Introduction
Overview of Industrial Control Systems (ICS)
Industrial Control Systems (ICS) are integral to managing critical infrastructure, such as energy, water, manufacturing, and transportation. ICS enables the automation and remote control of these systems to ensure efficiency, safety, and reliability.
Importance of Network Security in ICS
The role of network security in ICS is essential because a breach can lead to devastating consequences, such as operational disruption, financial loss, or even threats to human safety. Securing ICS networks is more challenging than traditional IT systems due to legacy technology and the critical nature of their functions.
Current Threat Landscape in ICS Environments
ICS environments face increasing cyber threats, ranging from malware attacks to state-sponsored cyber espionage. These threats are evolving rapidly, targeting not just traditional IT networks but the operational technology (OT) that underpins ICS. As a result, organizations must stay ahead of attackers by implementing robust security solutions.
Fundamentals of Industrial Control System (ICS) Networks
1 Components of ICS Networks
ICS networks typically consist of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), and Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs). These components work together to monitor and control physical processes within an industry.
2 Differences Between IT and ICS Networks
IT networks focus on data transmission and processing, while ICS networks prioritize availability and control of physical processes. Unlike IT systems, ICS cannot afford downtime, and security measures must ensure seamless operation while protecting sensitive operations.

3 Common ICS Network Protocols
ICS networks use protocols such as Modbus, DNP3, and OPC, which were not designed with security in mind. These protocols lack encryption, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks if not properly protected.
4 Security Challenges in ICS Networks
Due to the critical nature of physical processes controlled by ICS networks, they are frequent targets of cyberattacks. ICS systems were traditionally designed with a focus on availability and safety rather than cybersecurity. Consequently, ICS networks often lack modern security controls such as encryption and authentication mechanisms, leaving them vulnerable to threats like malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access. Implementing strict security protocols while maintaining system availability is essential.
5 Integration of ICS and IT Networks
Modern industrial environments are increasingly integrating ICS and IT networks to improve efficiency and enable advanced data analytics. This convergence creates additional cybersecurity challenges, as IT networks typically have higher levels of exposure to external threats compared to ICS. As a result, ensuring proper segmentation, implementing security zones, and using firewalls are vital to safeguard ICS components from vulnerabilities that can propagate from IT systems.
Types of Cyber Threats Facing ICS Networks
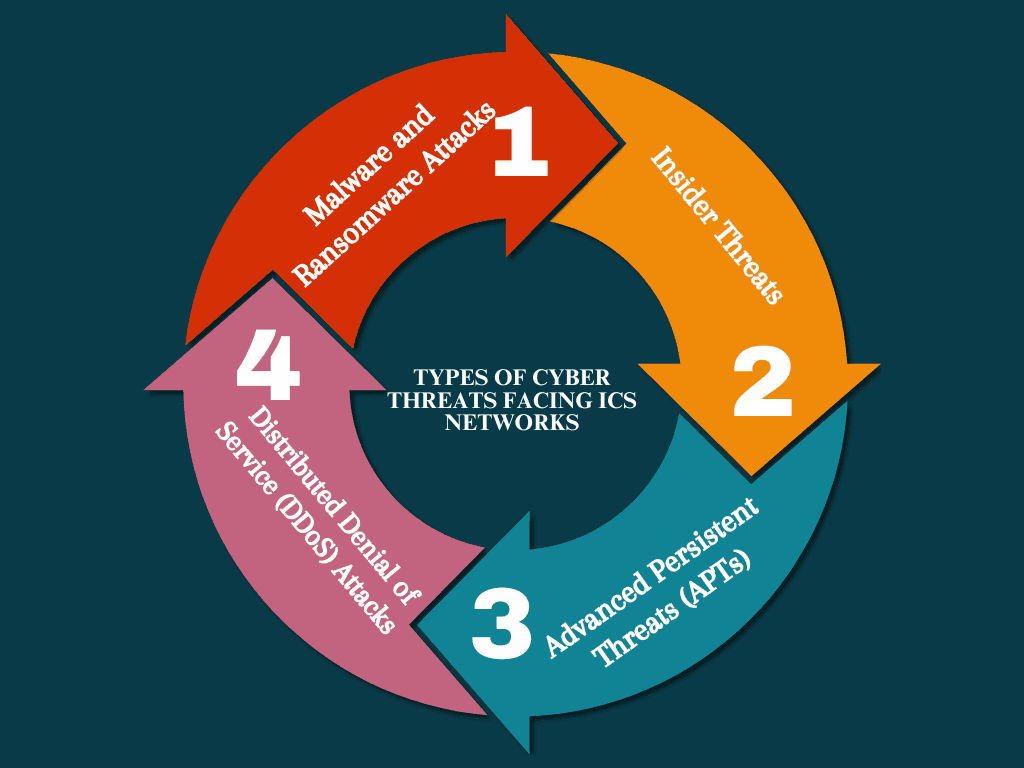
1 Malware and Ransomware Attacks
Malware can disrupt ICS operations by compromising key systems like PLCs or RTUs. Ransomware, in particular, can lock down essential control systems, demanding payment for their release.
