Network security has become one of the most pressing concerns in today’s digital world. As the number of cyber threats continues to grow, securing your business’s network has never been more important. Whether it’s protecting sensitive data or defending against unauthorized access, businesses need to implement comprehensive strategies to secure their networks. This guide will walk you through the best practices for keeping your network safe in 2024.
Introduction to Network Security
Network security refers to the processes and technologies that protect your business’s network from cyber-attacks, unauthorized access, and data breaches. In 2024, with businesses relying more heavily on digital tools, remote work, and cloud services, the stakes are higher than ever. The increasing complexity of cyber threats has made network security a fundamental aspect of business operations.
Importance of Network Security in 2024
There are several reasons why network security should be a priority in 2024:
- Rising cyber-attacks: Hackers are employing more sophisticated techniques to target businesses of all sizes. Common attacks include phishing, malware, and ransomware, which can cause serious damage to your systems and reputation.
- Remote work vulnerabilities: With more employees working from home or on the move, networks are more exposed. Employees often use unsecured devices or public Wi-Fi networks, increasing the chances of unauthorized access.
- Regulatory requirements: Laws like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) have imposed strict rules on data protection.
Key Network Security Challenges
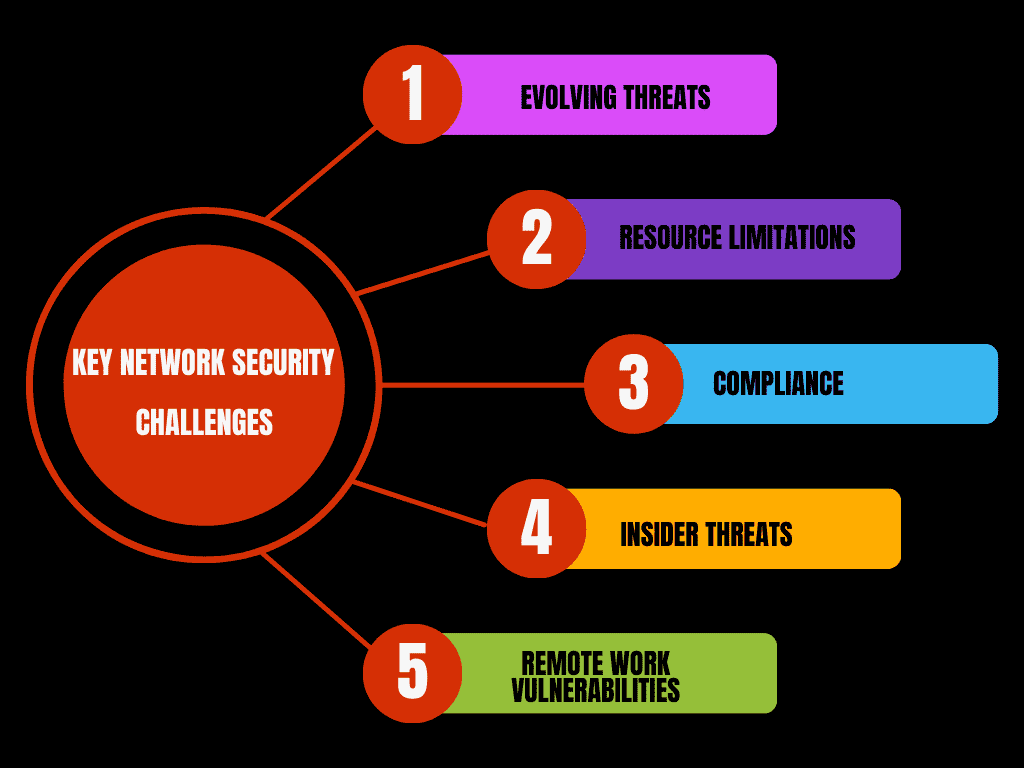
Businesses face numerous challenges when securing their networks, including:
1 Evolving threats: Cyber-attacks are continually evolving, with hackers finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities.
