In today’s digital age, protecting your network from cyber threats is more important than ever. A Network-Based Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) is one of the key tools organizations use to safeguard their data and systems from cyber-attacks. This article will walk you through the basics of NIDS, their importance, and how they can be effectively implemented.
Introduction
1 Overview of Network Security
Network security refers to the strategies and tools used to protect data as it flows across networks. With the increasing number of cyber threats, ensuring strong security measures is critical for businesses of all sizes. Network security focuses on monitoring, detecting, and preventing unauthorized access to network systems.
2 Importance of Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are essential components of a robust network security plan. They help monitor and detect suspicious activities or potential cyber-attacks within a network, allowing organizations to take immediate action. With more businesses relying on digital data, an IDS offers peace of mind by detecting threats early on.
3 Objectives of the Document
This article seeks to offer a comprehensive insight into Network-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS), exploring their different types, advantages, obstacles, and recommended practices. Additionally, we’ll delve into emerging trends that are expected to influence the future of network security.
Understanding Network-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS)
2.1 What is a Network-Based IDS?
A Network-Based Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) is a security tool that monitors network traffic for suspicious activities. Unlike Host-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS), which focus on individual devices, NIDS examines traffic across an entire network to identify threats.
2.2 How NIDS Differ from Host-Based IDS
While a Host-Based IDS focuses on protecting individual systems or devices, NIDS provides broader coverage by monitoring network activity across multiple devices. This allows NIDS to detect threats that might be targeting multiple systems within a network.
2.3 Key Components of NIDS
Key components of NIDS include sensors that collect data from the network, a central server for analyzing the data, and a management console for administrators to review alerts and take action. These components work together to identify and report any suspicious activity.
Types of Network-Based Intrusion Detection
Network-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) utilize several methods to identify potential threats. Here are five key types;
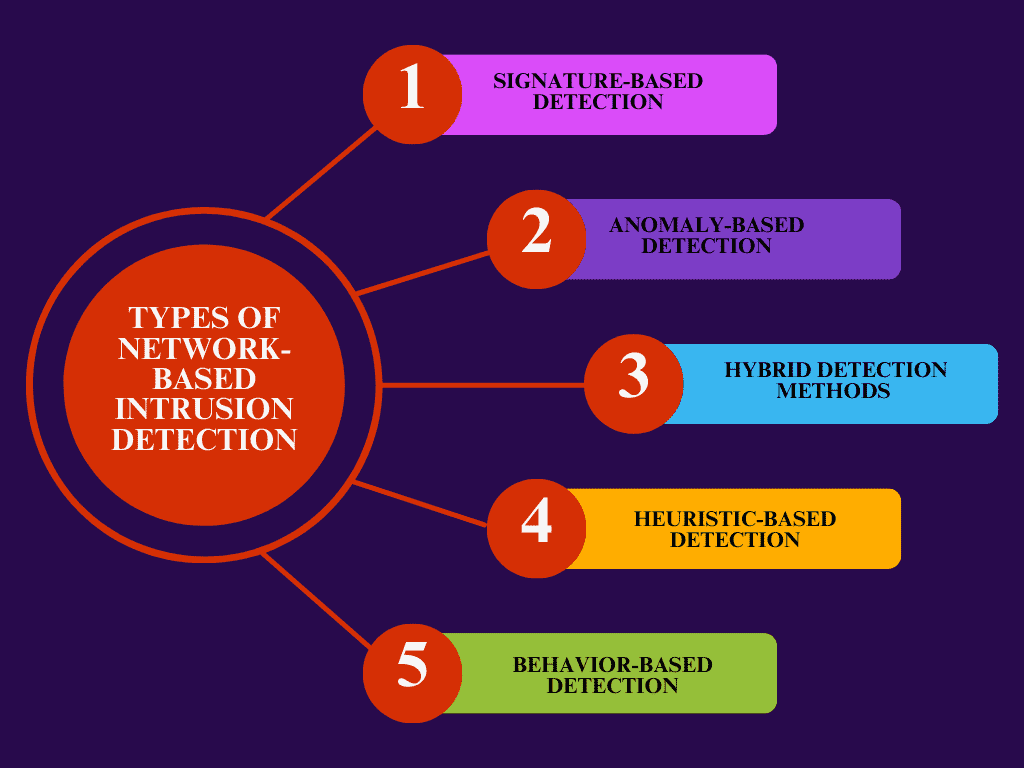
1 Signature-Based Detection
This method compares network traffic against a database of known attack patterns or signatures. When it finds a match, it flags the activity as a potential threat. It is effective for identifying known attacks but may miss new or evolving threats.
