Introduction to Business Information Security
Business information security refers to the processes and practices that protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats. In today’s digital age, where businesses rely heavily on technology, ensuring the security of information is more critical than ever. Understanding the importance of information security helps organizations safeguard their assets and maintain customer trust.
Fundamentals of Business Information Security
The core principles of business information security include confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
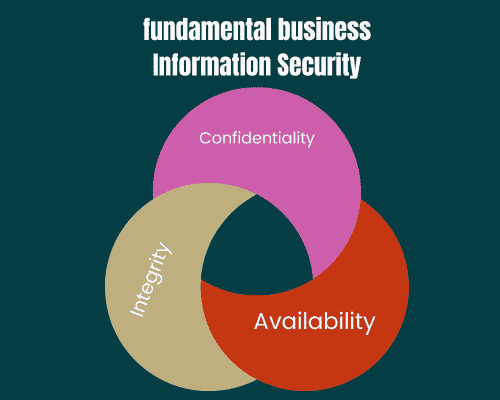
- Confidentiality safeguards sensitive data by restricting access solely to authorized individuals.
- Integrity ensures the preservation of data accuracy, preventing unauthorized modifications during both storage and transfer.
- Availability means that authorized users can access data and systems whenever needed.
Businesses must protect various types of data, including customer information, financial records, and intellectual property.
Identifying Threats to Business Information Security
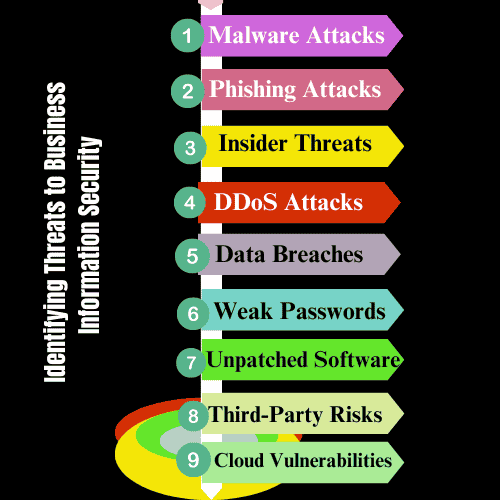
Malware Attacks
- Description: Malicious software, such as viruses, ransomware, and trojans, is designed to infiltrate and damage systems.
- Impact: Can corrupt files, steal data, or demand ransom payments.
- Mitigation: Use antivirus programs, regularly update systems, and conduct staff training.
Phishing Attacks
- Description: Deceptive attempts to acquire sensitive information, such as usernames and passwords, by posing as a trustworthy entity.
- Impact: Can lead to credential theft, unauthorized access, and financial losses.
- Mitigation: Educate employees to recognize phishing attempts and use email filters.
Insider Threats
- Description: Employees or trusted individuals with access to systems may intentionally or unintentionally cause harm by exposing sensitive information.
- Impact: Data breaches, intellectual property theft, or financial damage.
- Mitigation: Implement access controls, monitor employee activities, and conduct background checks.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
- Description: Overwhelming a server with traffic to make it unavailable to users.
- Impact: Downtime, loss of productivity, and potential reputational damage.
- Mitigation: Use DDoS protection services and establish traffic monitoring protocols.
Data Breaches
- Description: Unauthorized access to sensitive data such as customer details, financial records, or proprietary information.
- Impact: Legal consequences, loss of customer trust, and financial penalties.
- Mitigation: Encrypt sensitive data, implement strong authentication, and monitor for suspicious activities.
Weak Passwords
- Description: Simple or reused passwords that are easily guessable.
- Impact: Increases vulnerability to brute-force attacks.
- Mitigation: Enforce strong password policies, use multi-factor authentication (MFA), and encourage password managers.
Unpatched Software
- Description: Systems running outdated software with known vulnerabilities.
- Impact: Easier for attackers to exploit weaknesses.
- Mitigation: Regularly update and patch all systems, including third-party applications.
Third-Party Risks
- Description: Vendors or partners with insufficient security measures may introduce vulnerabilities into your systems.
- Impact: Data exposure or breach through insecure third-party systems.
- Mitigation: Perform security audits of third parties, establish strict security protocols, and limit access to critical data.
