breaches may go unnoticed until significant damage has occurred, complicating recovery efforts. |
| 8. Recovery Efforts | Addressing vulnerabilities often involves systemic changes and long-term strategies. | Recovery from data breaches or losses typically requires immediate incident response, including data restoration and breach notifications. |
9 FAQs
1: What are the common causes of data breaches in cloud computing?
Common causes of data breaches in cloud computing include weak passwords, insecure application programming interfaces (APIs), phishing attacks, misconfigured cloud storage, and insider threats. These vulnerabilities can allow unauthorized access to sensitive data, leading to potential breaches.
2: How can organizations prevent data loss in the cloud?
Organizations can prevent data loss in the cloud by implementing regular backup solutions, using strong authentication practices (like multi-factor authentication), ensuring data encryption both at rest and in transit, and conducting continuous monitoring of cloud environments to detect and respond to anomalies promptly.
3: What impact can a data breach have on an organization?
A data breach can have severe impacts on an organization, including financial losses due to recovery efforts and legal fees, reputational damage leading to loss of customer trust, regulatory penalties, and operational disruptions that hinder service delivery and productivity.
4: How can organizations detect vulnerabilities in their cloud environments?
Organizations can detect vulnerabilities in their cloud environments by conducting regular security audits, utilizing automated security assessment tools, performing vulnerability scanning, and implementing continuous monitoring systems to identify and address potential threats proactively.
5: What steps should an organization take after a data breach occurs?
After a data breach occurs, an organization should follow these steps:
Conduct a post-incident review to understand the cause and improve security measures to prevent future breaches.
Activate the incident response plan.
Contain the breach to prevent further data loss.
Assess the extent of the breach and identify affected data.
Notify affected customers and regulatory authorities, as required by law.
10 Conclusion
Conclusion
In today’s digital landscape, the significance of addressing cloud computing vulnerabilities cannot be overstated. Data breaches and data loss pose substantial risks that can lead to severe financial, operational, and reputational consequences for organizations. By recognizing the primary causes of these vulnerabilities—such as weak security practices and misconfigurations—organizations can implement effective preventive measures. Establishing robust security protocols, conducting regular audits, and fostering employee training are crucial steps in safeguarding sensitive data. Additionally, having a well-defined incident response plan ensures quick recovery from breaches, minimizing potential damage. As cloud services continue to evolve, prioritizing security and compliance will enable organizations to leverage the benefits of the cloud while protecting their valuable assets. Ultimately, a proactive approach to cloud security is essential for maintaining trust and ensuring the long-term success of any organization in the digital age.
