1. Introduction to Physical Intrusion Detection Systems
Overview
Physical intrusion detection systems (PIDS) have become integral to the protection of homes, businesses, and government facilities. These systems are designed to detect unauthorized access and breaches by analyzing changes in physical parameters, such as motion, pressure, and temperature. With rising concerns over security threats, a growing number of industries and individuals are adopting these systems to prevent damage or theft.
What is a Physical Intrusion Detection System?
A physical intrusion detection system refers to a combination of hardware and software designed to monitor and detect unusual activity within a defined perimeter. These systems work by using various sensors that trigger an alert when specific conditions are met, such as detecting movement, breaking glass, or opening doors or windows.
Historical Development of PIDS
The concept of detecting physical intrusion has been around for centuries, starting from simple manual locks and guards to complex electronic systems. The development of modern intrusion detection systems began with motion sensors in the 20th century. Today’s systems have evolved significantly, integrating artificial intelligence, remote monitoring, and real-time notifications for advanced security needs.
Why Physical Intrusion Detection Systems Matter
The need for heightened security has never been greater, with both personal and corporate threats on the rise. PIDS provide an effective way to deter, detect, and respond to intrusions. Whether it’s protecting valuable assets, maintaining business continuity, or ensuring personal safety, these systems are crucial for modern security solutions.
2. Components of Physical Intrusion Detection Systems
Overview
A physical intrusion detection system consists of various interconnected components that work together to detect, alert, and prevent unauthorized access. Each part of the system plays a key role in ensuring comprehensive security coverage. Below, we break down the critical components that form a PIDS.
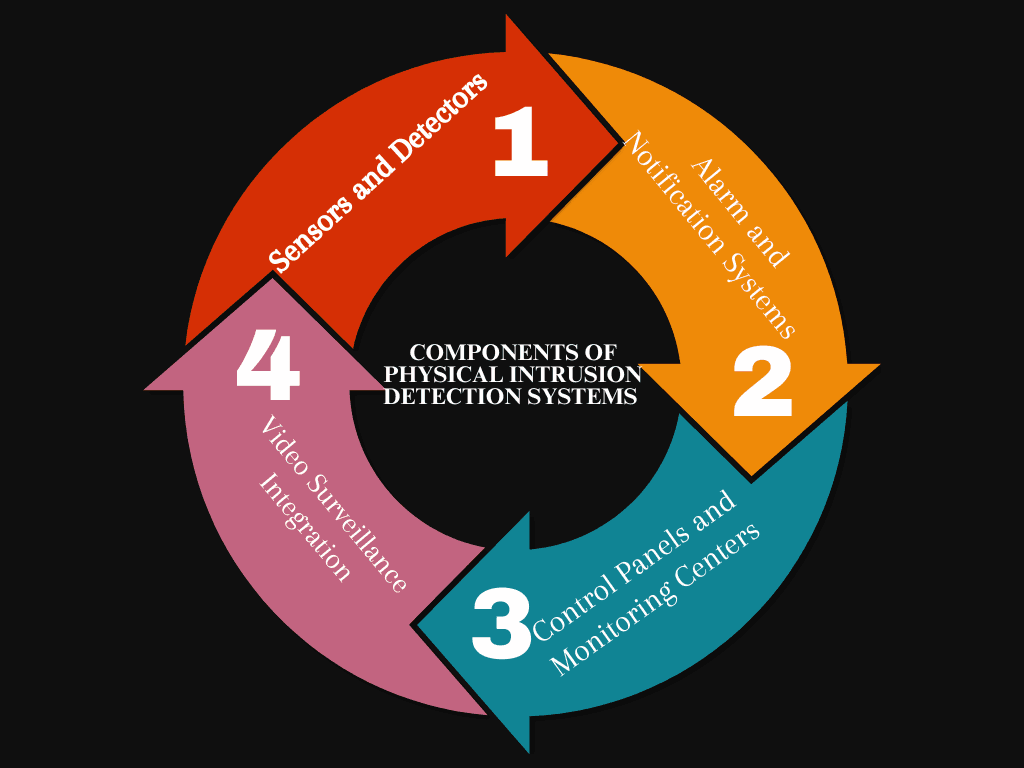
1 Sensors and Detectors
Sensors are the backbone of any physical intrusion detection system. These devices are strategically placed around a property to detect motion, sound, or changes in environmental conditions. Common sensors include:
- Motion Detectors: Detect movement using infrared or ultrasonic waves.
- Glass Break Sensors: React to the sound frequency of breaking glass.
