In today’s digital world, businesses are increasingly adopting multi-cloud environments to meet their needs for flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. However, this shift brings about new security challenges. To fully benefit from multi-cloud systems, businesses must ensure robust security measures are in place. This article will walk you through the best practices for multi-cloud security, focusing on protecting your data and making your cloud environment safe and secure.
Introduction to Best Practices for Multi-Cloud Security
The rise of multi-cloud environments has transformed the way businesses operate, offering greater flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. However, with this shift comes the responsibility of ensuring robust security across multiple cloud platforms. Whether you’re using Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, or other cloud providers, it’s essential to adopt best practices that protect sensitive data and secure applications from cyber threats.
Multi-cloud security focuses on implementing measures that safeguard data and resources across various cloud infrastructures. By having a well-structured security strategy, businesses can protect themselves from data breaches, unauthorized access, and other security risks. In this article, we’ll explore the key security challenges, solutions, and future trends that will help ensure the safety of your multi-cloud environment.
Understanding Multi-Cloud Environments
Multi-cloud environments allow businesses to use different cloud providers for various tasks, ensuring they get the best features and services from each one. This strategy not only boosts efficiency but also prevents vendor lock-in, offering companies more flexibility in managing their operations.
Importance of Data Protection in Multi-Cloud Security
With data spread across different cloud platforms, ensuring data protection becomes a top priority. A breach in one cloud can have ripple effects on the entire infrastructure, making it critical to secure data both at rest and in transit. By prioritizing data protection, businesses can maintain trust with customers and partners while staying compliant with industry regulations.
Identifying Security Challenges in Multi-Cloud
While multi-cloud environments offer numerous benefits, they also introduce several security challenges. Managing multiple cloud providers means dealing with different security policies, configurations, and tools, which can make it harder to ensure a consistent security posture.
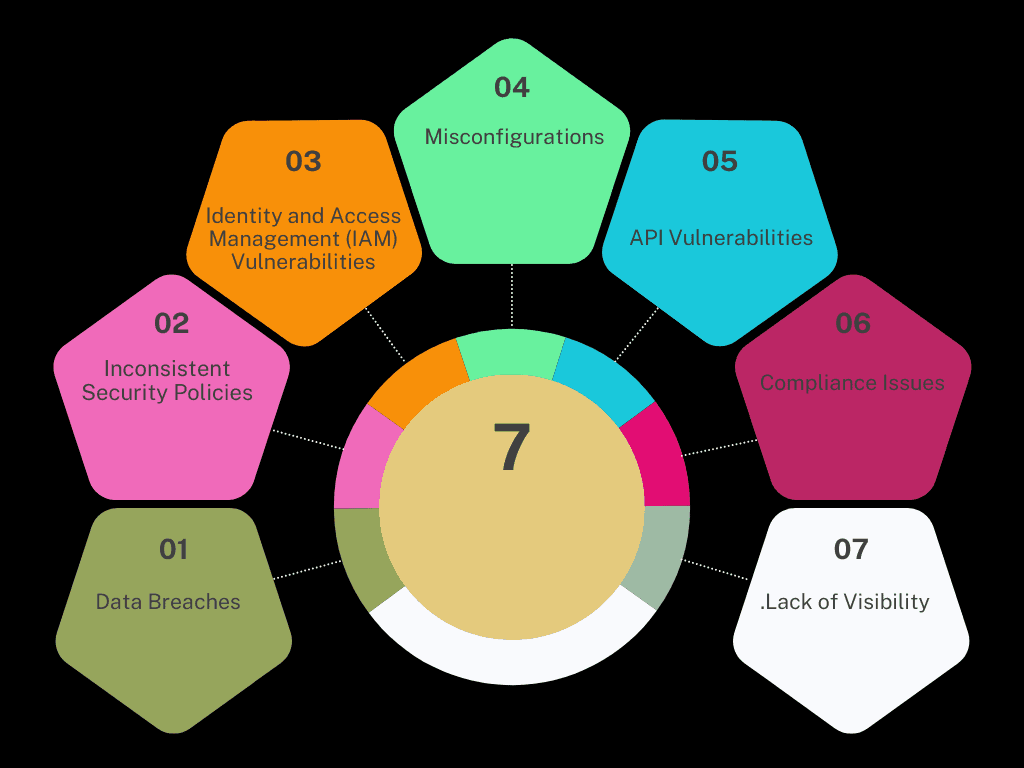
Common Threats in Multi-Cloud Systems
1 Data Breaches
Multi-cloud setups increase the likelihood of data breaches because sensitive data is distributed across several providers. A misconfiguration in any environment, such as open storage buckets or weak encryption, can expose confidential information. This makes it crucial to ensure that consistent security measures are applied across all cloud platforms.