2 Anomaly-Based Detection
This method monitors traffic patterns and compares them to a baseline of normal network behavior. Anything that deviates from this baseline is flagged. While it’s adaptable to detecting new threats, it may generate more false positives than other methods.
3 Hybrid Detection Methods
Hybrid Detection combines Signature-Based and Anomaly-Based approaches, providing comprehensive protection against both known and unknown threats. It minimizes the weaknesses of each method while enhancing detection capabilities.
4 Heuristic-Based Detection
This method evaluates network traffic using rules and algorithms, analyzing the behavior of various elements in the network. By examining how network components interact, it can detect threats beyond signature recognition, though it may still result in some false positives.
5 Behavior-Based Detection
This method profiles the usual behavior of users and devices on the network, flagging deviations as potential intrusions. It’s effective for spotting insider threats or compromised accounts but requires a solid baseline of normal activity to function effectively.
Implementation of Network-Based Intrusion Detection

1 Deployment Strategies
Effective deployment of NIDS involves placing sensors at strategic points within the network to capture data from key areas. This ensures full visibility of all network activities, allowing the system to detect threats before they cause damage.
2 Integration with Existing Security Infrastructure
NIDS should be integrated with other security tools, such as firewalls and antivirus software, to create a layered defense strategy. This ensures that even if one system misses a threat, another can catch it.
3 Configuration and Tuning
Proper configuration and tuning are essential for minimizing false positives and ensuring that the system can accurately detect threats. Regular updates to the detection rules and signatures help keep the system current with the latest attack methods.
Benefits of Network-Based Intrusion Detection
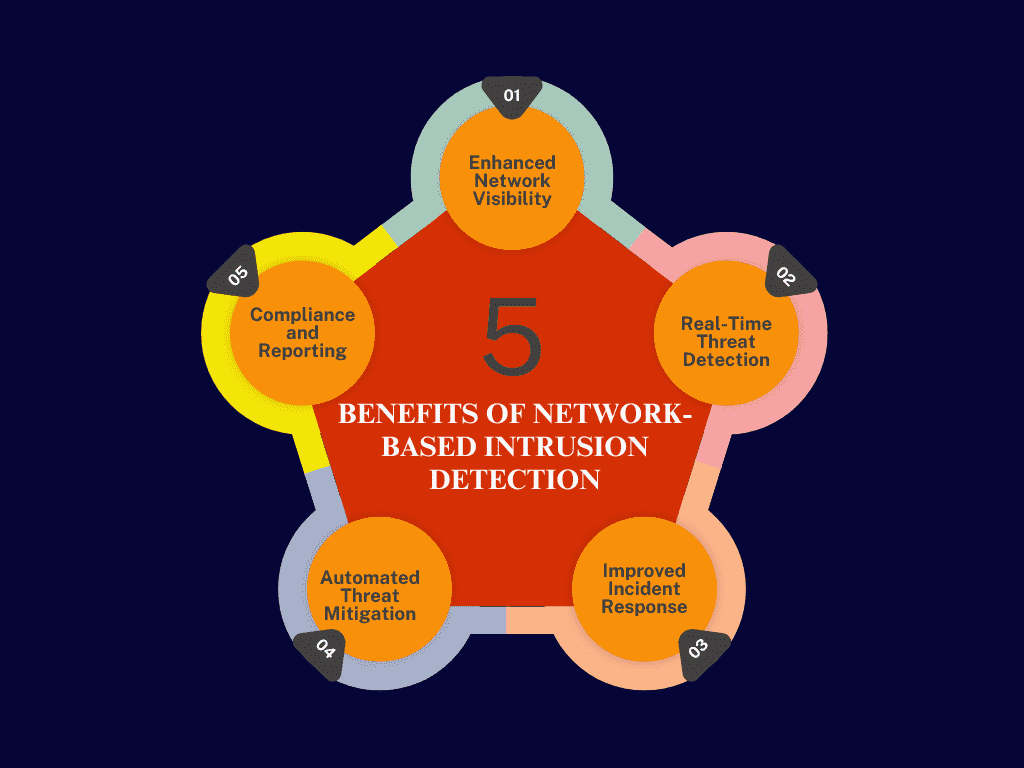
1. Enhanced Network Visibility
NIDS provides enhanced visibility into your entire network, allowing you to monitor all traffic and detect potential threats before they can cause damage. This visibility is essential for identifying both external attacks and internal misuse of resources.