- Pressure Sensors: Monitor changes in pressure on floors, windows, or doors.
- Magnetic Contact Sensors: Installed on doors or windows to detect opening or closing.
These sensors continuously monitor their surroundings and alert the control panel if they detect any anomaly.
2 Alarm and Notification Systems
Once a sensor detects suspicious activity, an alarm is triggered. The alarm system includes audible sirens, flashing lights, and silent notifications to alert the property owner or security personnel. Advanced systems send notifications via phone, email, or a dedicated security app, enabling rapid response.
3 Control Panels and Monitoring Centers
The control panel acts as the brain of the PIDS. It receives input from the sensors, processes the information, and decides whether to trigger an alarm. The control panel is typically located in a secure area and may include backup power to ensure continuous operation. In larger systems, monitoring centers staffed with security personnel can oversee real-time activity and respond to alarms.
4 Video Surveillance Integration
Many PIDS integrate with video surveillance systems, allowing for visual confirmation of detected events. When an intrusion is detected, cameras automatically record footage, providing evidence for law enforcement or security teams.
3. How Physical Intrusion Detection Systems Work
Overview
Physical intrusion detection systems operate by continuously monitoring the environment for irregularities. The effectiveness of a PIDS depends on how well it can detect and respond to threats while minimizing false alarms. Understanding the basic working principles of these systems helps users maximize their security setup.
Detection Mechanisms
The detection mechanisms of a PIDS are primarily based on the type of sensors employed. Different types of detection include:
- Motion Detection: Utilizes infrared, microwave, or ultrasonic technology to sense movement.
- Vibration Detection: Sensors detect vibrations caused by breaking glass or forced entry.
- Temperature Detection: Some sensors can detect rapid changes in temperature, such as those caused by fire or explosives.
- Light and Sound Sensors: These detect changes in the environment, like sudden light or sound disturbances.
Each sensor feeds data to the control panel, which processes and interprets the signals, deciding if they indicate a real threat.
Signal Processing and Alerts
Once the control panel receives a signal from the sensors, it processes the information to determine if the event is a legitimate threat. Modern systems use algorithms and AI to reduce false alarms. If a threat is confirmed, the system triggers an alarm and sends notifications to the owner or a monitoring service.
Integration with Other Security Systems
Physical intrusion detection systems often integrate with other security technologies, such as:
- Access Control Systems: Allow or restrict entry based on identity verification.
- Fire and Safety Systems: Alert authorities in case of fire or other environmental hazards.
By integrating with multiple security layers, PIDS provide comprehensive protection.
4. Types of Physical Intrusion Detection Systems
Overview
Various types of physical intrusion detection systems exist, each tailored to specific security needs. The choice of system depends on the area to be protected, the nature of the threat, and the level of security required. Here, we explore the different types of PIDS and their unique advantages.
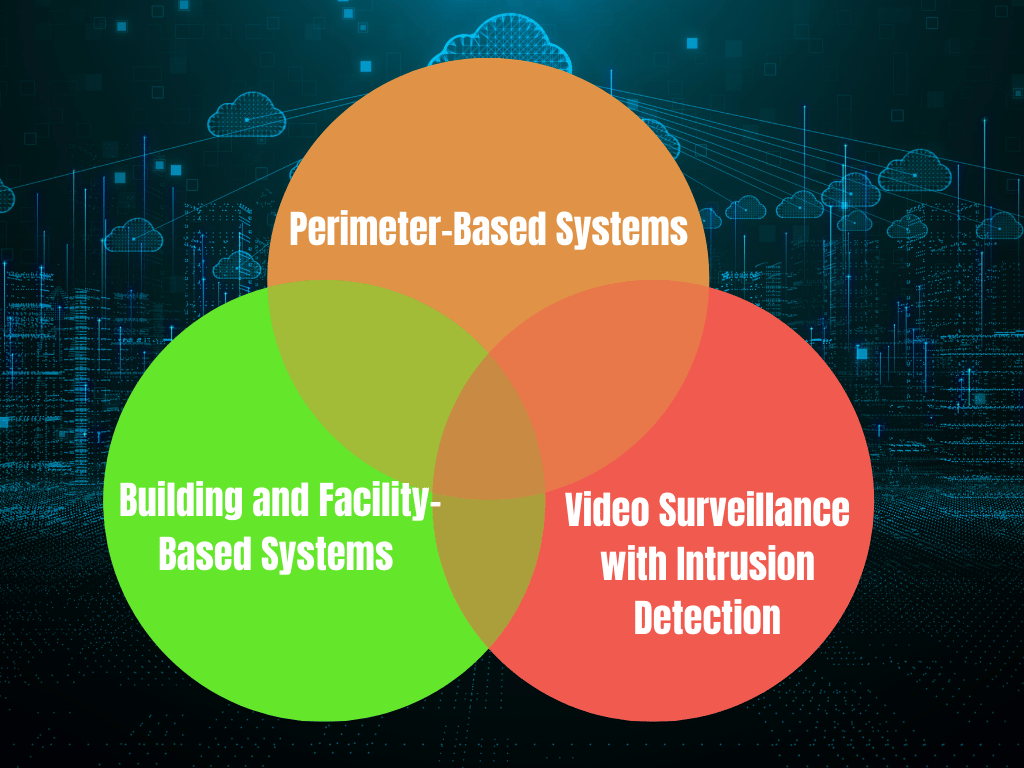
1Perimeter-Based Systems
Perimeter-based systems are designed to protect the outer boundary of a property. These systems are ideal for large properties, such as industrial facilities, military bases, and residential estates. Types of perimeter detection systems include:
- Fence-Mounted Sensors: Detect vibrations or pressure on fences.