Cloud Vulnerabilities
- Description: Misconfigurations or weak access controls in cloud environments.
- Impact: Data breaches, loss of control over data, and unauthorized access.
- Mitigation: Use encryption, secure API access, and regularly review cloud configurations.
Sical premises with access controls, CCTV, and regular security audits.
Establishing a Security Framework
Establishing a robust security framework begins with developing a comprehensive business information security policy. This policy serves as the backbone of an organization’s security efforts, clearly defining the purpose, scope, and objectives of information security. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of various stakeholders, ensuring everyone understands their part in protecting sensitive data. The policy should also establish specific security standards that must be met to safeguard information assets. By having a well-documented policy, organizations can ensure that all employees are aligned with the security goals and are aware of the expectations placed upon them.

Creating a security governance structure is equally important for effective information security management. This involves forming a security committee that includes representatives from various departments, such as IT, legal, and compliance. The committee is responsible for overseeing security initiatives, assessing risks, and recommending policy updates. Regular reviews and updates to the security framework are essential to keep pace with the evolving threat landscape and technological advancements. Additionally, compliance monitoring processes should be implemented to ensure that all employees adhere to established security policies, fostering a culture of accountability within the organization.
A critical aspect of the security framework is the continuous assessment and management of risks. Organizations must begin by identifying all information assets, including hardware, software, and sensitive data, to understand what needs protection. Conducting thorough evaluations of potential threats and vulnerabilities associated with these assets allows organizations to prioritize risks based on their severity. Once risks are identified, implementing appropriate security controls becomes crucial. This includes deploying physical, technical, and administrative controls to mitigate risks effectively. By establishing a culture of security and focusing on continuous improvement, organizations can enhance their overall resilience against cyber threats and protect their valuable information.
Data Protection Strategies
Encryption
Encryption ensures that sensitive data is converted into an unreadable format, protecting it even if it is intercepted or stolen. Only authorized users with the correct decryption key can access the information.

Access Control
Access control restricts data access to authorized personnel only by using role-based permissions and multi-factor authentication. This ensures that only those who need access to certain information have it, reducing the chances of a breach. Proper access control is essential for maintaining data security within an organization.
Backup and Recovery
Regularly backing up critical data ensures that it can be recovered in the event of data loss or corruption. Storing backups securely, either offsite or in the cloud, guarantees that data is protected against physical damage or cyberattacks. It’s also important to test recovery plans to ensure they work when needed.
Data Masking
Data masking replaces sensitive information with fictitious data, allowing it to be used for testing and development without exposing the real data. This method protects privacy while still making data functional for non-production environments. Masked data ensures that even if it is accessed, no sensitive information is leaked.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) systems monitor and control the movement of sensitive information within and outside the organization. DLP tools help prevent unauthorized sharing, accidental leaks, or data theft. They are critical for enforcing policies that safeguard against intentional or unintentional data breaches.
Security Audits
Regular security audits are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities within a system. These audits ensure compliance with data protection policies and help address security gaps before they are exploited. By conducting routine assessments, businesses can stay ahead of potential threats and maintain data security.
Cloud Security
Cloud security involves storing data securely in the cloud by using encryption, strong access controls, and monitoring tools. It is essential to follow data protection regulations when using cloud services, as misconfigurations or weak protections can lead to breaches. A well-secured cloud environment ensures data is safe from unauthorized access.
Employee Training
Training employees on data security best practices helps prevent common security incidents such as phishing or social engineering attacks. Regular training ensures that staff are aware of the latest threats and know how to handle sensitive data properly.
Data Minimization
Data minimization involves collecting and storing only the necessary amount of data. By reducing the volume of sensitive data, organizations minimize the potential damage in the event of a breach. This approach limits exposure and helps maintain tighter control over sensitive information.
Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan outlines how an organization will react to a data breach or security incident. Having a clear plan ensures that all team members know their roles and can respond quickly to contain the breach. A well-executed incident response minimizes damage and accelerates recovery.
Data Deletion and Destruction
When data is no longer needed, securely deleting or destroying it prevents unauthorized recovery. Certified tools and physical destruction methods ensure that old or obsolete data cannot be accessed by unauthorized parties. Proper disposal of data is a critical part of the data lifecycle management process.