2 Inconsistent Security Policies
Each cloud provider has its own security controls, and managing multiple clouds can lead to uneven enforcement of security policies. If security policies are not aligned across clouds, certain environments may be more vulnerable to attacks. This inconsistency can create exploitable gaps that attackers may use to breach the system.
3 Identity and Access Management (IAM) Vulnerabilities
Effective IAM is essential in a multi-cloud system to ensure that only authorized users can access resources. However, inconsistent IAM practices across different clouds can result in privilege escalation or unauthorized access. Centralized IAM and proper management of credentials are crucial for reducing this risk.
4 Misconfigurations
Cloud environments require precise configurations to function securely, but the complexity of multi-cloud setups increases the risk of mistakes. For example, leaving a storage bucket open to the public or misconfiguring firewalls can create vulnerabilities. These errors can lead to unintended exposure of resources or data.
5 API Vulnerabilities
APIs are essential for integrating services across cloud environments, but if they are not secured properly, they can be a weak point. Attackers can exploit vulnerable APIs to gain unauthorized access to cloud resources. Regular audits and strict API security protocols are necessary to safeguard these entry points.
6 Compliance Issues
Multi-cloud environments often operate in multiple jurisdictions, complicating compliance with data residency regulations like GDPR. Data might be stored or processed in locations that don’t meet legal requirements, leading to fines or other legal consequences. Ensuring compliance across all cloud platforms is vital.
7 Lack of Visibility
Monitoring and managing security in a multi-cloud system can be challenging due to the complexity of integrating different cloud environments. This lack of visibility can make it difficult to detect anomalies, threats, or breaches in real time. Implementing centralized monitoring tools is important for maintaining oversight across the entire infrastructure.
Key Risks to Data Protection
Aside from breaches and misconfigurations, insider threats also pose a risk to multi-cloud environments. Malicious insiders or disgruntled employees may misuse their access privileges to steal or compromise data. Businesses must also be mindful of compliance risks—failing to meet data protection regulations like GDPR or HIPAA can lead to hefty fines and reputational damage.
By identifying these threats early on, businesses can implement better security measures to protect their multi-cloud systems from attack.
Best Practices for Multi-Cloud Security: Protect Your Data
To protect your data in a multi-cloud environment, several essential best practices must be implemented. These practices ensure that sensitive information is safe, and access is restricted to authorized users only.

1Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM solutions are critical for securing multi-cloud environments. By controlling who has access to different parts of the cloud infrastructure, businesses can minimize the risk of unauthorized access. IAM enforces the principle of least privilege, meaning users are given only the access they need to perform their job functions and no more.
Using IAM, businesses can set role-based permissions, track user activity, and enforce security policies across all cloud platforms. This approach reduces the chances of security breaches caused by compromised or misused credentials.
2 Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Across Platforms
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an additional layer of security to the login process by requiring users to provide two or more forms of identification before accessing cloud resources. This could be a password, combined with a one-time code sent to their phone, or biometric verification like fingerprints.
By implementing MFA across all platforms, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of account hijacking. Even if an attacker gains access to a user’s password, they would still need the second authentication factor to complete the login process.
3 Data Encryption for Protecting Cloud Data
Encryption is one of the most effective ways to protect data in multi-cloud environments. By encrypting data both at rest (when it’s stored) and in transit (when it’s being transferred), businesses can ensure that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key.