- Ground-Based Sensors: Detect movement or weight on the ground around a perimeter.
- Infrared and Microwave Barriers: Create invisible beams that trigger an alarm when crossed.
2 Building and Facility-Based Systems
These systems are installed inside buildings to protect against unauthorized access to specific rooms or areas. They often use a combination of motion sensors, door and window contacts, and glass break detectors to secure entrances. They are commonly used in offices, banks, and government buildings.
3 Video Surveillance with Intrusion Detection
Video surveillance systems can be equipped with advanced analytics that detect motion, unauthorized access, or unusual behavior. When integrated with a PIDS, the cameras provide visual confirmation of potential intrusions, allowing security personnel to respond appropriately.
5. Benefits of Physical Intrusion Detection Systems
Overview
Physical intrusion detection systems offer numerous benefits for individuals, businesses, and government facilities. These systems provide reliable, cost-effective protection, allowing users to safeguard their assets and prevent unauthorized access. Below are some key advantages of implementing PIDS.
1 Enhanced Security and Prevention
The primary benefit of a PIDS is the early detection of potential threats. By alerting security personnel or property owners immediately, these systems help prevent theft, vandalism, and damage before they occur.
2 Real-Time Monitoring and Response
Modern PIDS provide real-time monitoring, enabling security teams to respond quickly to potential threats. Instant notifications sent to mobile devices or monitoring centers allow for rapid action, minimizing damage and preventing escalation.
3 Cost-Effective Security Solution
Compared to hiring full-time security personnel, physical intrusion detection systems are a cost-effective solution. They provide 24/7 surveillance without the need for constant human presence, reducing overall security costs while maintaining high levels of protection.
4 Deterrent to Criminals
Visible physical intrusion detection systems, such as cameras or alarm signs, act as a strong deterrent to potential intruders. Criminals are less likely to attempt a break-in if they know a property is equipped with advanced security technology.
6. Applications of Physical Intrusion Detection Systems
Overview
Physical intrusion detection systems (PIDS) are versatile and can be applied across various industries and environments. From residential homes to critical infrastructure, these systems offer protection in areas where the risk of unauthorized access, theft, or damage is high. Below are some common applications of PIDS.
1 Industrial and Commercial Facilities
Factories, warehouses, and industrial complexes are large areas that require constant surveillance. PIDS are essential for protecting valuable assets, machinery, and inventory from theft or sabotage. Perimeter-based systems are often used to monitor large areas, with additional sensors installed at entry points and loading docks to detect breaches. Moreover, commercial facilities such as retail stores and office buildings also rely on PIDS to secure entrances and protect sensitive areas, such as server rooms and safes.
- Example: In a warehouse, motion detectors and video surveillance systems can monitor valuable stockpiles and automatically alert security teams in case of an intrusion.
2 Residential Areas
In homes, PIDS can be used to secure doors, windows, and outdoor areas. Systems like motion detectors, glass break sensors, and CCTV cameras can detect intrusions and provide homeowners with real-time alerts. These systems are often integrated with home automation devices, allowing for remote monitoring and control through mobile apps.
- Example: A residential PIDS system might include door and window sensors that alert homeowners when they are opened, and outdoor motion detectors to detect movement around the property during the night.