Privacy by Design
Privacy by design integrates data protection into the development of systems and applications from the very beginning. By considering privacy at every stage, companies can proactively reduce risks to data. This approach ensures that security is built into the system rather than added later.
Third-Party Risk Management
When sharing data with third-party vendors or partners, it’s crucial to ensure they follow strict security standards. Vetting and monitoring these external entities help avoid introducing vulnerabilities into your system. Managing third-party risk reduces the likelihood of data breaches from external sources.
Data Tokenization
Data tokenization replaces sensitive information with random tokens that are meaningless outside specific systems. This technique reduces the risk of data exposure during storage or transmission. Tokens add an additional layer of security, especially when processing credit card numbers or personal information.
Endpoint Security
Endpoint security protects devices such as laptops, desktops, and smartphones from malware and unauthorized access. Regularly updating and patching these devices, along with using antivirus software and encryption, helps secure them. Protecting endpoints is essential as they are often entry points for cyberattacks.

User Awareness and Training
User awareness and training are essential components of a strong business information security strategy. Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats, making it crucial for them to recognize potential risks. Regular training sessions can equip staff with the knowledge to identify phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and other malicious activities. By fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood of successful attacks, as informed employees are more vigilant and proactive in protecting sensitive information.
To maximize the effectiveness of training programs, organizations should adopt a variety of educational methods. Interactive workshops, online courses, and real-life scenarios can engage employees and enhance their understanding of security protocols. Incorporating gamification elements, such as quizzes and competitions, can also make learning more enjoyable and memorable. Additionally, providing ongoing training and refresher courses ensures that employees stay updated on the latest security threats and best practices, reinforcing the importance of their role in maintaining information security.
Moreover, organizations should establish clear communication channels for reporting security incidents or suspicious activities. Employees should feel empowered to speak up without fear of reprisal, as prompt reporting can help mitigate potential damage from security breaches. Regularly sharing security tips, updates on new threats, and success stories of thwarted attacks can further reinforce the importance of vigilance. By prioritizing user awareness and training, organizations not only enhance their security posture but also foster a collaborative environment where everyone contributes to protecting valuable data.
Technology Solutions for Enhancing Security
Firewalls
Investing in technology solutions is vital for enhancing business information security and protecting sensitive data. One of the fundamental tools in this arsenal is firewalls, which act as a barrier between an organization’s internal network and external threats. Firewalls can monitor incoming and outgoing traffic, blocking unauthorized access while allowing legitimate communication. By regularly updating firewall configurations, businesses can adapt to evolving threats and maintain a robust defense against cyber-attacks.
Antivirus Software
Antivirus software is another essential component of a comprehensive security strategy. This software detects, quarantines, and removes malware from devices, ensuring that harmful programs do not compromise sensitive information. Regular updates are crucial, as new malware variants are constantly emerging. Additionally, many antivirus solutions come with features like real-time scanning and web protection, which can prevent users from inadvertently downloading malicious files or visiting harmful websites.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
In addition to firewalls and antivirus software, organizations should consider utilizing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS). These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can respond in real-time to potential threats. By analyzing patterns and behaviors, IDPS can identify and block malicious actions before they escalate into serious security incidents. Combining these technology solutions with employee training and awareness efforts creates a multi-layered defense strategy that significantly enhances overall business information security.
Future of Business Information Security
The future of business information security is set to evolve rapidly as new technologies and threats emerge. As businesses become increasingly digitized, the attack surface for cybercriminals expands, necessitating more advanced and adaptive security measures. Here are key trends shaping the future of business information security
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)
AI and ML are transforming cybersecurity by enabling real-time threat detection and response. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict potential attacks, and automate responses to mitigate risks. As threats become more sophisticated, AI-driven solutions will play a pivotal role in enhancing security, reducing the time between detection and action.
Zero Trust Architecture
The Zero Trust model, which assumes no user or system should be trusted by default, is gaining traction. It necessitates ongoing verification of users, devices, and applications prior to granting access to ensure secure and authorized entry. This shift away from traditional perimeter-based security models ensures that even if attackers breach one part of a network, they won’t have unrestricted access to sensitive information.