2 Resource limitations: Smaller businesses often struggle to invest in expensive security measures.
3 Compliance: Staying up-to-date with data protection regulations is difficult but necessary to avoid legal issues.
4 Insider threats: Employees, whether intentionally or unintentionally, can create security risks through mishandling sensitive information.
5 Remote work vulnerabilities: The shift to remote work has increased the risk of unsecured connections and devices, making networks more susceptible to attacks.
Best Practices for Network Security: Core Principles
Effective network security starts with understanding and implementing core principles that form the backbone of a robust defense system. Following these practices ensures that your business is better protected against the growing array of cyber threats in 2024.

Regular Security Audits
Conducting regular security audits is one of the most effective ways to identify vulnerabilities in your network. Security audits assess the security protocols, infrastructure, and data handling procedures of your organization. Audits should be conducted at least annually, though quarterly or even monthly assessments may be required for high-risk environments.
During an audit, consider the following areas:
- Firewall configurations: Ensure your firewalls are properly set up to block harmful traffic.
- System updates: Outdated software and hardware are prone to vulnerabilities, so regular updates are essential.
- Access control: Review the permissions granted to users and ensure they are restricted based on their roles.
Fixing vulnerabilities identified during the audit should be prioritized. Audits help you stay ahead of potential breaches by proactively addressing weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Firewalls and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a security barrier that filters and blocks unauthorized access to protect networks from cyber threats. They monitor incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules. In 2024, advanced firewalls, such as Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW), offer additional features like malware detection and intrusion prevention.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA enhances security by requiring users to authenticate their identity through multiple verification steps. For example, in addition to a password, users may need to enter a code sent to their mobile device or use biometric authentication (e.g., fingerprints).
Securing Wireless Networks
Wireless networks are essential for modern business operations, but they can also pose significant security risks if not properly secured. Hackers can exploit unprotected Wi-Fi networks to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Essential Wireless Security Practices
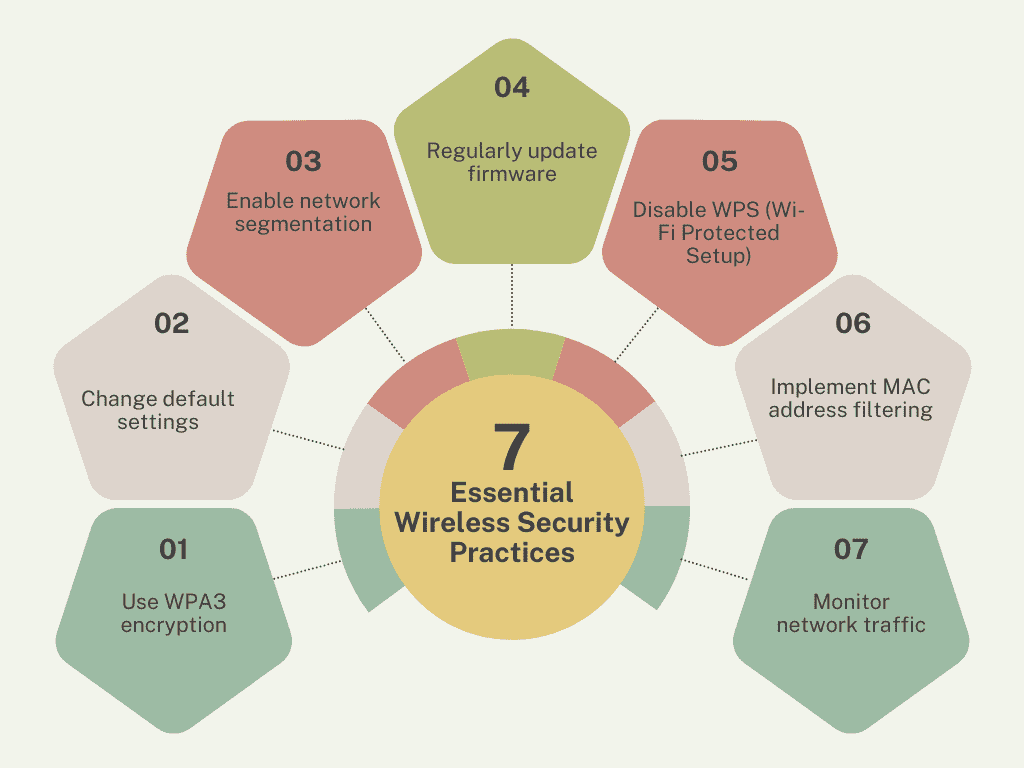
1 Use WPA3 encryption: Protect your network using WPA3, the latest and most secure Wi-Fi encryption standard. It significantly enhances data protection and prevents unauthorized access. This is more robust compared to older encryption methods like WPA2 or WEP.