3 Critical Infrastructure and Government Facilities
Facilities such as power plants, water treatment plants, and military bases require the highest level of security. PIDS are crucial for protecting these sensitive sites from external threats like terrorism or vandalism. These systems are often integrated with access control and video surveillance technologies to ensure only authorized personnel can access restricted areas.
- Example: In a government building, advanced perimeter-based sensors combined with facial recognition software and security cameras ensure that any unauthorized access is immediately detected and dealt with.
4 Healthcare and Educational Institutions
Hospitals and schools can benefit from PIDS by protecting patients, staff, students, and critical infrastructure such as laboratories or data centers. In these environments, intrusion detection systems are also integrated with other safety measures, such as fire alarms and emergency exit control systems.
- Example: A hospital might use PIDS to secure medicine storage areas, prevent unauthorized access to confidential records, and monitor restricted areas, such as operating rooms.
7. Challenges in Physical Intrusion Detection
Overview
While physical intrusion detection systems offer significant benefits, they also face challenges that can impact their effectiveness. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring that a PIDS functions optimally. Below are some of the most common challenges in PIDS.
1 False Alarms and Detection Accuracy
One of the biggest challenges in PIDS is false alarms. These occur when sensors are triggered by non-threatening events, such as animals, weather changes, or movement from nearby objects. False alarms not only reduce the system’s reliability but can also cause desensitization, leading to slower responses during actual threats.
- Solution: Modern systems use AI and machine learning algorithms to distinguish between genuine threats and false triggers. Regular calibration of sensors and adjustment of sensitivity levels can also reduce false alarms.
2 System Maintenance and Calibration
Like any technology, PIDS require regular maintenance to ensure they continue functioning effectively. Sensors may lose accuracy over time due to environmental factors like dust, moisture, or temperature changes. Failure to maintain these systems can lead to missed detections or frequent false alarms.
- Solution: Regular maintenance schedules should be established to clean and recalibrate sensors, update software, and test the system’s functionality. Backup power systems should also be tested to ensure uninterrupted operation during power outages.
3 Integrating with Legacy Systems
Many organizations that already have security systems in place face challenges when upgrading to new PIDS technologies. Older systems may not be compatible with newer intrusion detection technologies, leading to difficulties in integration and communication between devices.
- Solution: When upgrading or expanding security systems, choosing PIDS that are compatible with existing infrastructure or opting for modular systems that can be integrated in stages can help overcome this challenge.
4 High Initial Costs
The cost of implementing an advanced PIDS, especially in large industrial or government facilities, can be prohibitive. The installation, hardware, and software required for a comprehensive intrusion detection system can strain security budgets.
Solution: Businesses and organizations should evaluate their specific security needs and invest in scalable systems that allow for gradual expansion. Cloud-based solutions or systems that integrate with existing security measures can also help lower initial costs.
8. Technological Advancements in Physical Intrusion Detection
Overview
Technology has dramatically improved the capabilities of physical intrusion detection systems. Innovations such as artificial intelligence, smart sensors, and cloud-based systems have revolutionized how security systems detect and respond to potential threats. These advancements have made PIDS more accurate, scalable, and easier to manage.

1 AI and Machine Learning in Intrusion Detection
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are transforming intrusion detection by improving accuracy and reducing false alarms. AI-powered systems can learn from past incidents to identify patterns and differentiate between real and false threats.
- Example: An AI-based system can analyze movement patterns to detect whether motion in a monitored area is caused by an animal, a person, or a vehicle, and respond appropriately.
Machine learning algorithms enable systems to adapt to changing environments and continuously improve their accuracy over time. This means that the system becomes more efficient at detecting real threats while minimizing unnecessary alerts.
2 Smart Sensors and IoT Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) has introduced smart sensors that can communicate with each other and with a central control system. These sensors are capable of monitoring multiple conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and sound, in addition to detecting motion or pressure.
- Example: Smart motion detectors can be combined with temperature and humidity sensors to detect not only intrusions but also potential environmental hazards, such as fires or water leaks.
Smart sensors can also be controlled remotely via mobile apps, allowing users to monitor and manage their security systems from anywhere. This level of integration enhances security by providing real-time updates and control over multiple systems simultaneously.
3 Remote Monitoring and Cloud-Based Systems
Cloud-based intrusion detection systems allow for remote monitoring and control. By using cloud services, security teams or property owners can access live feeds, receive alerts, and manage system settings from any location with an internet connection.
- Example: A business owner can receive a real-time alert on their smartphone if an intrusion is detected at their store, even if they are miles away. They can also view the CCTV footage, contact authorities, or trigger an alarm directly from their phone.