Organizations should adopt end-to-end encryption methods, where data is encrypted from the point it leaves one system until it arrives at its destination. This guarantees that sensitive information is protected throughout its entire lifecycle, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
Securing Multi-Cloud Networks and Applications
Securing networks and applications across different cloud platforms is critical to ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of your multi-cloud environment.
Network Segmentation and Firewalls
Network segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the spread of an attack. In a multi-cloud environment, businesses can apply segmentation to separate critical systems from less sensitive ones. This way, even if one part of the network is compromised, attackers won’t be able to move freely between segments.
Firewalls are also essential for filtering traffic between different parts of the network. By using cloud-native firewalls and configuring them correctly, businesses can monitor incoming and outgoing traffic, detect potential threats, and prevent unauthorized access to cloud resources.
Protecting Applications in Multi-Cloud Environments
Applications hosted in the cloud are frequent targets for attackers, so it’s crucial to secure them through regular vulnerability assessments and patch management. Application security should be a top priority, with frequent updates to fix vulnerabilities and improve defenses.
Implementing security measures like web application firewalls (WAFs) can help block malicious traffic aimed at exploiting vulnerabilities in cloud-hosted applications. WAFs can also prevent common attacks such as SQL injections and cross-site scripting (XSS).
Ensuring Data Protection in Multi-Cloud Systems
Data protection is not just about preventing breaches; it’s also about ensuring your data remains accessible and intact even in the event of a disaster.
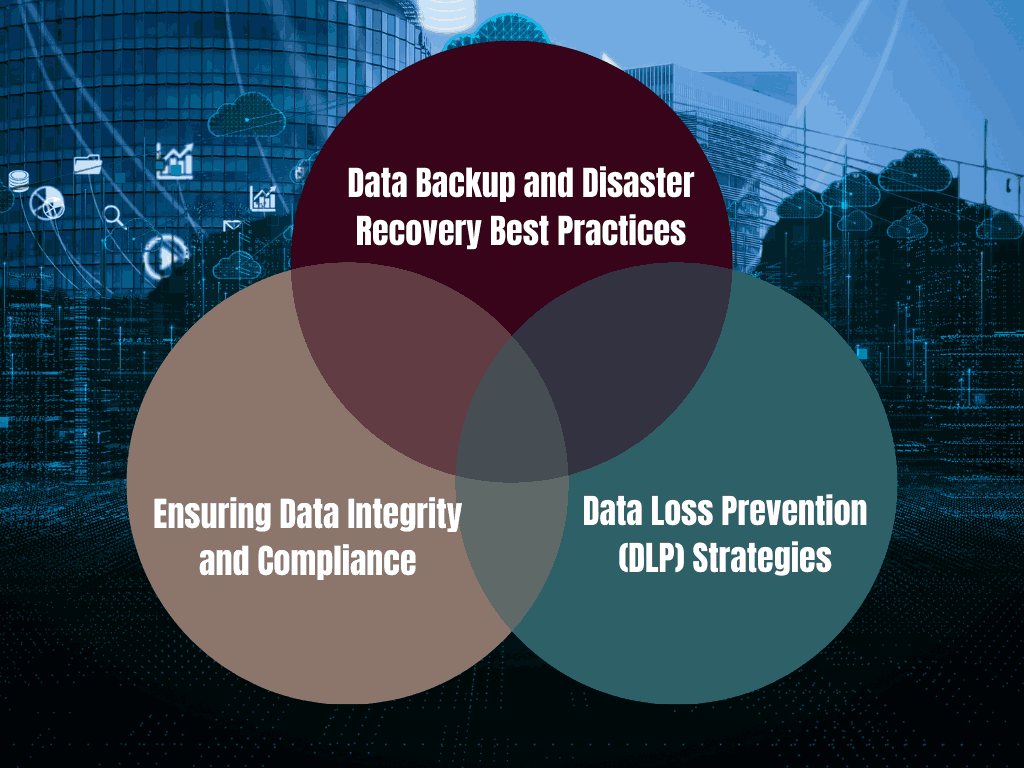
1 Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Best Practices
Data backup is essential to ensuring that your business can recover quickly in case of a breach or system failure. By regularly backing up data and storing copies in different cloud locations, you ensure that data can be restored in case of loss or corruption.