2 Change default settings: Many routers come with default usernames and passwords, making them easy targets for hackers. Change these default credentials immediately to something unique and strong. This simple step adds a critical layer of protection.
3 Enable network segmentation: Create separate networks for guests and your main business operations. This isolates sensitive systems, preventing unauthorized access to critical data. It limits the impact of potential breaches.
4 Regularly update firmware: Router manufacturers release firmware updates to fix security vulnerabilities. Ensure your router’s firmware is always up-to-date. Regular updates strengthen your network’s defense against evolving threats.
5 Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup): WPS can make your network vulnerable to brute-force attacks. Turn it off to prevent easy access by hackers. This helps eliminate a known security weakness.
6 Implement MAC address filtering: Restrict access to your network by only allowing devices with approved MAC addresses. This adds an extra layer of control over which devices can connect. It’s a simple way to block unauthorized devices.
7 Monitor network traffic: Use network monitoring tools to track unusual or suspicious activity. This helps identify potential threats early and allows for quick action. Continuous monitoring strengthens your overall security posture.
Preventing Unauthorized Access
Limiting who can connect to your wireless network is a critical aspect of securing it. To do this:
- Restrict device connections: Only allow authorized devices to connect to the network. Regularly monitor devices and remove any unknown devices from the network.
- Use a hidden SSID: Your network’s SSID (Service Set Identifier) is its broadcasted name. Hiding the SSID prevents it from appearing on the list of available networks, making it harder for hackers to find.
- Use strong passwords: Set complex passwords for your wireless network and change them regularly.
Data Encryption and Protection
In today’s digital landscape, data encryption is a critical aspect of network security. Encryption converts readable data into an unreadable format, making it difficult for unauthorized users to access sensitive information.
Importance of Data Encryption
Data encryption is vital because it ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be read or misused without the decryption key. This is particularly important for businesses that handle sensitive customer information, financial data, or intellectual property.
- Data breaches: Cybercriminals target valuable data such as credit card information, personal identification details, and trade secrets. Encryption acts as a final defense, ensuring that even if attackers manage to infiltrate your network, they cannot access your data.
Encrypting Data in Transit and at Rest
There are two primary areas where encryption is necessary:
- Data in transit: This refers to data that is being transferred across the network. Ensure that data is encrypted using protocols like HTTPS for web-based communication or TLS (Transport Layer Security) for secure email transmission.
- Data at rest: This refers to data stored on servers, hard drives, or in the cloud. Even if attackers gain physical access to your systems, encryption ensures that they cannot access sensitive information stored on these devices.
Access Control and User Management
Access control is one of the most fundamental aspects of network security. It guarantees that access to critical systems and data is restricted to authorized individuals only. Poor access control can leave a business vulnerable to insider threats or external attacks.
User Access Control Best Practices
User access control revolves around granting the least amount of privilege necessary for employees to perform their jobs. This principle, known as the principle of least privilege, minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and reduces the damage that can be caused if credentials are compromised.
Best practices for user access control include:
- Regularly updating access rights: Periodically review who has access to sensitive systems and data. Remove permissions from employees who no longer require access.