2. Real-Time Threat Detection
One of the key advantages of NIDS is its ability to detect threats in real-time. It generates immediate alerts when suspicious activity is detected, allowing administrators to respond quickly and minimize the impact of cyber-attacks.
3. Improved Incident Response
NIDS improves incident response by providing detailed information on detected threats. This allows security teams to quickly assess the severity of an attack and take the necessary steps to mitigate it, speeding up the entire response process.
4. Automated Threat Mitigation
Through integration with other security tools, NIDS can automate certain responses, such as blocking malicious IP addresses or isolating compromised devices. This automation reduces the time needed to respond to threats and helps prevent further damage.
5. Compliance and Reporting
NIDS supports compliance by generating detailed logs and reports on network activity, helping organizations meet regulatory requirements. These reports are useful during audits and for demonstrating adherence to industry standards, ensuring better legal protection.
Benefits of Network-Based Intrusion Detection
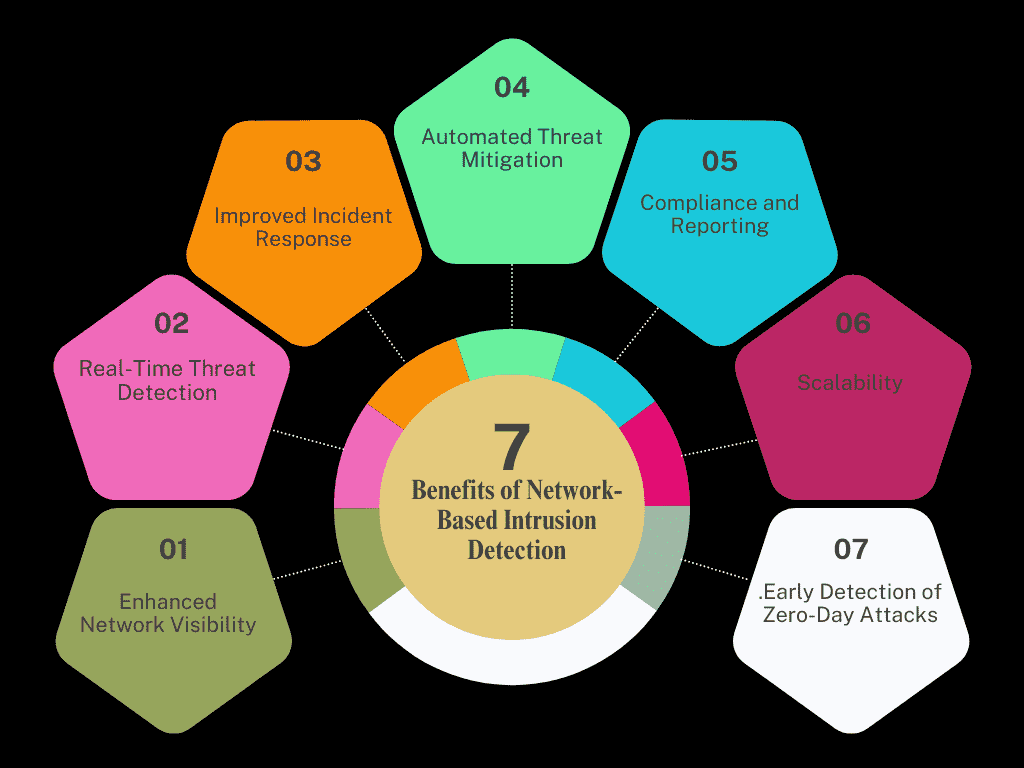
1. Enhanced Network Visibility
NIDS provides enhanced visibility into your network, allowing you to monitor all traffic and detect potential threats before they can cause damage. This visibility is crucial for identifying both external attacks and internal misuse of resources.
2. Real-Time Threat Detection
One of the biggest advantages of NIDS is its ability to detect threats in real-time. Immediate alerts allow administrators to respond quickly, minimizing the risk of damage from cyber-attacks and helping prevent large-scale incidents.
3. Improved Incident Response
NIDS helps improve incident response by providing detailed information about detected threats. Security teams can assess the severity of an attack more effectively and take quick actions to mitigate it, reducing downtime and damage.
4. Automated Threat Mitigation
NIDS can be integrated with other security tools to automate responses to threats, such as blocking suspicious IP addresses or isolating compromised devices. This automation reduces manual intervention, speeding up the reaction time to potential attacks.
