Network security has become a critical concern for organizations, businesses, and individuals alike. With cyber threats evolving at an alarming rate, understanding these challenges and how to mitigate them is essential. In this article, we will dive into the most common and emerging network security challenges and explore how to address them effectively.
Introduction to Network Security
Importance of Network Security
Network security involves protecting a computer network and its data from breaches, intrusions, and other malicious activities. It is essential for businesses and individuals to ensure their networks are secure, as cyberattacks can result in significant financial loss, data theft, and reputational damage.
Evolution of Network Security Challenges
In the past, network security was simpler, focusing primarily on securing physical servers and basic firewalls. However, with the rise of the internet, mobile devices, and cloud computing, network security challenges have evolved, becoming more complex and harder to manage.
Common Network Security Challenges
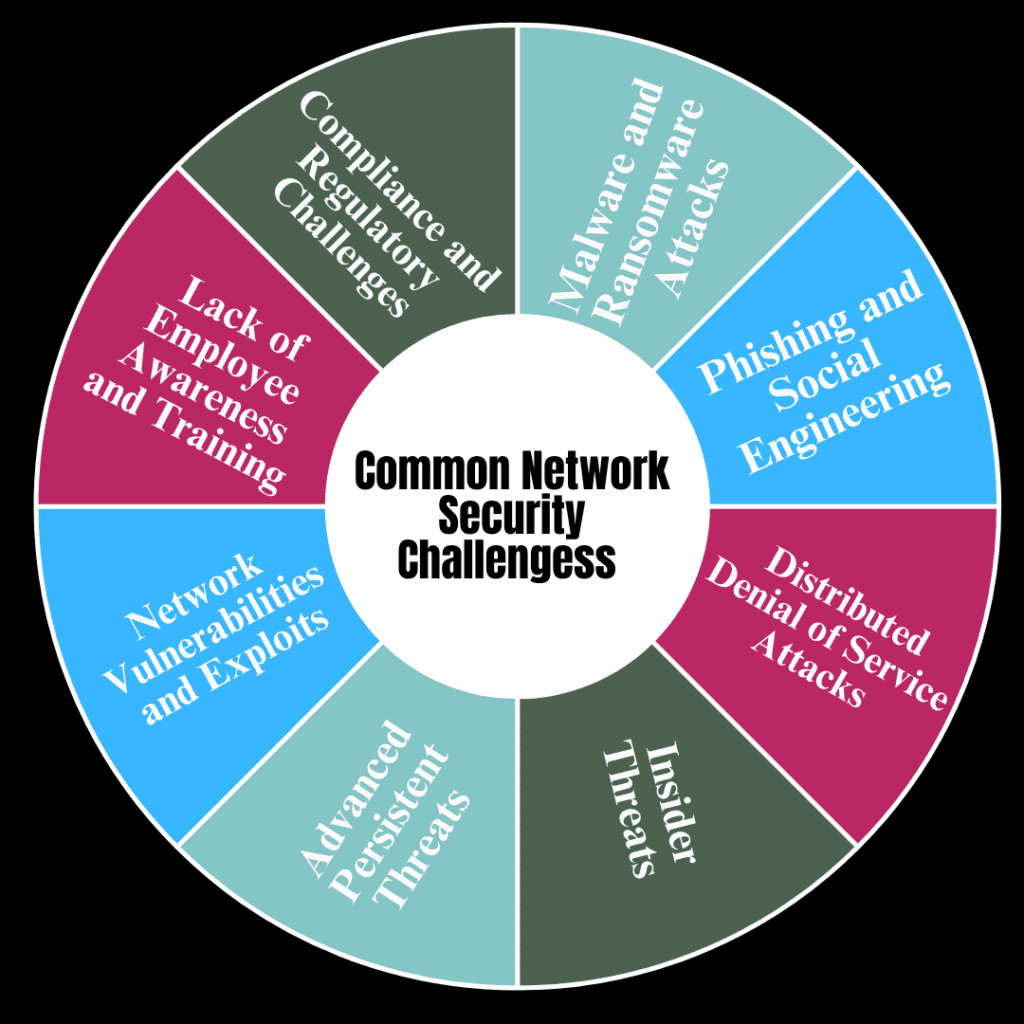
1. Malware and Ransomware Attacks
Malware, such as viruses and ransomware, can infect devices and networks, leading to data breaches or locking users out of systems. Ransomware attacks have become more common, with hackers demanding payments to restore access to files and systems.
2. Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing involves tricking users into revealing sensitive information, like passwords or credit card details, by posing as a legitimate entity. Social engineering manipulates individuals into bypassing security protocols, often leading to compromised systems.
3. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks overwhelm a network with excessive traffic, causing service outages and disruptions. These attacks result in significant downtime, financial losses, and damaged reputations for businesses.
4. Insider Threats
Insider threats come from employees, contractors, or partners with authorized access to sensitive data. Whether intentional or accidental, these threats can lead to data leaks, sabotage, or misuse of network resources.
5. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs are long-term attacks where hackers infiltrate a network undetected, collecting data or causing gradual damage. APTs are highly sophisticated and challenging to detect, often requiring specialized solutions for identification and removal.
6. Network Vulnerabilities and Exploits
Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in network software or hardware to gain unauthorized access. Unpatched systems or outdated security measures are prime targets, making regular updates and patches critical for defense.
7. Lack of Employee Awareness and Training
Human error is a significant challenge in network security. Many breaches occur due to employees inadvertently clicking on malicious links, using weak passwords, or failing to recognize phishing attempts.
8. Compliance and Regulatory Challenges
Organizations must comply with various security regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS, depending on their industry and location. Ensuring that a network meets these compliance requirements can be complex, especially as regulations evolve. Failing to comply can lead to hefty fines and legal consequences.
Emerging Network Security Challenge
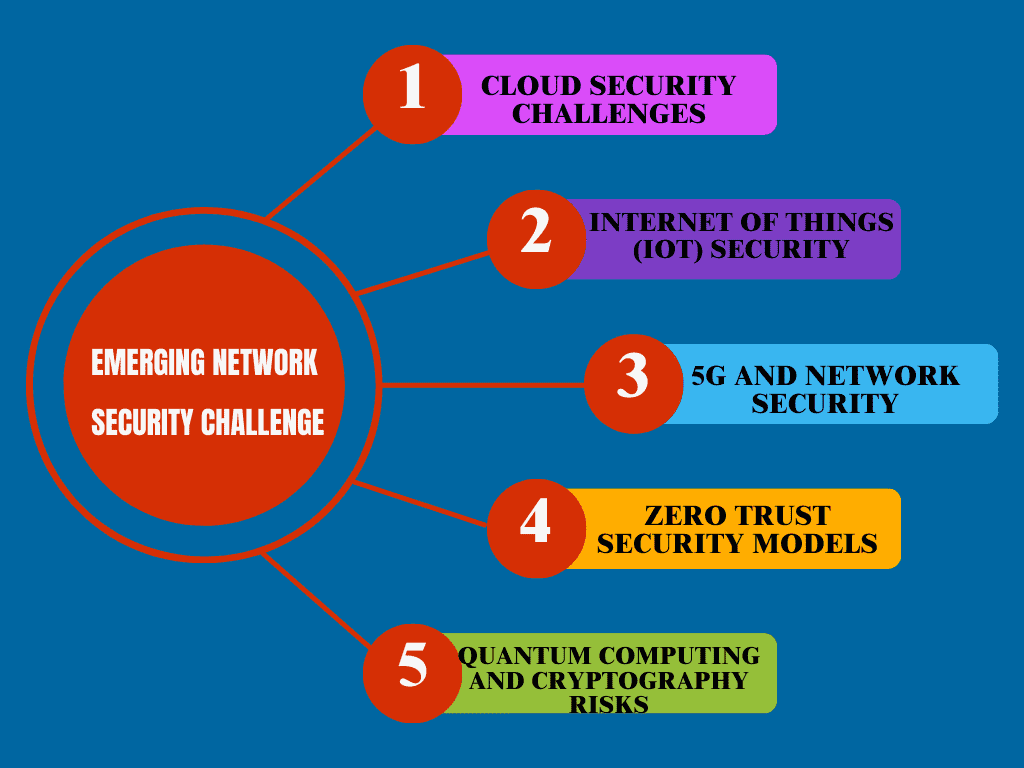
1 Cloud Security Challenges
With many organizations shifting to cloud services, ensuring the security of data stored online has become a new challenge. Misconfigured cloud settings, insecure APIs, and data breaches are common concerns.