- Strong password policies: Enforce the use of strong passwords and require regular updates. Passwords should include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) It grants permissions according to the user’s specific role within the organization. This limits access to sensitive information based on job responsibilities and ensures that users only have the necessary permissions to perform their duties. RBAC also reduces the chances of human error, such as an employee accidentally accessing and sharing sensitive data.
By properly managing user access, businesses can reduce the risk of internal and external threats, ensuring that their most critical systems remain secure.
Regular Software and System Updates
Hackers often exploit outdated software as a frequent entry point for attacks. Regularly updating your systems is a simple but highly effective way to protect your network from cyber-attacks.
Patching Security Vulnerabilities
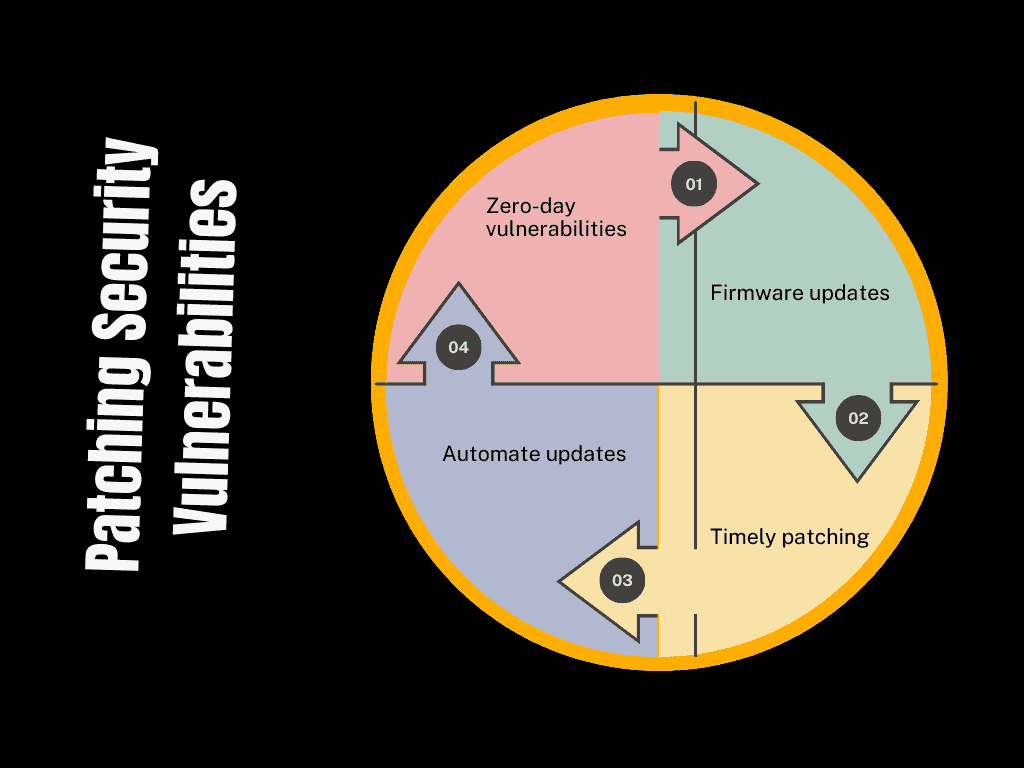
When software developers identify security vulnerabilities, they release patches—software updates that fix these weaknesses. Failing to apply patches promptly leaves your network open to exploitation.
- Zero-day vulnerabilities: These are flaws that hackers discover before developers can issue patches. Updating your software regularly helps reduce the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit these vulnerabilities.
- Firmware updates: Don’t forget to update the firmware on your network devices, such as routers and firewalls. Firmware updates often contain critical security enhancements.
- Timely patching: Apply patches immediately after they are released to fix security weaknesses and prevent potential exploitation.
- Automate updates: Where possible, enable automatic updates to ensure patches are applied without delay, reducing the chances of security gaps.