Cloud Security
As businesses migrate more data to the cloud, securing cloud environments will be paramount. The future will see a focus on multi-cloud security solutions, automated cloud compliance, and end-to-end encryption of cloud-based data. Securing cloud-native applications and managing the complexity of hybrid environments will also be critical.
Quantum Computing Threats
Quantum computing poses both an opportunity and a challenge for cybersecurity. While quantum computing can revolutionize data processing, it also threatens to break existing encryption methods. Businesses will need to adopt quantum-resistant encryption techniques to safeguard their data against future quantum-powered attacks.
Increased Regulatory Compliance
With growing concerns about data privacy, businesses will face more stringent regulatory requirements. New data protection laws, such as GDPR and CCPA, are just the beginning. The future will likely see more global standards, requiring businesses to adopt transparent data practices and ensuring robust protection measures are in place.
IoT and 5G Security
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the rollout of 5G networks will introduce new security challenges. IoT devices often have limited security, making them vulnerable to attacks. As 5G expands connectivity, businesses will need to secure a larger and more diverse array of devices and endpoints.
Biometric Authentication
The use of biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, will become more prevalent in securing business systems. These methods offer enhanced security by reducing reliance on passwords, which are often vulnerable to phishing and brute-force attacks. The future will likely see more sophisticated and secure biometric technologies integrated into business systems.
Cybersecurity Skills Gap
As cybersecurity threats increase, there will be a growing demand for skilled professionals. The cybersecurity skills gap is a challenge that businesses will need to address through workforce development, training, and collaboration with educational institutions. Automation and AI may help fill some gaps, but human expertise will remain essential for strategic planning and threat management.
Decentralized Identity Management
Decentralized identity management using blockchain technology may become more widespread. This approach allows individuals and businesses to manage their digital identities securely without relying on a central authority. It offers increased privacy and security, reducing the risk of identity theft and breaches.
Adaptive Security Frameworks
The future will move towards adaptive security frameworks that are dynamic and responsive to changing threats. These frameworks constantly monitor and adjust security measures based on the evolving threat landscape. This approach allows businesses to stay one step ahead of attackers by adapting their defenses in real-time
Zero Trust Architecture
The Zero Trust model, which assumes no user or system should be trusted by default, is gaining traction. It necessitates ongoing verification of users, devices, and applications prior to granting access to ensure secure and authorized entry. This shift away from traditional perimeter-based security models ensures that even if attackers breach one part of a network, they won’t have unrestricted access to sensitive information.
Cloud Security
As businesses migrate more data to the cloud, securing cloud environments will be paramount. The future will see a focus on multi-cloud security solutions, automated cloud compliance, and end-to-end encryption of cloud-based data. Securing cloud-native applications and managing the complexity of hybrid environments will also be critical.
Quantum Computing Threats
Quantum computing poses both an opportunity and a challenge for cybersecurity. While quantum computing can revolutionize data processing, it also threatens to break existing encryption methods. Businesses will need to adopt quantum-resistant encryption techniques to safeguard their data against future quantum-powered attacks.
Increased Regulatory Compliance
With growing concerns about data privacy, businesses will face more stringent regulatory requirements. New data protection laws, such as GDPR and CCPA, are just the beginning. The future will likely see more global standards, requiring businesses to adopt transparent data practices and ensuring robust protection measures are in place.
IoT and 5G Security
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the rollout of 5G networks will introduce new security challenges. IoT devices often have limited security, making them vulnerable to attacks. As 5G expands connectivity, businesses will need to secure a larger and more diverse array of devices and endpoints.
Biometric Authentication
The use of biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, will become more prevalent in securing business systems. These methods offer enhanced security by reducing reliance on passwords, which are often vulnerable to phishing and brute-force attacks. The future will likely see more sophisticated and secure biometric technologies integrated into business systems.
Cybersecurity Skills Gap
As cybersecurity threats increase, there will be a growing demand for skilled professionals. The cybersecurity skills gap is a challenge that businesses will need to address through workforce development, training, and collaboration with educational institutions. Automation and AI may help fill some gaps, but human expertise will remain essential for strategic planning and threat management.
Decentralized Identity Management
Decentralized identity management using blockchain technology may become more widespread. This approach allows individuals and businesses to manage their digital identities securely without relying on a central authority. It offers increased privacy and security, reducing the risk of identity theft and breaches.