2 Internet of Things (IoT) Security
IoT devices, from smart home systems to industrial sensors, often lack robust security measures, making them easy targets for hackers. Securing these devices is becoming increasingly important as their usage grows.
3 5G and Network Security
The rollout of 5G technology is transforming how devices connect, but it also opens up new vulnerabilities. Securing 5G networks and the devices connected to them is critical as this technology becomes more widespread.
4 Zero Trust Security Models
Traditional network security assumes that users within a network are trusted, but Zero Trust models operate on the principle of verifying every user or device before granting access. This approach is gaining popularity in combating insider threats and external attacks.
5 Quantum Computing and Cryptography Risks
Quantum computing, while still in its early stages, poses a potential risk to cryptography as it could break current encryption methods. Organizations need to stay ahead of this threat by preparing for quantum-resistant encryption methods.
Technological Advancements Impacting Network Security
1 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Security
AI and machine learning technologies are increasingly used to monitor and detect network threats in real time. These tools analyze vast amounts of data to identify unusual patterns or anomalies, automating threat detection and response, which helps minimize reaction time to security incidents.
2. Blockchain for Network Security
Blockchain provides a decentralized framework for secure data exchange, making it difficult for hackers to alter or compromise information. By ensuring data integrity and offering tamper-proof transactions, blockchain adds an extra layer of security to network operations, especially in financial or communication systems.
3. Role of Big Data Analytics in Network Security
Big data analytics processes large volumes of data to detect potential security threats. By analyzing patterns, anomalies, and behaviors within network traffic, big data helps predict and prevent cyberattacks more effectively, enabling proactive measures to mitigate risks.
4. Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust is a security model that operates under the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It assumes that threats can originate from both inside and outside the network, so continuous verification and strict access control are required for every user and device. This approach minimizes the risk of internal and external breaches.
5. Cloud Security Solutions
As more organizations shift their operations to the cloud, securing cloud-based infrastructures has become a priority. Cloud security solutions include encryption, identity management, and multi-factor authentication to protect data and ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive information.