2 Insider Threats
Insider threats come from employees or contractors who have access to sensitive ICS systems. Whether intentional or accidental, their actions can compromise system security.
3 Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs are long-term, targeted attacks carried out by skilled hackers, often sponsored by nation-states. These threats are designed to infiltrate, monitor, and control ICS networks without detection.
4 Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks can overload ICS networks, preventing legitimate control signals from being processed. This type of attack can result in significant operational downtime and safety risks.
Security Challenges in Industrial Control Systems
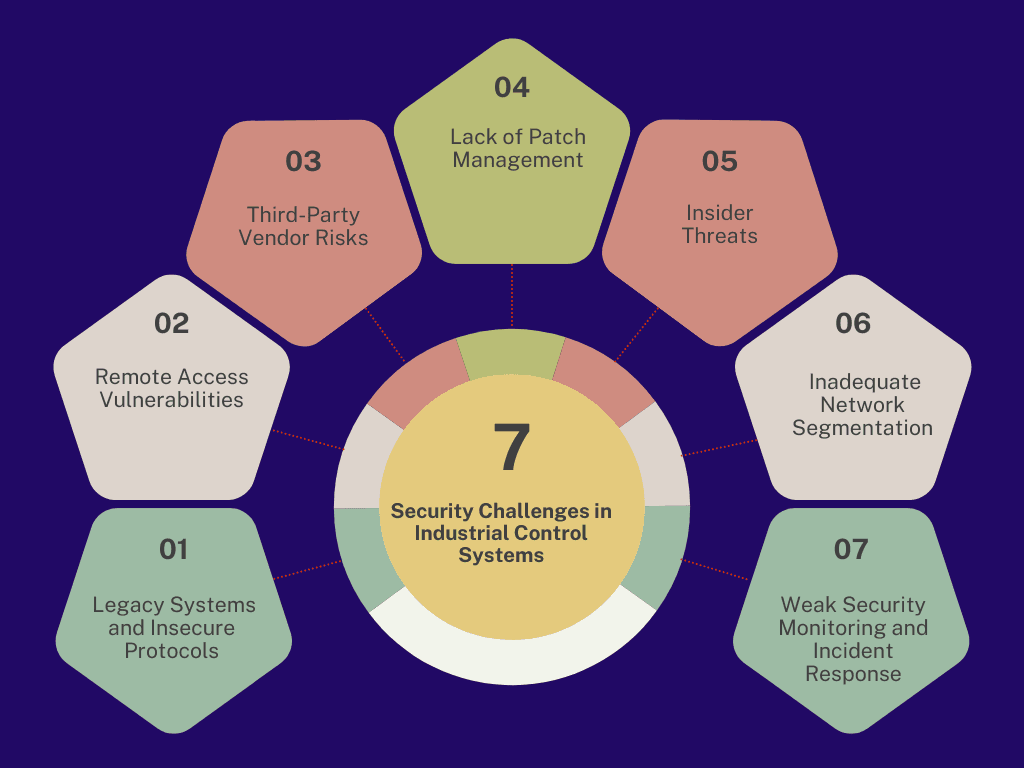
1 Legacy Systems and Insecure Protocols
Many ICS environments rely on legacy systems that were not designed with modern security features. These outdated systems often use insecure communication protocols like Modbus and DNP3, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks and exploitation.
2 Remote Access Vulnerabilities
The increased integration of remote monitoring and control in ICS introduces significant vulnerabilities. If remote access systems are not properly secured with strong encryption and authentication, attackers can easily exploit these vulnerabilities, gaining unauthorized control of critical industrial processes.
3 Third-Party Vendor Risks
Many ICS systems depend on third-party vendors for services such as maintenance and system upgrades. These vendors may not always follow stringent security practices, which increases the attack surface. Inadequate vetting of third-party vendors can introduce backdoor access points for cyberattacks.
4 Lack of Patch Management
Due to the critical nature of ICS operations, systems are often left unpatched for extended periods to avoid downtime. This lack of regular patching leaves ICS environments vulnerable to known exploits and makes them susceptible to malware attacks or other security breaches.
5 Insider Threats
ICS environments face risks not only from external attackers but also from insiders. Employees or contractors with access to ICS components may intentionally or unintentionally compromise system security. Insider threats are difficult to detect and can cause significant harm to system integrity.
