Cloud computing has transformed how organizations manage their IT systems, streamlining operations and enhancing flexibility. Public and private cloud models provide different approaches to handling data and services in the cloud. In this article, we will explore these two models and discuss their key differences, helping you choose the best option for your organization.
1Introduction to Cloud Computing
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a technology that allows businesses and individuals to access computing resources over the Internet instead of relying on local servers or personal computers. These resources encompass servers, storage solutions, databases, networking components, software applications, and additional services. This method eliminates the need for organizations to invest in physical hardware and allows them to access these resources on demand.
Cloud computing is now a cornerstone of modern businesses, providing scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. With it, businesses can launch applications and services faster and more efficiently without managing their own data centers. Cloud technology is also the foundation for other innovations like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics.
Types of Cloud Computing: Public vs Private Cloud
When we talk about cloud computing, there are two primary models: public cloud and private cloud. These models differ in terms of infrastructure management, cost, security, and customization.
- Public Cloud: Shared resources managed by third-party providers, which are available to anyone.
- Private Cloud: Dedicated resources exclusively for a single organization, offering higher control and security.
Each model has its own set of advantages and drawbacks, which we will explore further in this article.
2 Public Cloud: Definition and Key Features
1 What is Public Cloud?
A public cloud is a cloud service where the infrastructure and resources are managed by third-party providers. These resources are delivered over the internet, making them available to anyone who wants to use them. Public cloud services are shared among multiple clients, making them cost-effective and accessible to businesses of all sizes.
2 Public Cloud Infrastructure
Public cloud providers manage and maintain all the infrastructure, which includes data centers, servers, storage systems, and networking equipment. Users access these resources via the internet, and the provider is responsible for maintenance, security, and software updates.
The infrastructure is highly scalable, meaning businesses can increase or decrease their resources as needed. This flexibility makes the public cloud an attractive option for businesses with varying workloads.
3 Benefits of Public Cloud Services
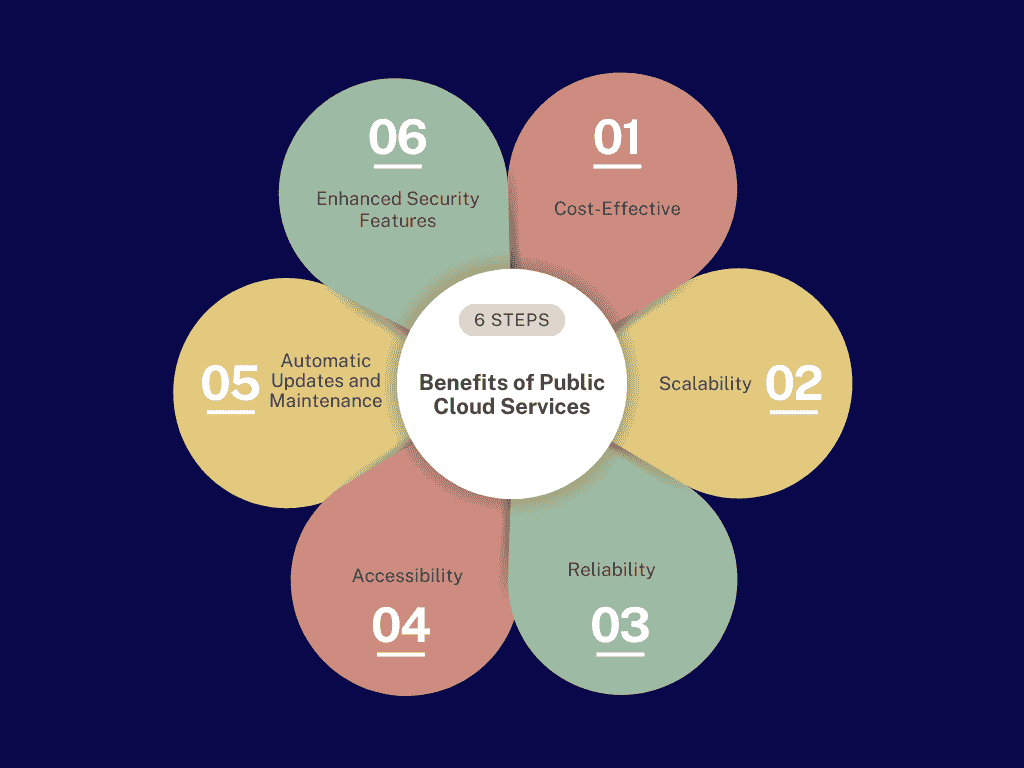
- Cost-Effective:
Public cloud services are generally more affordable since the infrastructure is shared among multiple users. Organizations pay only for the resources they consume, which helps reduce capital expenditures and operational costs, making it a great option for startups and small businesses. - Scalability:
Public clouds offer exceptional scalability, allowing businesses to easily adjust their resources to meet changing demands. Companies can quickly increase or decrease their computing power, storage, or bandwidth as needed, making it ideal for organizations with fluctuating workloads or those experiencing growth. - Reliability:
Leading public cloud providers operate multiple data centers across various locations, ensuring high availability and redundancy. This distributed architecture minimizes downtime and provides robust disaster recovery options, allowing businesses to maintain continuity and access their applications even during outages. - Accessibility:
Public cloud resources can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting collaboration among remote and distributed teams. Employees can easily share files, collaborate on projects, and access essential applications on various devices, enhancing productivity and flexibility in the workplace. - Automatic Updates and Maintenance:
Public cloud providers handle all infrastructure maintenance, including software updates and security patches. This means businesses can focus on their core operations without worrying about managing the underlying hardware or software, ensuring that they always have access to the latest features and security enhancements. - Enhanced Security Features:
While security is often a concern in public cloud environments, many leading providers offer advanced security measures, including encryption, identity management, and access controls. These features help protect sensitive data and comply with regulatory requirements, allowing businesses to benefit from sophisticated security without needing extensive in-house expertise.