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
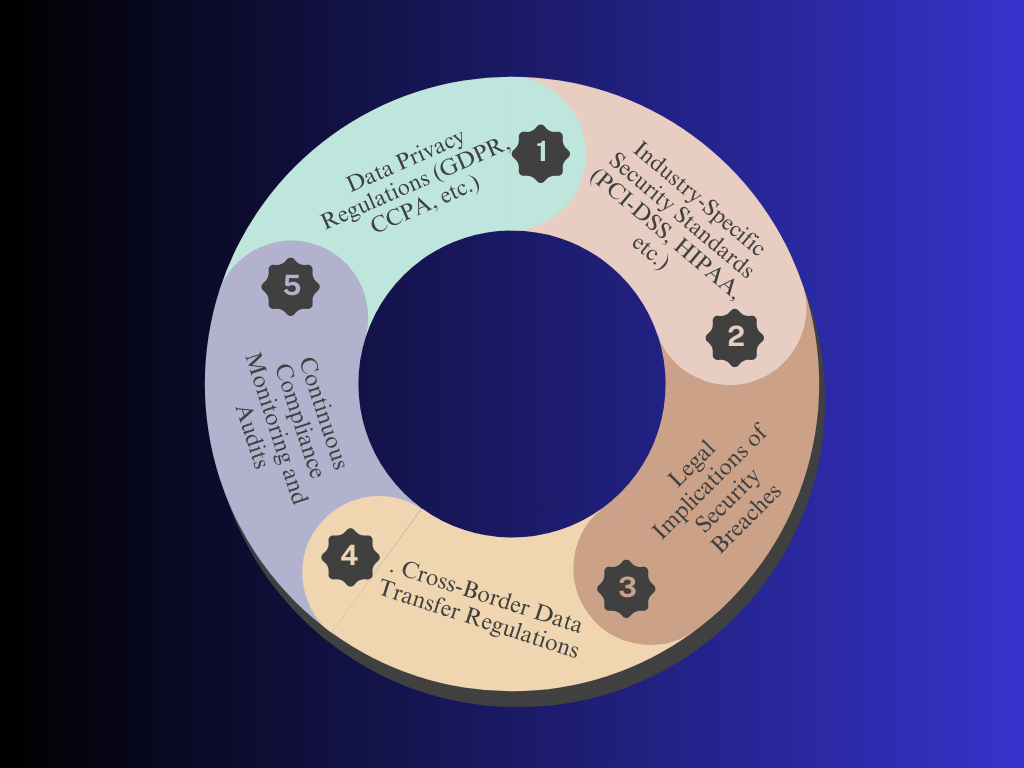
1. Data Privacy Regulations (GDPR, CCPA, etc.)
Data privacy laws like the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in the U.S. require organizations to handle personal data responsibly. Non-compliance can result in substantial fines and legal actions, making it crucial for organizations to ensure data privacy and protection protocols are in place.
2. Industry-Specific Security Standards (PCI-DSS, HIPAA, etc.)
Certain industries are required to follow specific security regulations to protect sensitive information. For example, HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in healthcare and PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) in financial services enforce strict security measures to safeguard personal and payment data.
3. Legal Implications of Security Breaches
Security breaches can expose organizations to legal consequences such as lawsuits, penalties, and compensation claims. Having proper legal protections, response plans, and insurance coverage is essential to minimize the legal risks associated with a cyberattack or data breach.
4. Cross-Border Data Transfer Regulations
Many organizations operate across international borders, making compliance with data transfer regulations complex. Laws such as the GDPR impose strict rules on how data can be transferred between countries, particularly outside of the European Union. Failure to comply can result in fines and restrictions on international operations.
5. Continuous Compliance Monitoring and Audits
Maintaining compliance is not a time task but an ongoing process. Organizations must continuously monitor and audit their security practices to ensure they meet the evolving standards and regulations. Regular audits and assessments help detect vulnerabilities and ensure that security measures are up to date.
Mitigating Network Security Challenges
1 Best Practices for Network Security
To reduce the risk of network security breaches, organizations should implement strong passwords, update software regularly, and use firewalls and antivirus programs.
2 Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity with more than just a password, such as using a phone or fingerprint.
3 Encryption and Secure Communication Protocols
Encrypting sensitive data ensures that even if it is intercepted, it cannot be read by unauthorized parties. Secure communication protocols like HTTPS help protect data in transit.
4 Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Human error continues to be a major contributor to security breaches, often leading to vulnerabilities that are easily exploited by attackers. Regular training on security best practices can reduce the likelihood of employees falling for phishing attacks or accidentally exposing sensitive data.
5 Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Conducting security audits and penetration testing can help identify vulnerabilities before hackers do. This proactive approach ensures a network stays secure over time.