Cloud-based systems also simplify the management of multiple security sites, as all the data is centralized and easily accessible. These systems are scalable, making them ideal for businesses or institutions with multiple locations.
9. Physical Intrusion Detection Systems in Modern Security Strategies
Overview
Physical intrusion detection systems are integral to modern security strategies. Whether for personal safety, business protection, or national security, PIDS play a crucial role in preventing unauthorized access and deterring crime. The integration of PIDS with other security measures ensures comprehensive protection against a wide range of threats.
Role in Comprehensive Security Plans
A comprehensive security plan involves multiple layers of defense, including physical barriers, surveillance, access control, and intrusion detection systems. PIDS provide the first line of defense by alerting authorities or property owners of any unauthorized access attempts.
In many cases, PIDS are combined with other systems, such as video surveillance, fire alarms, and access control systems, to create a holistic approach to security. This layered security model ensures that potential threats are detected, monitored, and addressed before they can cause harm.
Case Studies of Effective Implementation
Numerous case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of PIDS in various sectors. For example, a retail chain implemented a PIDS that reduced shoplifting incidents by 40%. By integrating motion detectors with video surveillance, the system provided real-time alerts, enabling security personnel to act quickly.
Another case study involves a government building where a PIDS prevented unauthorized entry by alerting security personnel the moment a breach occurred. The integration of facial recognition and perimeter detection sensors ensured that any unauthorized access was detected and addressed immediately.
Future Trends in Intrusion Detection Systems
The future of physical intrusion detection systems lies in further integration with AI and machine learning, as well as the adoption of more sophisticated smart sensors. As these technologies evolve, we can expect PIDS to become even more accurate, capable of predicting potential threats before they occur.
Another emerging trend is the integration of PIDS with drones and autonomous robots. These technologies can patrol large areas, such as industrial complexes or border regions, and provide real-time surveillance and intrusion detection without the need for human intervention.
Differences between Physical Intrusion Detection Systems (PIDS) and Cyber Intrusion Detection Systems (CIDS)
| Aspect | Physical Intrusion Detection Systems (PIDS) | Cyber Intrusion Detection Systems (CIDS) |
|---|
| Focus | Detects unauthorized physical access or breaches in a location | Detects unauthorized access or threats within digital networks or systems |
| Medium of Operation | Operates in the physical world (buildings, perimeters, and restricted areas) | Operates in the digital environment (networks, servers, and databases) |
| Detection Methods | Uses sensors, cameras, and alarms to detect physical movements or breaches | Analyzes network traffic, system logs, and user behaviors for cyber threats |
| Response Mechanism | Triggers alarms, locks doors, or alerts security personnel for physical response | Alerts system admins, blocks IPs, or isolates compromised devices |
| Examples of Use | Protecting homes, offices, and critical infrastructure | Securing corporate networks, preventing data breaches, and protecting sensitive information |
FAQs
What is a Physical Intrusion Detection System (PIDS)?
A PIDS is a security system designed to detect unauthorized physical access or breaches in a specific location, such as a home, office, or restricted area, using sensors, cameras, and alarms.
How does a Physical Intrusion Detection System work?
PIDS use various sensors, such as motion detectors, pressure sensors, and glass break sensors, to monitor activity. When a breach or unusual movement is detected, the system triggers an alarm or notification, allowing for a timely response.
What are the main components of a Physical Intrusion Detection System?
The primary components include sensors and detectors, alarm systems, control panels, and sometimes video surveillance for real-time monitoring. These elements work together to detect and alert against any unauthorized physical access.
What are the benefits of using a Physical Intrusion Detection System?
PIDS provide enhanced security, real-time alerts, and quick responses to potential threats. They help deter intruders, reduce the risk of theft or damage, and can be more cost-effective than relying solely on physical security personnel.
Can a Physical Intrusion Detection System be integrated with other security systems?
Yes, PIDS can be integrated with other systems like video surveillance, access control, and fire alarms to create a comprehensive security solution. This integration allows for better monitoring and more efficient responses to security threats.
Conclusion
In conclusion, physical intrusion detection systems are an essential component of modern security strategies. These systems provide a reliable, cost-effective means of detecting and responding to potential threats, ensuring the safety of people, property, and assets. By integrating PIDS with other security measures, such as surveillance cameras, access control, and AI technologies, individuals and organizations can create a comprehensive security system that protects against a wide range of threats. As technology continues to advance, physical intrusion detection systems will become even more effective, offering enhanced accuracy, reduced false alarms, and improved response times.