Automating Updates for Network Security
To avoid the risk of human error, consider automating software updates. Automation ensures that your systems are always running the latest security patches without relying on manual updates. This approach not only improves security but also reduces the workload on your IT team.
Staying current with updates is one of the most straightforward ways to protect your network against ever-evolving cyber threats.
Network Monitoring and Intrusion Detection
Continuous network monitoring is essential for identifying and responding to potential security threats. With advanced tools, businesses can keep an eye on network activity in real-time and detect suspicious behaviors before they escalate into major incidents.
Continuous Network Monitoring
Monitoring your network means constantly checking for unusual traffic patterns or activity. This is especially important for large networks with multiple access points. Network monitoring tools can provide real-time insights, alerting you to anomalies such as spikes in data traffic or repeated login attempts from unknown locations.
- Anomaly detection: Sophisticated monitoring tools can identify patterns that deviate from normal behavior, which may indicate a potential breach. By responding to these anomalies quickly, businesses can prevent larger attacks.
Implementing Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) works by analyzing network traffic for signs of malicious activity or policy violations. If the IDS detects any suspicious behavior, it alerts the network administrator to take action.
There are two types of IDS:
- Network-based IDS (NIDS): Monitors network traffic and can detect attacks as they happen.
- Host-based IDS (HIDS): Monitors activities on individual devices, identifying threats that may bypass network monitoring.
By integrating IDS into your network security strategy, you can detect and mitigate potential threats before they cause significant damage.
Securing Remote Work Connections
The increase in remote work has brought new challenges to maintaining network security. Employees working from home or on the move often connect to business networks through unsecured devices and networks, creating potential vulnerabilities.
VPN Security for Remote Access
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) provides a secure connection between remote workers and your corporate network by encrypting the data being transmitted. VPNs also hide the user’s IP address, making it difficult for hackers to track their online activity.
When setting up VPNs for remote employees:
- Use strong encryption: Ensure that your VPN uses advanced encryption standards, such as AES-256.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): Require remote employees to verify their identity using MFA before connecting to the VPN.
Protecting Remote Devices
Remote workers often use personal devices that may not be as secure as corporate ones. Protect these devices by:

- Installing antivirus software: Ensure that all devices have up-to-date antivirus programs.
- Enforcing strong passwords: Require the use of strong, unique passwords for all devices.
- Avoiding public Wi-Fi: Encourage employees to use secure, private networks instead of public Wi-Fi, which is often unsecured and easy for hackers to exploit.
By implementing strong VPN security and device protection measures, businesses can secure their remote workforces against cyber threats.
Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
No matter how strong your network security measures are, you must prepare for the possibility of a breach. A comprehensive disaster recovery plan ensures that your business can recover quickly from an attack.
Best Practices for Data Backup
Backing up your data regularly is essential for minimizing the impact of a cyber-attack or system failure. Best practices for data backup include:
- Use both onsite and offsite backups: Onsite backups allow for quick recovery, while offsite (cloud-based) backups protect against physical damage to your office (e.g., in the event of a fire).
- Schedule automatic backups: Automate your backups to ensure that they happen regularly without relying on manual processes.
Planning for Cybersecurity Incidents
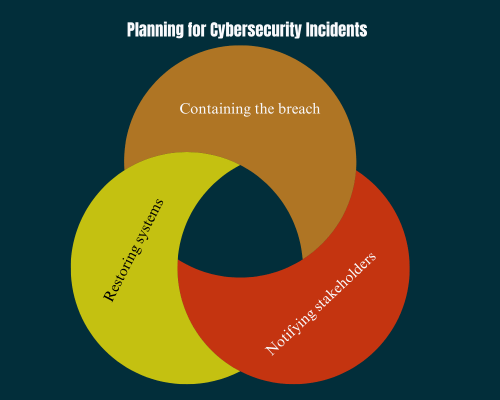
A disaster recovery plan should outline the steps to take in the event of a security breach. This includes:
- Containing the breach: Quickly isolate affected systems to prevent further damage.