4 Public Cloud Providers
Some of the most popular public cloud providers are:
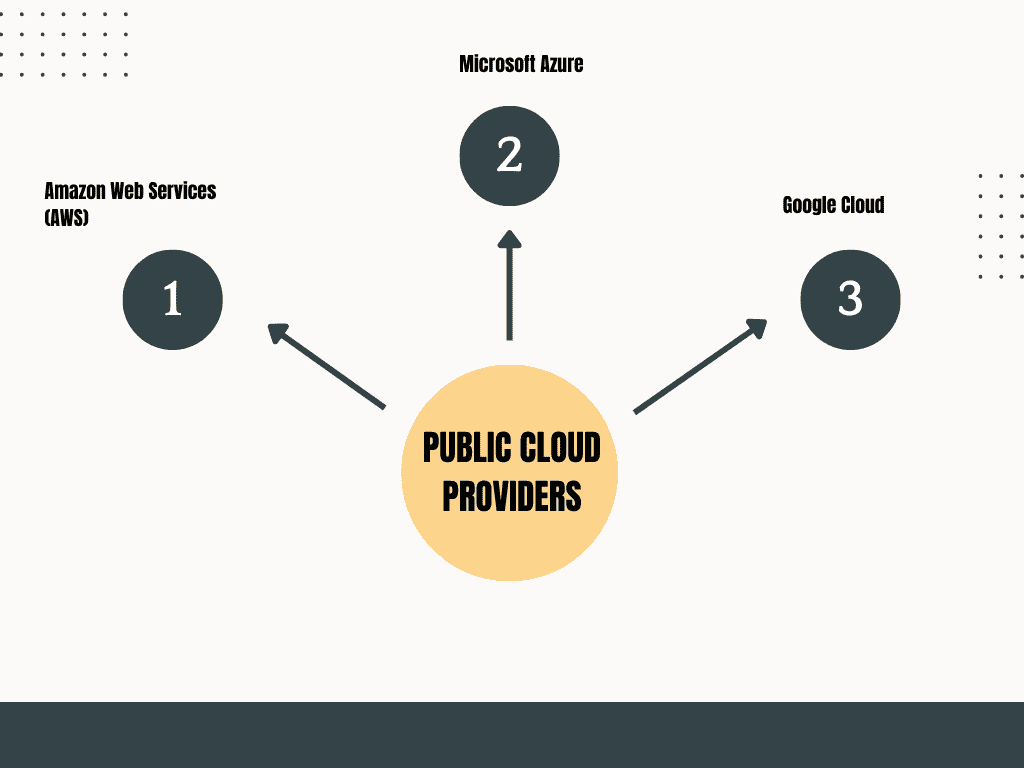
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): A comprehensive cloud platform that offers a range of services, including computing power, storage, and databases.
- Microsoft Azure: Known for its strong integration with Microsoft products like Windows Server and Active Directory.
- Google Cloud: Offers powerful data analytics, machine learning, and AI services.
5 Public Cloud Use Cases
Public cloud solutions are commonly used by startups, businesses looking to reduce infrastructure costs, and companies with fluctuating workloads. Use cases include hosting websites, deploying applications, and running big data analytics.
3 Private Cloud: Definition and Key Features
1 What is Private Cloud?
A private cloud is a cloud infrastructure that is dedicated exclusively to one organization. This means that the hardware, storage, and networking resources are not shared with other clients. Private clouds offer greater control over the infrastructure and can be hosted either on-premises or by a third-party service provider.