A comprehensive disaster recovery plan should include detailed steps on how to restore data, infrastructure, and services after an incident. Automated tools can help regularly test backups and ensure they are working correctly.
2 Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Strategies
Data loss prevention (DLP) solutions monitor data as it moves across the cloud environment and prevent unauthorized sharing or leaks. DLP tools use predefined policies to flag sensitive data, ensuring that it doesn’t end up in the wrong hands.
By integrating DLP solutions into your multi-cloud environment, you can ensure that sensitive information is protected and that employees are following data protection policies.
3 Ensuring Data Integrity and Compliance
Data integrity ensures the continuous accuracy, reliability, and consistency of data throughout its entire lifecycle, safeguarding it from unauthorized changes or corruption. In a multi-cloud environment, ensuring data integrity requires regular audits and checks to confirm that data hasn’t been tampered with.
Compliance with industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS is critical to avoid fines and maintain the trust of customers. Implementing strong data protection policies that align with these regulations ensures that businesses remain compliant and protect their reputation.
Automating Security in Multi-Cloud Environments
Automation is a game-changer in the field of multi-cloud security. By automating routine security tasks, businesses can reduce the risk of human error and improve overall security.
Automation of Security Policies Across Clouds
Automating security policies ensures that they are applied consistently across all cloud platforms. For example, automated tools can enforce IAM policies, monitor for misconfigurations, and even respond to incidents in real-time.
Automation also helps businesses scale their security efforts without having to manually adjust settings every time they add a new cloud provider or deploy new resources.

Benefits of Security Orchestration for Data Protection
Security orchestration integrates different security tools into a unified platform, automating threat detection, incident response, and remediation processes. Orchestration reduces the time it takes to respond to threats, ensuring that businesses can act quickly to protect their data.
By using orchestration, businesses can improve their overall security posture and ensure that their multi-cloud environment remains protected, even as new threats emerge.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Continuous monitoring is crucial for identifying security threats in real-time. Without it, businesses risk leaving vulnerabilities undetected for long periods, increasing the chances of a successful attack.
Real-Time Monitoring for Multi-Cloud Security
Real-time monitoring tools provide businesses with full visibility into their cloud environments, allowing them to detect suspicious activity as it happens. This includes unusual login attempts, data transfers, or changes to cloud configurations.
By implementing real-time monitoring, businesses can spot potential threats early and take action before they escalate into serious incidents.
Incident Response Plans to Protect Data
An incident response plan is a predefined set of actions that a business takes in the event of a security breach. Having a clear and detailed incident response plan ensures that your organization can act quickly to contain the threat, minimize damage, and restore operations.
The plan should include steps for identifying the source of the breach, containing the attack, and notifying affected stakeholders. Regularly testing the incident response plan ensures that everyone knows their role and can respond effectively when needed.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements for Data Protection
Compliance with data protection regulations is a key concern for businesses using multi-cloud environments. Failure to meet regulatory requirements can lead to fines, legal issues, and reputational damage.
**Navigating Regulatory Standards (GDPR, HIPAA,
etc.)**
Different industries have different regulations regarding data protection. For example, GDPR sets strict rules for protecting personal data in the European Union, while HIPAA governs the handling of health information in the United States.
Businesses using multi-cloud environments must ensure that their security measures meet the standards of these regulations, regardless of which cloud providers they use.
Ensuring Compliance Across Cloud Providers
Each cloud provider may have its own compliance certifications, but it’s the business’s responsibility to ensure that all their data is protected according to regulatory requirements. Regular audits, documentation, and communication with cloud providers are essential for maintaining compliance.
Collaborating with Cloud Providers for Optimal Security
Cloud security is a collaborative responsibility, where the business and the cloud provider share roles in safeguarding data, systems, and infrastructure within the cloud environment. While cloud providers handle the security of the infrastructure, businesses must secure the data and applications they host on the cloud.