Future Trends in Network Security
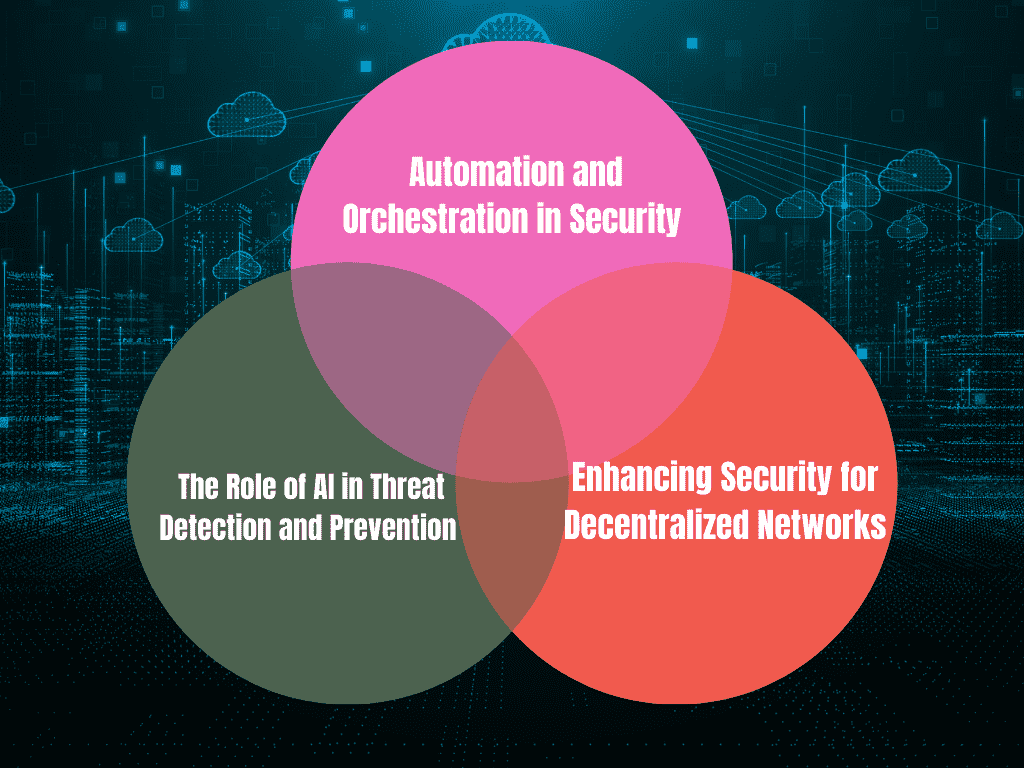
1 Automation and Orchestration in Security
Automation is becoming more important in managing network security. Automated systems can quickly respond to threats, making it easier for organizations to protect their networks.
2 The Role of AI in Threat Detection and Prevention
AI is being used to monitor network activity and detect threats in real-time. This technology is constantly improving, making it a powerful tool in the fight against cyberattacks.
3 Enhancing Security for Decentralized Networks
As businesses move towards decentralized networks, ensuring security across various systems and devices becomes a challenge. Future security solutions will focus on protecting these decentralized environments.
Differences between Common Network Security Challenges and Emerging Network Security Challenges
| Aspect | Common Network Security Challenges | Emerging Network Security Challenges |
|---|
| Malware and Ransomware | Widespread attacks targeting data and systems | Advanced ransomware tactics and malware targeting IoT |
| Phishing Attacks | Traditional email phishing with simple bait tactics | Spear-phishing and AI-driven phishing campaigns |
| DDoS Attacks | Basic volumetric attacks overwhelming bandwidth | Application layer DDoS attacks and multi-vector DDoS |
| Insider Threats | Employees misusing access intentionally or accidentally | Increased risk with remote work and cloud services |
| Cloud and IoT Security | Basic network and application vulnerabilities | Securing distributed devices and complex cloud services |
FAQs
What are the most common network security threats?
Common threats include malware, ransomware, phishing, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, and insider threats. These can disrupt networks, steal data, or cause financial loss.
How can organizations protect against phishing attacks?
Organizations can protect against phishing by implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA), conducting regular employee training, and using email filters to block suspicious content.
What is the difference between a DDoS attack and an insider threat?
A DDoS attack is an external attack that overwhelms a network with traffic to make it unavailable, while an insider threat originates from within the organization, often due to misuse of access by employees.
How has cloud computing impacted network security?
Cloud computing introduces new challenges like misconfigured settings, insecure APIs, and data breaches. Ensuring cloud security requires constant monitoring and proper configurations.
What emerging technologies are helping to improve network security?
Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, blockchain, and zero trust security models are emerging technologies helping to enhance real-time threat detection and prevent network breaches.
Conclusion
Network security is facing both traditional and emerging threats, from malware and phishing to the growing risks associated with IoT devices and 5G networks. These challenges demand a proactive approach, integrating advanced technologies like AI-driven threat detection and blockchain for secure data management. Strong password policies, encryption, and multi-factor authentication are essential. Employee training and adherence to regulatory compliance are equally important. Organizations must remain vigilant, updating their security strategies regularly. Embracing new security models and real-time monitoring will be key to staying ahead of these evolving threats.