5. Compliance and Reporting
NIDS generates detailed logs and reports that are critical for meeting regulatory compliance. These reports help organizations maintain proper documentation for audits, demonstrating adherence to industry standards and legal requirements.
6. Scalability
NIDS is highly scalable, making it adaptable for organizations of all sizes. As your network grows, NIDS can easily expand to monitor increased traffic, ensuring continuous protection without compromising performance.
7. Early Detection of Zero-Day Attacks
While traditional methods may miss zero-day threats, NIDS that incorporates anomaly-based detection can identify unusual behavior that might indicate new or previously unknown attacks. This ability to detect zero-day vulnerabilities offers a crucial layer of defense.
Challenges and Limitations
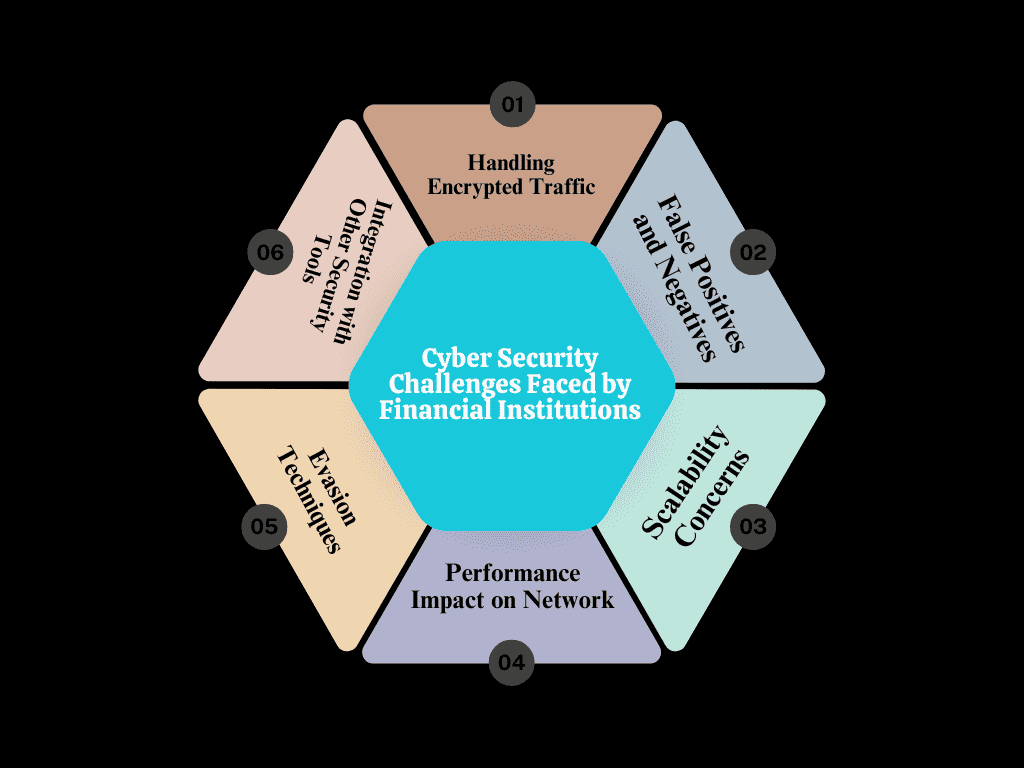
1 Handling Encrypted Traffic
Encrypted traffic presents a significant challenge for NIDS, as it cannot easily inspect the contents of encrypted data. This can limit its ability to detect threats. However, using decryption techniques or analyzing traffic patterns can help mitigate this issue and allow for better threat detection within encrypted streams.
2 False Positives and Negatives
False positives occur when the system incorrectly identifies normal activity as a threat, while false negatives happen when a real threat goes undetected. These can hinder the effectiveness of NIDS. Regular tuning, updates, and setting more accurate thresholds are essential for reducing these errors and improving detection accuracy.
3 Scalability Concerns
As organizations grow, network traffic increases, potentially overwhelming NIDS. Scalability is crucial to ensure the system can handle high volumes of data without degrading performance. Choosing an NIDS solution that scales efficiently with your network’s growth is key for long-term security success.
4 Performance Impact on Network
NIDS can introduce latency into the network as it processes and analyzes traffic. The more sophisticated the detection mechanisms, the higher the potential performance impact. It’s important to balance the need for security with the operational performance of the network.