Shared Responsibility Model: Ensuring Data Protection
In the shared responsibility model, cloud providers are responsible for securing the physical infrastructure, network, and hardware. Businesses, on the other hand, are responsible for securing their data, applications, and user access.
Understanding this model is key to creating a secure multi-cloud environment. Businesses need to know what security responsibilities lie with the cloud provider and what steps they need to take on their own.
Working with Providers to Secure Multi-Cloud Infrastructure
Building strong relationships with cloud providers helps businesses understand the security tools and services available to them. Many providers offer services such as automated patch management, security monitoring, and encryption, which can enhance overall security.
By collaborating with cloud providers, businesses can ensure that they are using the full range of security features available to them, optimizing protection across their multi-cloud environment.
Future Trends in Multi-Cloud Security
As technology evolves, so do the threats facing multi-cloud environments. Staying ahead of these trends is crucial for businesses that want to maintain secure environments.
Evolving Best Practices for Multi-Cloud Security
As new technologies emerge, businesses need to update their security practices. For example, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly being used to detect threats and automate responses.
By adopting AI and ML technologies, businesses can enhance their ability to detect sophisticated threats and respond to incidents faster.
Preparing for New Threats to Cloud Data Protection
New types of cyberattacks, such as AI-powered phishing or deep fake-based social engineering, are expected to emerge in the coming years. Businesses must stay vigilant and adapt their security strategies to protect against these evolving threats.
Continuous learning and investment in the latest security technologies will ensure that businesses remain secure in the future.
Difference between Single-Cloud and Multi-Cloud environments
| Feature/Aspect | Single-Cloud Environment | Multi-Cloud Environment |
|---|
| Vendor Dependency | Entirely dependent on one cloud provider | Uses multiple cloud providers, reducing reliance |
| Risk of Vendor Lock-In | High risk of being locked into one provider’s services | Lower risk as businesses can switch between providers |
| Security Management | Easier to manage, one consistent security policy | More complex, requires managing different security policies |
| Disaster Recovery | Less redundancy, single point of failure | More redundancy, with data spread across multiple clouds |
| Flexibility and Scalability | Limited by the capabilities of a single provider | Greater flexibility, with access to diverse services from multiple providers |
| Compliance Management | Easier to ensure compliance with one provider | More challenging to maintain compliance across providers |
| Cost Efficiency | May be cheaper in some cases but limited in optimization | Potential for better cost optimization by choosing services across clouds |
FAQS
What is a multi-cloud environment?
A multi-cloud environment refers to the use of two or more cloud services from different providers, such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure. This approach helps businesses optimize workloads, improve flexibility, and avoid vendor lock-in by leveraging the unique capabilities of each provider.
Why is multi-cloud security important?
Multi-cloud security is important because it helps protect data, applications, and networks across multiple cloud platforms. As data moves between providers, security risks increase, so having robust security practices in place reduces the chances of breaches, misconfigurations, and unauthorized access.
What are the biggest security challenges in a multi-cloud setup?
The biggest security challenges in multi-cloud environments include managing different security policies across platforms, preventing misconfigurations, ensuring consistent identity and access management (IAM), and maintaining compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA across all providers.
How can I improve data protection in a multi-cloud environment?
To improve data protection in a multi-cloud environment, use strong Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems, enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), encrypt data both at rest and in transit, and implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategies to prevent unauthorized access and sharing.
What is the shared responsibility model in cloud security?
The shared responsibility model separates security duties between the cloud provider, managing the infrastructure, and the customer, responsible for securing their data and applications within the cloud. Cloud providers secure the infrastructure (servers, storage, and networking), while the customer is responsible for securing the data, applications, and access controls that they run on the cloud platform.
Conclusion: Best Practices for Multi-Cloud Security
Securing a multi-cloud environment requires a multi-layered approach that includes strong identity management, encryption, real-time monitoring, and compliance with regulatory requirements. By following best practices, businesses can reduce vulnerabilities, ensure data protection, and stay ahead of emerging threats. Collaborating with cloud providers, automating security processes, and staying informed about future trends will help businesses make the most of their multi-cloud environments while keeping their data and systems safe from cyber threats.