Adaptive Security Frameworks
The future will move towards adaptive security frameworks that are dynamic and responsive to changing threats. These frameworks constantly monitor and adjust security measures based on the evolving threat landscape. This approach allows businesses to stay one step ahead of attackers by adapting their defenses in real-time
FAQs Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)
AI and ML are transforming cybersecurity by enabling real-time threat detection and response. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict potential attacks, and automate responses to mitigate risks. As threats become more sophisticated, AI-driven solutions will play a pivotal role in enhancing security, reducing the time between detection and action.
Zero Trust Architecture
The Zero Trust model, which assumes no user or system should be trusted by default, is gaining traction. It necessitates ongoing verification of users, devices, and applications prior to granting access to ensure secure and authorized entry. This shift away from traditional perimeter-based security models ensures that even if attackers breach one part of a network, they won’t have unrestricted access to sensitive information.
Cloud Security
As businesses migrate more data to the cloud, securing cloud environments will be paramount. The future will see a focus on multi-cloud security solutions, automated cloud compliance, and end-to-end encryption of cloud-based data. Securing cloud-native applications and managing the complexity of hybrid environments will also be critical.
Quantum Computing Threats
Quantum computing poses both an opportunity and a challenge for cybersecurity. While quantum computing can revolutionize data processing, it also threatens to break existing encryption methods. Businesses will need to adopt quantum-resistant encryption techniques to safeguard their data against future quantum-powered attacks.
Increased Regulatory Compliance
With growing concerns about data privacy, businesses will face more stringent regulatory requirements. New data protection laws, such as GDPR and CCPA, are just the beginning. The future will likely see more global standards, requiring businesses to adopt transparent data practices and ensuring robust protection measures are in place.
IoT and 5G Security
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the rollout of 5G networks will introduce new security challenges. IoT devices often have limited security, making them vulnerable to attacks. As 5G expands connectivity, businesses will need to secure a larger and more diverse array of devices and endpoints.
Biometric Authentication
Using biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, will become more prevalent in securing business systems. These methods offer enhanced security by reducing reliance on passwords, often vulnerable to phishing and brute-force attacks. In the future, more sophisticated and secure biometric technologies will likely be integrated into business systems.
Cybersecurity Skills Gap
As cybersecurity threats increase, there will be a growing demand for skilled professionals. The cybersecurity skills gap is a challenge that businesses will need to address through workforce development, training, and collaboration with educational institutions. Automation and AI may help fill some gaps, but human expertise will remain essential for strategic planning and threat management.
Decentralized Identity Management
Decentralized identity management using blockchain technology may become more widespread. This approach allows individuals and businesses to manage their digital identities securely without relying on a central authority. It offers increased privacy and security, reducing the risk of identity theft and breaches.
Adaptive Security Frameworks
The future will move towards adaptive security frameworks that are dynamic and responsive to changing threats. These frameworks constantly monitor and adjust security measures based on the evolving threat landscape. This approach allows businesses to stay one step ahead of attackers by adapting their defenses in real-time
FAQs
What is business information security?
Business information security refers to the practices and technologies used to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats. It ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information within an organization.
Why is user training important?
User training is crucial because employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. Educating them about recognizing potential risks and best practices helps reduce the likelihood of successful attacks.
What role do firewalls play in security?
Firewalls serve as a protective barrier, shielding an organization’s internal network from external threats and unauthorized access. They monitor and control incoming and outgoing traffic, blocking unauthorized access while allowing legitimate communication.
How often should antivirus software be updated?
Antivirus software should be updated regularly to protect against new malware variants. Most software solutions provide automatic updates, ensuring that devices are continually protected against emerging threats.
What is an intrusion detection system (IDS)?
An intrusion detection system (IDS) monitors network traffic for suspicious activities and potential threats. It can alert administrators to security breaches and, in some cases, take action to block those threats in real time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, business information security is essential for protecting sensitive data and maintaining customer trust. By understanding the fundamentals of security, identifying threats, and implementing effective strategies, organizations can safeguard their information assets. Continuous education, compliance with regulations, and investment in technology are critical components of a successful information security program.