5 Evasion Techniques
Cyber attackers often employ evasion techniques to bypass NIDS. These techniques, such as fragmented packets or obfuscating malicious traffic, can make it harder for the system to detect threats. Regular updates and incorporating advanced detection methods can help mitigate this challenge.
6 Integration with Other Security Tools
NIDS works best when integrated with other security tools like firewalls and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems. However, ensuring seamless integration can be complex and require considerable time and resources. Effective integration enhances the overall security posture by providing comprehensive defense.
Future Trends in Network-Based Intrusion Detection
1 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are becoming integral to NIDS, enhancing its ability to detect unknown threats. By analyzing patterns from past attacks and continuously learning, AI and ML enable the system to predict and identify new, previously unseen threats more effectively, reducing false positives and improving overall accuracy.
2 Cloud-Based Intrusion Detection Solutions
With the growing adoption of cloud computing, Cloud-Based Intrusion Detection Systems are on the rise. These solutions offer flexibility, scalability, and seamless integration with cloud platforms. They provide organizations with the ability to monitor their cloud infrastructure for potential threats, ensuring security across hybrid or fully cloud-based environments.
3 Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) Security
As the Internet of Things (IoT) expands, NIDS must evolve to monitor and protect IoT networks. IoT devices, which often have minimal built-in security, are highly susceptible to cyber-attacks. NIDS integrated with IoT security can detect vulnerabilities and protect against threats targeting these connected devices.
4 Behavioral Analytics for Enhanced Detection
Future NIDS will likely incorporate advanced behavioral analytics to improve threat detection. By analyzing user and device behavior patterns, NIDS can identify abnormal activities that might indicate insider threats or compromised accounts. Behavioral analytics provide a more adaptive approach to evolving cybersecurity challenges.
5 Zero Trust Architecture Integration
As the zero-trust security model gains traction, NIDS will play a key role in supporting this architecture. NIDS will focus on monitoring every device and user interaction within the network, ensuring that no traffic is trusted by default. This integration will further enhance security by limiting the potential impact of both external and internal threats.
Differences between Network-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) and Host-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS)
| Aspect | Network-Based IDS (NIDS) | Host-Based IDS (HIDS) |
|---|
| Monitoring Focus | Monitors the entire network for suspicious traffic and threats | Monitors individual devices or hosts for suspicious activity |
| Deployment Location | Placed at strategic points in the network | Installed directly on individual systems or devices |
| Detection Scope | Detects threats across multiple devices and the entire network | Detects threats targeting a specific host or device |
| Response Time | May experience a slight delay in detection due to network analysis | Detects intrusions in real-time on the specific host |
| Visibility | Provides broad visibility into network traffic | Limited to monitoring events and activities on a single host |
FAQs
1 What is a Network-Based Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)?
A Network-Based Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) is a cybersecurity mechanism designed to monitor and analyze traffic across a network to identify suspicious behaviors, vulnerabilities, or potential cyber-attacks. It helps detect anomalies in real time, alerting administrators to possible threats before they can cause damage. It inspects data as it moves across the network, identifying patterns that might indicate attacks.
2. How does a Network-Based IDS differ from a Host-Based IDS?
A Network-Based IDS (NIDS) monitors traffic across an entire network, providing a broad overview of network security. In contrast, a Host-Based IDS (HIDS) monitors individual devices or hosts, detecting threats targeting specific systems.
3. What types of detection methods are used in NIDS?
NIDS typically use Signature-Based Detection (matching known attack patterns), Anomaly-Based Detection (identifying abnormal behavior), or Hybrid Detection Methods, which combine both approaches for more comprehensive protection.
4. What are the key benefits of using a Network-Based Intrusion Detection System?
The key benefits include enhanced visibility across the network, real-time threat detection, and improved incident response by alerting administrators as soon as suspicious activity is detected, allowing for quick action.
5. What are some challenges of implementing NIDS?
Some challenges include handling encrypted traffic, managing false positives and negatives, and scalability concerns as networks grow. Proper configuration and regular updates are essential for maintaining effectiveness.
Conclusion
In today’s digital world, a Network-Based Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) is essential for safeguarding networks from cyber threats. It provides real-time monitoring of network traffic, identifying suspicious activity before it causes damage. NIDS enhances network visibility and improves incident response, making it a vital tool for businesses. While there are challenges, such as managing encrypted traffic and false positives, regular updates and monitoring can optimize its performance. With advancements in AI and cloud technologies, NIDS will continue to evolve, providing even stronger security solutions.