2 Private Cloud Architecture
Private cloud infrastructure is tailored to the organization’s needs. Businesses have the flexibility to design their cloud environment, ensuring that it aligns with their security, compliance, and performance requirements. Private cloud architecture can be more complex compared to public cloud because it requires significant management and maintenance.
3 Benefits of Private Cloud Solutions
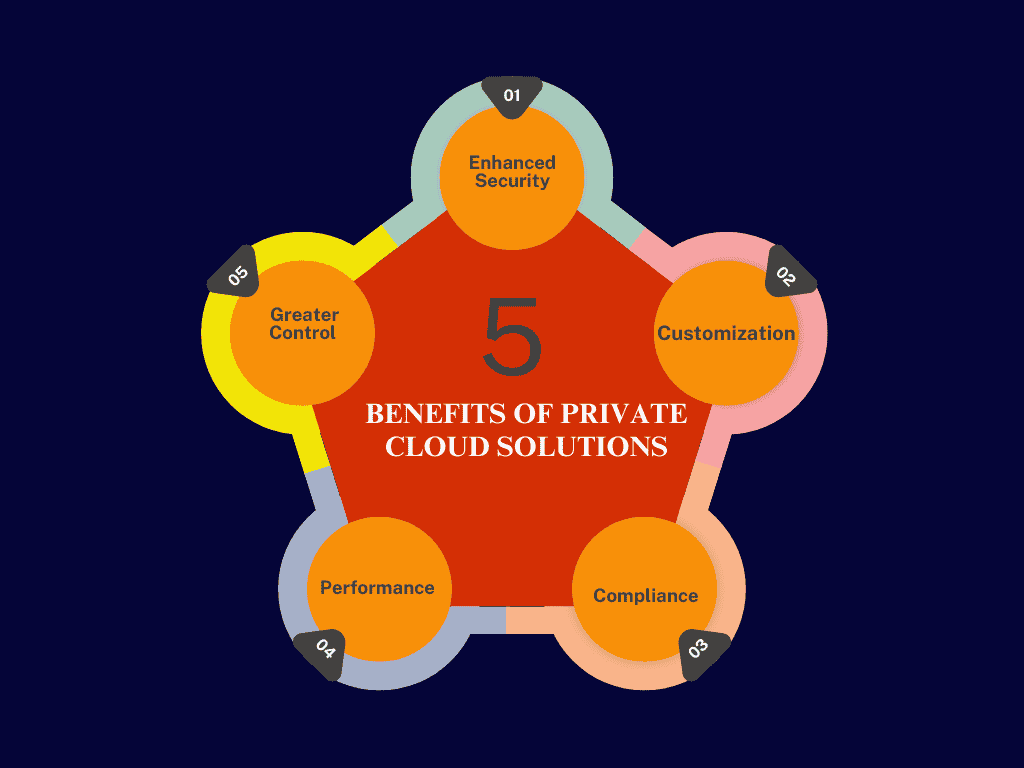
1 Enhanced Security:
Private clouds provide a higher level of security as the infrastructure is dedicated exclusively to a single organization. This exclusivity allows for tailored security protocols and greater control over data access and protection measures, which can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches compared to public cloud environments.
2 Customization:
Organizations have the flexibility to design and configure their private cloud environments according to their specific needs and preferences. This level of customization allows businesses to optimize resources, integrate legacy systems, and implement specific software solutions that align with their operational requirements, enhancing overall performance and efficiency.
3 Compliance:
Many industries, such as healthcare, finance, and government, face strict regulatory requirements regarding data storage and management. Private clouds can be structured to meet these compliance standards more easily than public clouds, allowing organizations to maintain control over their data and ensure adherence to legal and industry regulations.
4 Performance:
Private clouds typically offer improved performance for critical applications, as resources are not shared with other organizations. This dedicated environment can result in faster processing speeds and lower latency, making it ideal for businesses that require high-performance computing for mission-critical operations.
5 Greater Control:
Organizations have full control over their private cloud infrastructure, including hardware selection, software configuration, and security measures. This control enables businesses to align their IT strategies with their specific goals, making it easier to implement changes and updates as needed without relying on third-party providers.
4 Private Cloud Providers and Platforms
Several platforms offer private cloud services, such as:
- VMware vSphere: A virtualization platform that allows businesses to create private cloud environments.
- Microsoft Azure Stack: Extends the capabilities of Microsoft Azure to private cloud environments.
- OpenStack: An open-source platform that allows businesses to build and manage private clouds.
5 Private Cloud Use Cases
Private clouds are ideal for industries with strict regulatory requirements or those handling sensitive information, such as financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies. Use cases include hosting mission-critical applications and running workloads that require high security.
4 Public and Private Cloud: Core Differences
1Public Cloud vs Private Cloud: Cost Comparison
Public clouds are generally more cost-effective because resources are shared among multiple users. Private clouds, while offering greater control and security, can be more expensive due to the dedicated infrastructure and the need for ongoing maintenance.