- Notifying stakeholders: Inform employees, customers, and any relevant authorities about the breach.
- Restoring systems: Use backups to restore data and get your business operations back on track.
By having a clear disaster recovery plan in place, businesses can minimize the disruption caused by a cyber-attack and resume operations more quickly.
The Role of AI and Automation in Network Security
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, businesses are turning to Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation to bolster their network security efforts. These technologies offer new ways to detect and respond to threats in real-time.
How AI Enhances Network Security
AI can analyze vast amounts of network data quickly and accurately, making it easier to identify suspicious patterns that could indicate an attack. For example:
- Behavioral analysis: AI can learn normal network behaviors and flag any deviations that might signal a threat.
- Threat detection: AI-powered systems can detect previously unknown malware by analyzing its behavior rather than relying on signature-based detection methods.
AI can also help automate responses to certain threats, reducing the time it takes to mitigate an attack.
Using Automation to Improve Security Efficiency
Automation tools handle repetitive security tasks, such as:
- Applying patches: Automatically patching software ensures that your systems are always up-to-date with the latest security fixes.
- Generating security reports: Automation can create detailed reports of network activity and potential threats, allowing IT teams to focus on higher-priority tasks.
By integrating AI and automation into your security strategy, businesses can improve their overall defense posture and respond to threats faster.
Differences between Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
| Feature | Firewall | Intrusion Detection System (IDS) |
|---|
| Primary Function | Monitors and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic based on pre-established security rules | Monitors network traffic to detect and alert on suspicious activity or known threats |
| Action | Blocks or allows traffic based on security policies | Detects and raises alerts but does not take direct action to block threats (unless integrated with IPS) |
| Position in Network | Placed at the network perimeter (gateway) to control traffic flow between trusted and untrusted networks | Can be placed at multiple points in the network, including inside the network, for broader monitoring |
| Response Time | Immediate – automatically blocks unauthorized traffic | Alert-based – requires manual intervention or integration with Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) for automated response |
| Focus Area | Primarily focuses on preventing external threats from entering the network | Focuses on identifying both external and internal threats, including malicious insider activity |
| Complexity | Relatively simple to configure with predefined rules | More complex, requiring analysis of traffic patterns and behavior to identify potential threats |
| Type of Protection | Preventive – acts as a barrier to keep unwanted traffic out | Detective – identifies and alerts on suspicious activity after it occurs |
| Example of Usage | Prevents unauthorized access to internal network resources | Detects abnormal behavior, such as unauthorized data exfiltration or malware activity |
FAQs
What is the difference between WPA2 and WPA3 encryption?
WPA3 provides stronger encryption, better protection against brute-force attacks, and enhanced security for weak passwords compared to WPA2. It’s recommended to upgrade for better network security.
How do firewalls and IDS work together?
Firewalls block unauthorized traffic, while IDS detects suspicious activity inside the network. Together, they provide comprehensive protection by preventing and detecting threats.
Why is multi-factor authentication (MFA) important?
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring more than just a password, making it harder for hackers to access your network even if they obtain login credentials.
How often should I conduct security audits?
Security audits should be conducted at least annually, but high-risk environments may require quarterly or monthly checks to ensure the network’s security.
What is the role of AI and automation in network security?
AI helps detect threats faster by analyzing patterns, while automation handles routine tasks like patching and monitoring, improving overall network security efficiency.
Conclusion
In 2024, network security requires a proactive approach that integrates multiple layers of defense. From regular audits and encryption to securing remote work connections and leveraging AI, businesses must adopt a comprehensive strategy to protect their networks from evolving cyber threats. Implementing these best practices will not only safeguard your systems and data but also build trust with your clients and partners. By staying informed and vigilant, businesses can ensure the ongoing security of their networks and reduce the risk of costly data breaches. With the right tools and strategies, network security in 2024 can be manageable and effective