6 Inadequate Network Segmentation
In many ICS environments, there is insufficient segmentation between critical and non-critical network segments. This allows attackers to move laterally across networks once they gain access, potentially affecting vital systems. Proper network segmentation can limit the scope of an attack.
7 Weak Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Many ICS environments lack robust security monitoring systems and incident response plans. Without continuous monitoring and well-defined response procedures, ICS operators may not detect attacks quickly enough, allowing cybercriminals to cause extensive damage before any defensive action is taken.
Network Security Solutions for ICS
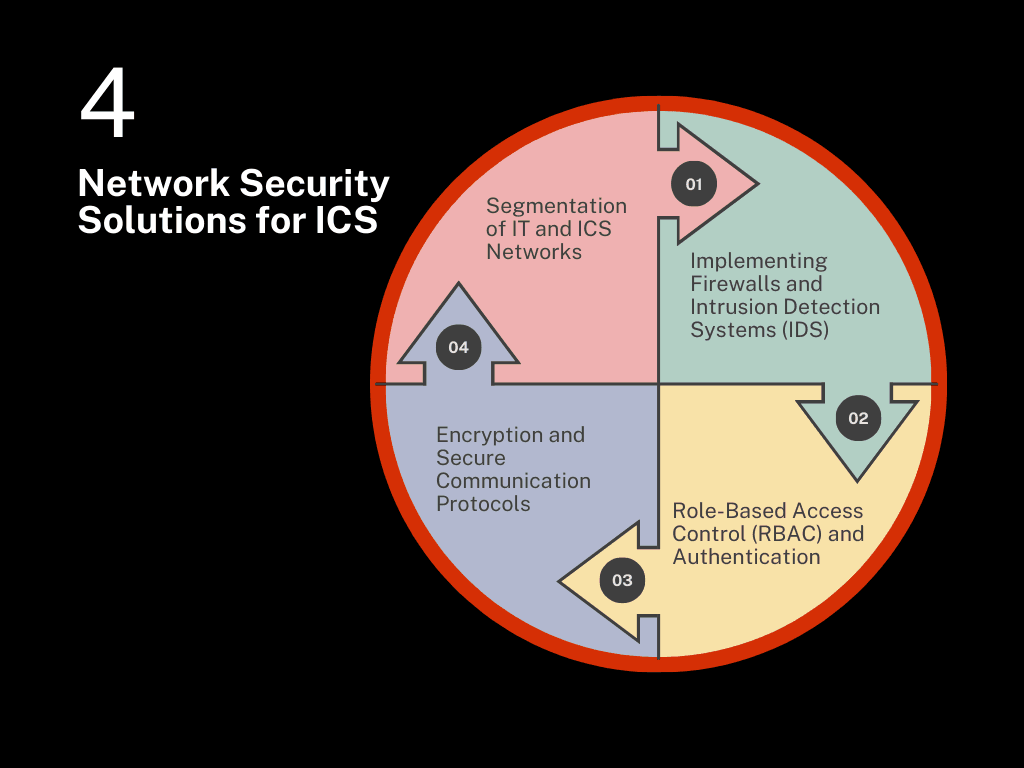
1 Segmentation of IT and ICS Networks
One effective way to enhance ICS security is by segmenting IT and ICS networks. By separating critical control systems from the broader IT network, organizations can reduce the risk of cross-contamination from an IT-based cyberattack.
2 Implementing Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Firewalls help control traffic between IT and ICS networks, ensuring that only authorized data flows through. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and can alert operators of potential breaches.
3 Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Authentication
RBAC restricts access to ICS systems based on the user’s role within the organization. Strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication, help ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive control systems.
4 Encryption and Secure Communication Protocols
ICS networks should utilize encryption to protect data from being intercepted or altered. Secure communication protocols, like HTTPS and TLS, are essential for ensuring data integrity and confidentiality across ICS environments.
Advanced ICS Security Technologies
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in ICS Security
AI and ML can analyze vast amounts of network traffic to detect anomalies that might indicate a cyberattack. These technologies can also learn from previous attacks to improve defenses against emerging threats.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems
SIEM systems collect and analyze security events across the ICS environment, providing real-time insights into potential security incidents. SIEM systems are vital for monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats in real time.
Industrial Intrusion Detection Systems (IIDS)
IIDS are specialized IDS systems designed specifically for ICS environments. They monitor industrial protocols and systems for any suspicious activity that could indicate a cyberattack.
6 Best Practices for Securing ICS Networks
1 Developing an ICS Security Policy
A well-defined ICS security policy serves as the foundation for protecting the network. This policy should clearly outline protocols, roles, and responsibilities regarding network segmentation, access control, security monitoring, and incident response. Regularly updating the policy to address emerging threats is essential for effective defense.