2 Security and Privacy in Public and Private Clouds
While public clouds offer security measures like encryption and identity management, private clouds provide a higher level of control over data security. In private clouds, businesses can implement their own security protocols and ensure data compliance with regulatory standards.
3 Control and Management Differences
Private clouds offer complete control over the infrastructure, allowing businesses to customize the environment to their needs. Public clouds, on the other hand, are managed by the provider, offering limited control but reducing the complexity of management.
4 Public Cloud vs Private Cloud in Scalability
Public clouds are highly scalable, allowing businesses to quickly add or reduce resources. Private clouds, while scalable, may require significant investments to expand the infrastructure.
5 Customization Options in Public and Private Clouds
Private clouds offer more customization options since the infrastructure is built specifically for one organization. Public clouds are more standardized, providing fewer opportunities for customization.
6 Compliance in Public and Private Clouds
Private clouds are often preferred by businesses with strict compliance requirements, as they offer more control over data storage and security measures. Public clouds can still meet compliance needs, but they require careful management of security settings and access controls.
5 Public Cloud vs Private Cloud: Pros and Cons
Advantages and Disadvantages of Public Cloud
Pros:
- Lower initial costs
- High scalability and flexibility
- Reduced management complexity
Cons:
- Limited customization
- Shared infrastructure may pose security risks
- Ongoing subscription costs
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private Cloud
Pros:
- Full control over infrastructure
- Enhanced security and data privacy
- Customizable to business needs
Cons:
- Higher costs
- Complex management
- Limited scalability compared to public cloud
6 Public, Private, or Hybrid Cloud? Choosing the Right Solution
1 How to Decide Between Public and Private Cloud
The choice between public and private cloud depends on several factors, including cost, security, scalability, and compliance. Public cloud is ideal for businesses with flexible workloads, while private cloud is better for organizations that require strict control and security.
2 Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Solutions
A hybrid cloud combines the benefits of both public and private clouds, allowing businesses to keep sensitive data in a private cloud while leveraging the scalability of public cloud services for less critical workloads.
3 Industry-Specific Cloud Needs
Each industry has unique cloud needs. For example, healthcare organizations prioritize security and compliance, making private or hybrid clouds a better choice. On the other hand, startups and small businesses often prefer public cloud services due to lower costs and ease of use.
7 Differences between Public Cloud and Private Cloud
| Infrastructure | Shared infrastructure managed by third-party providers | Dedicated infrastructure exclusively for one organization |
| Cost | Cost-effective due to shared resources | Higher cost due to dedicated resources and maintenance |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, resources can be added/removed easily | Scalable but may require significant investment for expansion |
| Control | Limited control, managed by the service provider | Full control over the infrastructure and environment |
| Security | Adequate security but less control over data | Enhanced security with greater control over protocols |
| Customization | Standardized environment with limited customization | Fully customizable to meet specific business needs |
| Compliance | Can meet compliance requirements but requires careful management | Easier to meet industry-specific compliance requirements |
| Management | Managed by the cloud provider, reducing complexity | Managed by the organization, requiring more resources and expertise |
| Use Cases | Ideal for startups, small businesses, or companies with flexible workloads | Ideal for industries with strict security and compliance requirements (e.g., healthcare, finance) |
FAQs
1. What are the main advantages of using public cloud services?
Public cloud services are cost-effective, highly scalable, and require minimal management from users. They allow businesses to pay only for the resources they use, making them ideal for startups and organizations with fluctuating workloads.
2. How does a private cloud ensure better security compared to a public cloud?
A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, allowing for customized security protocols and greater control over data. This exclusivity reduces the risk of data breaches that can occur in a shared environment like the public cloud.
3. Can businesses use both public and private clouds?
Yes, many organizations adopt a hybrid cloud approach, combining the benefits of both public and private clouds. This allows them to keep sensitive data in a private cloud while leveraging the scalability of public cloud services for less critical applications.
4. What types of businesses typically use private cloud solutions?
Industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as healthcare, finance, and government, often prefer private cloud solutions. These sectors prioritize data security, compliance, and control over their IT environments.
5. Is it expensive to maintain a private cloud?
Yes, maintaining a private cloud can be more expensive than using public cloud services due to the need for dedicated hardware, ongoing maintenance, and management. However, for organizations that require higher security and control, the investment can be justified.
Conclusion
Cloud computing offers businesses a range of options, from cost-effective public clouds to highly secure private clouds. The key to making the right decision is understanding your organization’s specific needs in terms of cost, scalability, security, and compliance. For many, a hybrid cloud solution offers the best of both worlds, providing the flexibility of the public cloud and the control of the private cloud.