2 Security Awareness Training for ICS Personnel
Personnel who interact with ICS systems should receive ongoing security awareness training. Employees must be able to identify phishing attempts, recognize signs of system tampering, and understand best practices for secure system access. Regular training ensures the workforce is up-to-date on evolving threats and internal security protocols.
3 Incident Response and Recovery Plans
It is critical for organizations to have a well-developed incident response plan in place. This plan should outline procedures for mitigating the impact of security incidents, such as cyberattacks or system failures. A recovery plan ensures that organizations can quickly restore operations, minimizing system downtime and financial losses.
4 Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
Continuous monitoring of ICS systems is crucial for detecting anomalous behavior and potential security breaches early. Regular auditing of security protocols and configurations ensures compliance with the organization’s security policy. Monitoring tools should be integrated with automated alerts for prompt threat detection and response.
5 Network Segmentation and Access Control
Implementing proper network segmentation helps isolate critical ICS components from non-critical or more exposed segments. By limiting the lateral movement of attackers, network segmentation minimizes the impact of a breach. Additionally, implementing strict access controls ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive systems.
6 Regular Patch Management and System Updates
Maintaining an up-to-date system is essential for reducing vulnerabilities. Regular patch management and timely updates of ICS software and hardware can prevent cyberattacks that exploit known vulnerabilities. While downtime must be managed carefully in ICS environments, patching systems is critical to protecting against threats.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance for ICS Security
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides guidelines and best practices for managing and reducing cybersecurity risks in critical infrastructure like ICS.
IEC 62443 Standard for Industrial Cybersecurity
IEC 62443 is an international standard that provides a structured approach to implementing cybersecurity in industrial automation and control systems.
NERC CIP Standards for Power Grids
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) standards are designed to protect the cybersecurity of the power grid’s critical infrastructure.
Future Trends in ICS Network Security
Increasing Connectivity and IoT in ICS
As ICS environments increasingly integrate with IoT devices, the attack surface grows. Organizations must develop strategies to secure these connected devices and prevent them from becoming entry points for attacks.
The Role of 5G in ICS Security
5G technology promises faster and more reliable communication in ICS environments. However, it also introduces new security challenges that need to be addressed as industries adopt 5G for operational use.
Quantum Computing and ICS Encryption
Quantum computing could revolutionize encryption, making current encryption methods obsolete. As quantum computing technology advances, ICS environments must adapt to new encryption standards to ensure security.
Differences between IT Networks and ICS Networks
| Aspect | IT Networks | ICS Networks |
|---|
| Primary Focus | Data processing, storage, and transmission | Control and monitoring of physical processes |
| Downtime Tolerance | Can tolerate some downtime for updates | Downtime is critical and often unacceptable |
| Security Priorities | Prioritizes confidentiality and data integrity | Prioritizes availability and safety over confidentiality |
| Update Frequency | Regular updates and patching are common | Infrequent updates due to legacy systems and risk of disruption |
| Protocols Used | Standard protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, FTP | Specialized protocols like Modbus, DNP3, and OPC without built-in security |
FAQS
What is the difference between ICS networks and IT networks?
ICS networks are primarily designed to control and monitor physical processes in industries, such as energy, manufacturing, and transportation. IT networks, on the other hand, focus on data processing, storage, and transmission. ICS networks prioritize availability and safety, while IT networks prioritize confidentiality and data integrity.
Why is network segmentation important in ICS security?
Network segmentation helps isolate critical ICS components from the rest of the network, reducing the risk of cyberattacks spreading. By separating IT and ICS networks, organizations can protect sensitive control systems from threats that may arise in less secure parts of the network.
What are common cyber threats faced by ICS networks?
ICS networks face several threats, including malware attacks, ransomware, insider threats, Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. These threats can compromise the availability and safety of critical operations.
How can role-based access control (RBAC) enhance ICS security?
RBAC restricts access to specific systems based on an employee’s role in the organization. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access or control sensitive systems, minimizing the risk of accidental or malicious interference.
What are some best practices for securing ICS networks?
Best practices include developing a robust ICS security policy, implementing firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS), using encryption for secure communication, conducting regular security awareness training, and maintaining continuous monitoring and auditing of network activities.
Conclusion
Securing ICS networks requires a multi-faceted approach, including network segmentation, the use of firewalls and IDS, RBAC, encryption, and continuous monitoring. Implementing these solutions reduces the risk of cyberattacks and ensures the safe operation of critical infrastructure.As cyber threats continue to evolve, so must ICS network security. Organizations must remain proactive in adopting new technologies and standards, ensuring that their critical infrastructure remains secure in an increasingly connected world.